- RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT
Humans and bacteria rely on the same aeons-old immune defence
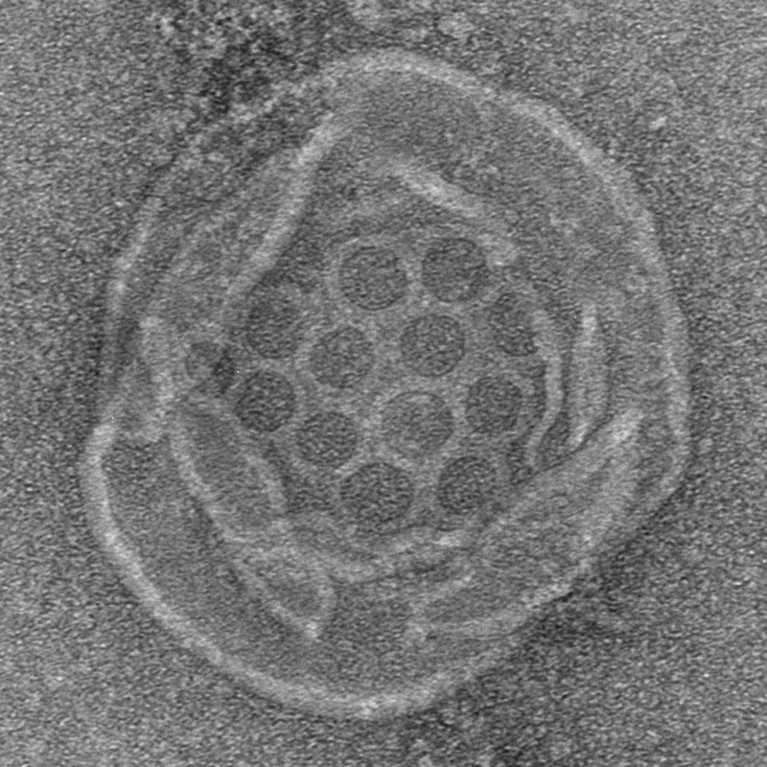
Some bacteria have a molecular pathway that creates destructive holes in cell membranes (honeycomb structure at centre) in response to pathogens — a mechanism already known in mammals Credit: A. G. Johnson et al./Science
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
from$1.95
to$39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 601, 300 (2022)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-022-00005-w
References
Johnson, A. G. et al. Science http://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abj8432 (2022).