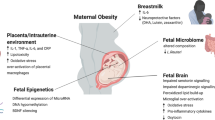
Abstract
Several human and animal studies have demonstrated that cardiometabolic parameters in infancy, childhood, adolescence and even adulthood are negatively influenced by many factors besides energy imbalance. Interestingly, maternal weight excess both before and during pregnancy seems to be a negative determinant of metabolic and cardiovascular outcomes in the offspring. This review includes both human and animal studies and finally highlights the link between maternal obesity and cardiometabolic disorders in offspring.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Y, Lobstein T. Worldwide trends in childhood overweight and obesity. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2006;1:11–25.
Reilly JJ, Ness AR, Sheriff A. Epidemiological and physiological approaches to understanding the etiology of pediatric obesity: finding the needle in the haystack. Pediatr Res. 2007;61:646–52.
Pelusi C, Altieri P, Gambineri A, Repaci A, Cavazza C, Fanelli F, et al. Behavioral, socio-environmental, educational and demographic correlates of excess body weight in Italian adolescences and young adults. Nutr Med Cardiovasc Dis. 2019;29:279–89.
Drake AJ, Reynolds RM. Impact of maternal obesity on offspring obesity and cardiometabolic disease risk. Reproduction. 2010;140:387–98.
Rooney K, Ozanne SE. Maternal over-nutrition and offspring obesity predisposition: targets for preventative interventions. Int J Obes (Lond). 2011;35:883–90.
Bekkers MB, Brunekreef B, Smit HA, Kerkhof M, Koppelman GH, Oldenwening M, et al. Early-life determinants of total and HDL cholesterol concentrations in 8-year-old children; the PIAMA birth cohort study. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e25533.
Boney CM, Verma A, Tucker R, Vohr BR. Metabolic syndrome in childhood: association with birth weight, maternal obesity, and gestational diabetes mellitus. Pediatrics. 2005;115:e290–6.
Catalano PM, Farrell K, Thomas A, Huston-Presley L, Mencin P, de Mouzon SH, et al. Perinatal risk factors for childhood obesity and metabolic dysregulation. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;90:1303–13.
Fraser A, Tilling K, Macdonald-Wallis C, Sattar N, Brion MJ, Benfield L, et al. Association of maternal weight gain in pregnancy with offspring obesity and metabolic and vascular traits in childhood. Circulation. 2010;121:2557–64.
Gaillard R, Steegers EA, Franco OH, Hofman A, Jaddoe VW. Maternal weight gain in different periods of pregnancy and childhood cardio-metabolic outcomes. The Generation R Study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2015;39:677–85.
Gaillard R, Steegers EA, Duijts L, Felix JF, Hofman A, Franco OH, et al. Childhood cardiometabolic outcomes of maternal obesity during pregnancy: the Generation R Study. Hypertension. 2014;63:683–91.
Kaar JL, Crume T, Brinton JT, Bischoff KJ, McDuffie R, Dabelea D. Maternal obesity, gestational weight gain, and offspring adiposity: the exploring perinatal outcomes among children study. J Pediatr. 2014;165:509–15.
Whitaker RC. Predicting preschooler obesity at birth: the role of maternal obesity in early pregnancy. Pediatrics. 2004;114:e29–36.
Wrotniak BH, Shults J, Butts S, Stettler N. Gestational weight gain and risk of overweight in the offspring at age 7 y in a multicenter, multiethnic cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87:1818–24.
Gillman MW, Rifas-Shiman SL, Kleinman K, Oken E, Rich-Edwards JW, Taveras EM. Developmental origins of childhood overweight: potential public health impact. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008;16:1651–6.
Li C, Goran MI, Kaur H, Nollen N, Ahluwalia JS. Developmental trajectories of overweight during childhood: role of early life factors. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2007;15:760–71.
Margerison Zilko CE, Rehkopf D, Abrams B. Association of maternal gestational weight gain with short- and long-term maternal and child health outcomes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;202:574. e1-8.
Oken E, Taveras EM, Kleinman KP, Rich-Edwards JW, Gillman MW. Gestational weight gain and child adiposity at age 3 years. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007;196:322.e1-8.
Rooney BL, Mathiason MA, Schauberger CW. Predictors of obesity in childhood, adolescence, and adulthood in a birth cohort. Matern Child Health J. 2011;201:1166–75.
Jedrychowski W, Maugeri U, Kaim I, Budzyn-Mrozek D, Flak E, Mroz E, et al. Impact of excessive gestational weight gain in non-smoking mothers on body fatness in infancy and early childhood. Prospective prebirth cohort study in Cracow. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011;62:55–64.
Crozier SR, Inskip HM, Godfrey KM, Cooper C, Harvey NC, Cole ZA, et al. Southampton Women’s Survey Study Group. Weight gain in pregnancy and childhood body composition: findings from the Southampton Women’s Survey. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91:1745–51.
Lawlor DA, Timpson NJ, Harbord RM, Leary S, Ness A, McCarthy MI, et al. Exploring the developmental overnutrition hypothesis using parental-offspring associations and FTO as an instrumental variable. PLoS Med. 2008;5:e33.
Perng W, Gillman MW, Mantzoros CS, Oken E. A prospective study of maternal prenatal weight and offspring cardiometabolic health in midchildhood. Ann Epidemiol. 2014;24:793–800.e1.
Lemas DJ, Brinton JT, Shapiro AL, Glueck DH, Friedman JE, Dabelea D. Associations of maternal weight status prior and during pregnancy with neonatal cardiometabolic markers at birth: the Healthy Start study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2015;39:1437–42.
Oostvogels AJ, Stronks K, Roseboom TJ, van der Post JA, van Eijsden M, Vrijkotte TG. Maternal prepregnancy BMI, offspring’s early postnatal growth, and metabolic profile at age 5-6 years: the ABCD Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:3845–54.
Tam CH, Wang Y, Luan J, Lee HM, Luk AO, Tutino GE, et al. Maternal history of diabetes is associated with increased cardiometabolic risk in Chinese. Nutr Diabetes. 2014;4:e112.
Tam CHT, Ma RCW, Yuen LY, Ozaki R, Li AM, Hou Y, et al. The impact of maternal gestational weight gain on cardiometabolic risk factors in children. Diabetologia. 2018;61:2539–48.
Dodd JM, McPhee AJ, Turnbull D, Yelland LN, Deussen AR, Grivell RM, et al. The effects of antenatal dietary and lifestyle advice for women who are overweight or obese on neonatal health outcomes: the LIMIT randomised trial. BMC Med. 2014;12:163. LIMIT Randomised Trial Group.
International Weight Management in Pregnancy (i-WIP) Collaborative Group. Effect of diet and physical activity based interventions in pregnancy on gestational weight gain and pregnancy outcomes: meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised trials. BMJ. 2017;358:j3119.
Gaillard R, Welten M, Oddy WH, et al. Associations of maternal prepregnancy body mass index and gestational weight gain with cardio-metabolic risk factors in adolescent offspring. A prospective cohort study. BJOG. 2016;123:207–16.
Groth SW, Holland ML, Smith JA, Meng Y, Kitzman H. Effect of Gestational Weight Gain and Prepregnancy Body Mass Index in Adolescent Mothers on Weight and Body Mass Index of Adolescent Offspring. J Adolesc Health. 2017;61:626–33.
Hrolfsdottir L, Rytter D, Olsen SF, Bech BH, Maslova E, Henriksen TB, et al. Gestational weight gain in normal weight women and offspring cardio-metabolic risk factors at 20 years of age. Int J Obes. 2015;39:671–6.
Laura HC, Menezes AB, Noal RB, Hallal PC, Araujo CL. Maternal anthropometric characteristics in pregnancy and blood pressure among adolescents: 1993 live birth cohort, Pelotas, southern Brazil. BMC Public Health. 2010;10:434–24.
Oken E, Rifas-Shiman SL, Field AE, Frazier AL, Gillman MW. Maternal gestational weight gain and offspring weight in adolescence. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;112:999–1006.
Stuebe AM, Forman MR, Michels KB. Maternal-recalled gestational weight gain, pre-pregnancy body mass index, and obesity in the daughter. Int J Obes (Lond). 2009;33:743–52.
Tequeanes AL, Gigante DP, Assunção MC, Chica DA, Horta BL. Maternal anthropometry is associated with the body mass index and waist:height ratio of offspring at 23 years of age. J Nutr. 2009;139:750–4.
Schack-Nielsen L, Michaelsen KF, Gamborg M, Mortensen EL, Sorensen TI. Gestational weight gain in relation to offspring body mass index and obesity from infancy through adulthood. Int J Obes. 2010;34:67–74.
Laitinen J, Power C, Järvelin MR. Family social class, maternal body mass index, childhood body mass index, and age at menarche as predictors of adult obesity. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001;74:287–94.
Eriksson JG, Sandboge S, Salonen M, Kajantie E, Osmond C. Maternal weight in pregnancy and offspring body composition in late adulthood: findings from the Helsinki Birth Cohort Study (HBCS). Ann Med. 2015;47:94–9.
Hochner H, Friedlander Y, Calderon-Margalit R, Meiner V, Sagy Y, Avgil-Tsadok M, et al. Associations of maternal prepregnancy body mass index and gestational weight gain with adult offspring cardiometabolic risk factors: the Jerusalem Perinatal Family Follow-up Study. Circulation. 2012;125:1381–9.
Reynolds RM, Osmond C, Phillips DI, Godfrey KM. Maternal BMI, parity, and pregnancy weight gain: influences on offspring adiposity in young adulthood. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:5365–9.
Reynolds RM, Allan KM, Raja EA, Bhattacharya S, McNeill G, Hannaford PC, et al. Maternal obesity during pregnancy and premature mortality from cardiovascular event in adult offspring: follow-up of 1 323 275 person years. BMJ. 2013;347:f4539.
Menting MD, Mintjens S, van de Beek C, Frick CJ, Ozanne SE, Limpens J, et al. Maternal obesity in pregnancy impacts offspring cardiometabolic health: Systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies. Obes Rev. 2019;20:675–85.
Samuelsson AM, Matthews PA, Argenton M, Christie MR, McConnell JM, Jansen EH, et al. Diet-induced obesity in female mice leads to offspring hyperphagia, adiposity, hypertension, and insulin resistance: a novel murine model of developmental programming. Hypertension. 2008;51:383–92.
Samuelsson AM, Morris A, Igosheva N, Kirk SL, Pombo JM, Coen CW, et al. Evidence for sympathetic origins of hypertension in juvenile offspring of obese rats. Hypertension. 2010;55:76–82.
Elahi MM, Cagampang FR, Mukhtar D, Anthony FW, Ohri SK, Hanson MA. Long-term maternal high-fat feeding from weaning through pregnancy and lactation predisposes offspring to hypertension, raised plasma lipids and fatty liver in mice. Br J Nutr. 2009;102:514–9.
Simonds SE, Pryor JT, Ravussin E, Greenway FL, Dileone R, Allen AM, et al. Leptin mediates the increase in blood pressure associated with obesity. Cell. 2014;159:1404–16.
Zhang YP, Huo YL, Fang ZQ, Wang XF, Li JD, Wang HP, et al. Maternal high-fat diet acts on the brain to induce baroreflex dysfunction and sensitization of angiotensin II-induced hypertension in adult offspring. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018;314:H1061–9.
Khan IY, Taylor PD, Dekou V, Seed PT, Lakasing L, Graham D, et al. Gender-linked hypertension in offspring of lard-fed pregnant rats. Hypertension. 2003;41:168–75.
Qiao L, Guo Z, Bosco C, Guidotti S, Wang Y, Wang M, et al. Maternal high-fat feeding increases placental lipoprotein lipase activity by reducing SIRT1 expression in mice. Diabetes. 2015;64:3111–20.
Ford SP, Zhang L, Zhu M, Miller MM, Smith DT, Hess BW, et al. Maternal obesity accelerates fetal pancreatic beta-cell but not alpha-cell development in sheep: prenatal consequences. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009;297:R835–43.
Gheorghe CP, Goyal R, Holweger JD, Longo LD. Placental gene expression responses to maternal protein restriction in the mouse. Placenta. 2009;30:411–7.
Aagaard-Tillery KM, Grove K, Bishop J, Ke X, Fu Q, McKnight R, et al. Developmental origins of disease and determinants of chromatin structure: maternal diet modifies the primate fetal epigenome. J Mol Endocrinol. 2008;41:91–102.
Vucetic Z, Kimmel J, Totoki K, Hollenbeck E, Reyes TM. Maternal high-fat diet alters methylation and gene expression of dopamine and opioid-related genes. Endocrinology. 2010;151:4756–64.
Drummond EM, Gibney ER. Epigenetic regulation in obesity. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2013;16:392–7.
Acknowledgements
Obesity Programs of nutrition, Education, Research and Assessment (OPERA) group members served as collaborators and approved the final version of the manuscript: Colao Annamaria, Savastano Silvia, Barrea Luigi, Muscogiuri Giovanna, Alviggi Carlo, Angrisani Luigi, Annunziata Giuseppe, Beguinot Francesco, Belfiore Annamaria, Belfiore Antonino, Bellastella Giuseppe, Biondi Bernadette, Bonaduce Domenico, Bordoni Laura, Brasacchio Caterina, Capaldo Brunella, Caprio Massimiliano, Cataldi Mauro, Cignarelli Angelo, Cittadini Antonello, Conforti Alessandro, Cuomo Rosario, De Placido Giuseppe, De Siena Marina, Di Carlo Costantino, Di Luigi Luigi, Di Nisio Andrea, Di Renzo Laura, Di Somma Carolina, Docimo Ludovico, Donini Lorenzo Maria, Federici Massimo, Foresta Carlo, Gabbianelli Rosita, Gambineri Alessandra, Gastaldelli Amalia, Giallauria Francesco, Giardiello Cristiano, Gnessi Lucio, Guida Brunella, Laudisio Daniela, Lenzi Andrea, Macchia Paolo Emidio, Manno Emilio, Marzullo Paolo, Migliaccio Silvia, Muratori Fabrizio, Musella Mario, Nardone Gerardo, Nicasto Vincenzo, Piazza Luigi, Pilone Vincenzo, Pivari Francesca, Pivonello Rosario, Pugliese Gabriella, Riccardi Gabriele, Ritieni Alberto, Salzano Ciro, Sanduzzi Alessandro, Sbraccia Paolo, Sesti Giorgio, Soldati Laura, Taglialatela Maurizio, Trimarco Bruno, Tuccinardi Dario.
Funding
The 2019 OPERA meeting was organized by Panta Rei Srl and sponsored by Novo Nordisk, Therascience, Bruno Pharma, Merck, Savio Pharma Italia Srl, IBSA Institut Biochimique SA, Bioitalia Srl, Cohesion Pharmaceutical, and Specchiasol Srl. Publication of this article as part of a supplement was sponsored by Panta Rei Srl, Naples, Italy. The meeting sponsors and organizer did not have access to the manuscripts and the authors maintained control of the content.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
The authors’ responsibilities were as follows: AG, AC, ADN and DL: were responsible for the concept of this paper and drafted the manuscript; GM, LB, SS and AC: provided a critical review of the paper. OPERA Group members participated to the revision of the manuscript. All authors and OPERA Group Members contributed to and agreed on the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
A Conforti received consulting fees from Merck Serono S.p.A. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gambineri, A., Conforti, A., Di Nisio, A. et al. Maternal obesity: focus on offspring cardiometabolic outcomes. Int J Obes Supp 10, 27–34 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41367-020-0016-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41367-020-0016-2
This article is cited by
-
Maternal high-fat diet programs white and brown adipose tissue lipidome and transcriptome in offspring in a sex- and tissue-dependent manner in mice
International Journal of Obesity (2022)
-
Pregnancy as a Fundamental Determinant of Child Health: a Review
Current Nutrition Reports (2022)