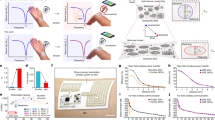
Abstract
This study investigated a sustainable method for preparing PEDOT:PSS/PNIPAM conductive hydrogels. The free radical polymerization of NIPAM to PNIPAM was simply initiated by ultrasonication in an ice bath. This was done in open air rather than spending hours under an N2 purge. The resulting conductive hydrogel had a uniform texture and good flexibility for rapid resistance and color changes when exposed to temperature stimulations. Furthermore, the dual actions of hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic aggregation weaken the Coulomb interaction between PEDOT+ and PSS− for better conductivity. When interacting and aligning with the PNIPAM chain, the partial growth of the conjugation of PEDOT+ molecules was evidenced by the redshift of the PEDOT:PSS characteristic peak of Raman spectra for better resistance-temperature responses. The temperature correspondences of the resistance and transparency of the hydrogel were distinctly inversed due to the transition of hydrophilic-hydrophobic interactions when the temperature was changed through the phase transition temperature (PTT). The unique R-T relationship of the thermosensitive conductive hydrogel was used as a wearable sensor to continuously monitor breathing patterns for sleeping patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grigoryan B, Paulsen SJ, Corbett DC, Sazer DW, Fortin CL, Zaita AJ, et al. Multivascular networks and functional intravascular topologies within biocompatible hydrogels. Science. 2019;364:458–64.
Yang H, Ji M, Yang M, Shi M, Pan Y, Zhou Y, et al. Fabricating hydrogels to mimic biological tissues of complex shapes and high fatigue resistance. Matter. 2021;4:1935–46.
Koons GL, Diba M, Mikos AG. Materials design for bone-tissue engineering. Nat Rev Mater. 2020;5:584–603.
Cao S, Tong X, Dai K, Xu Q. A super-stretchable and tough functionalized boron nitride/PEDOT:PSS/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogel with self-healing, adhesion, conductive and photothermal activity. J Mater Chem A. 2019;7:8204–9.
Alsaid Y, Wu S, Wu D, Du Y, Shi L, Khodambashi R, et al. Tunable Sponge‐Like Hierarchically Porous Hydrogels with Simultaneously Enhanced Diffusivity and Mechanical Properties. Adv Mater. 2021;33:e2008235.
Xu X, Ozden S, Bizmark N, Arnold CB, Datta SS, Priestley RD. A Bioinspired Elastic Hydrogel for Solar‐Driven Water Purification. Adv Mater. 2021;33:e2007833.
Li H, Liang Y, Gao G, Wei S, Jian Y, Le X, et al. Asymmetric bilayer CNTs-elastomer/hydrogel composite as soft actuators with sensing performance. Chem Eng J. 2021;415:128988.
Li C, Xue Y, Han M, Palmer LC, Rogers JA, Huang Y, et al. Synergistic photoactuation of bilayered spiropyran hydrogels for predictable origami-like shape change. Matter. 2021;4:1377–90.
Son H, Byun E, Yoon YJ, Nam J, Song SH, Yoon C. Untethered Actuation of Hybrid Hydrogel Gripper via Ultrasound. ACS Macro Lett. 2020;9:1766–72.
Yang W, Yamamoto S, Sueyoshi K, Inadomi T, Kato R, Miyamoto N. Perovskite Nanosheet Hydrogels with Mechanochromic Structural Color. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021;60:8466–71.
Feng H, Fu Q, Du W, Zhu R, Ge X, Wang C, et al. Quantitative Assessment of Copper(II) in Wilson’s Disease Based on Photoacoustic Imaging and Ratiometric Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. ACS Nano. 2021;15:3402–14.
Li X, Zhao D, Shea KJ, Li X, Lu X. In situformed thermogelable hydrogel photonic crystals assembled by thermosensitive IPNs. Mater Horiz. 2021;8:932–8.
Deng H, Xu X, Zhang C, Su JW, Huang G, Lin J. Deterministic Self-Morphing of Soft-Stiff Hybridized Polymeric Films for Acoustic Metamaterials. ACS Appl Mater Interfac. 2020;12:13378–85.
Wang Z, Ju Y, Ali Z, Yin H, Sheng F, Lin J, et al. Near-infrared light and tumor microenvironment dual responsive size-switchable nanocapsules for multimodal tumor theranostics. Nat Commun. 2019;10:4418.
Li L, Zeng Z, Chen Z, Gao R, Pan L, Deng J, et al. Microenvironment-Triggered Degradable Hydrogel for Imaging Diagnosis and Combined Treatment of Intraocular Choroidal Melanoma. ACS Nano. 2020;14:15403–16.
Guo J, Yu Y, Zhang D, Zhang H, Zhao Y. Morphological Hydrogel Microfibers with MXene Encapsulation for Electronic Skin. Research (Wash D C). 2021;2021:7065907.
Oh JH, Hong SY, Park H, Jin SW, Jeong YR, Oh SY, et al. Fabrication of High-Sensitivity Skin-Attachable Temperature Sensors with Bioinspired Microstructured Adhesive. ACS Appl Mater Interfac. 2018;10:7263–70.
Yue L, Zhang X, Li W, Tang Y, Bai Y. Quickly self-healing hydrogel at room temperature with high conductivity synthesized through simple free radical polymerization. J Appl Polym Sci. 2019;18:47379.
Ge G, Zhang YZ, Zhang W, Yuan W, El-Demellawi JK, Zhang P, et al. Ti3C2TxMXene-Activated Fast Gelation of Stretchable and Self-Healing Hydrogels: a molecular approach. ACS Nano. 2021;15:2698–706.
Li M, Liang Y, He J, Zhang H, Guo B. Two-Pronged Strategy of Biomechanically Active and Biochemically Multifunctional Hydrogel Wound Dressing To Accelerate Wound Closure and Wound Healing. Chem Mater. 2020;32:9937–53.
Distler T, Boccaccini AR. 3D printing of electrically conductive hydrogels for tissue engineering and biosensors – A review. Acta Biomater. 2020;101:1–13.
Wang H, Wang P, Ji Z, Chen Z, Wang J, Ling W, et al. Rechargeable quasi-solid-state aqueous hybrid Al3+/H+ battery with 10,000 ultralong cycle stability and smart switching capability. Nano Res. 2021;14:4154–62.
Dong H, Li J, Guo J, Lai F, Zhao F, Jiao Y, et al. Insights on Flexible Zinc‐Ion Batteries from Lab Research to Commercialization. Adv Mater. 2021;33:e2007548.
Hsu CP, Mandal J, Ramakrishna SN, Spencer ND, Isa L. Exploring the roles of roughness, friction and adhesion in discontinuous shear thickening by means of thermo-responsive particles. Nat Commun. 2021;12:1477.
Duan J, Yu B, Liu K, Li J, Yang P, Xie W, et al. P-N conversion in thermogalvanic cells induced by thermo-sensitive nanogels for body heat harvesting. Nano Energy. 2019;57:473–9.
Cao M, Shen Y, Yan Z, Wei Q, Jiao T, Shen Y, et al. Extraction-like removal of organic dyes from polluted water by the graphene oxide/PNIPAM composite system. Chem Eng J. 2021;405:126647.
Qureshi D, Nayak SK, Maji S, Anis A, Kim D, Pal K. Environment sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery applications. Eur Polym J. 2019;120:109220.
Lu F, Lin X, Wu Q, Zhou B, Lan R, Zhou S, et al. Observation of Unusual Thermoresponsive Volume Phase Transition Behavior of Cubic Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Microgels. ACS Macro Lett. 2020;9:266–71.
Zheng J, Xiao P, Le X, Lu W, Théato P, Ma C, et al. Mimosa inspired bilayer hydrogel actuator functioning in multi-environments. J Mater Chem C. 2018;6:1320–7.
Liu M, Song X, Wen Y, Zhu JL, Li J. Injectable Thermoresponsive Hydrogel Formed by Alginate-g-Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) That Releases Doxorubicin-Encapsulated Micelles as a Smart Drug Delivery System. ACS Appl Mater Interfac. 2017;9:35673–82.
Vahdati M, Ducouret G, Creton C, Hourdet D. Topology-Specific Injectable Sticky Hydrogels. Macromolecules. 2020;53:9779–92.
Guo B, Hoshino Y, Gao F, Hayashi K, Miura Y, Kimizuka N, et al. Thermocells Driven by Phase Transition of Hydrogel Nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;142:17318–22.
Xiong K, Xu L, Lin J, Mou F, Guan J. Mg-Based Micromotors with Motion Responsive to Dual Stimuli. Research (Wash D C). 2020;2020:6213981.
Cook MT, Haddow P, Kirton SB, McAuley WJ. Polymers Exhibiting Lower Critical Solution Temperatures as a Route to Thermoreversible Gelators for Healthcare. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30:2008123.
Mu Q, Zhang Q, Yu W, Su M, Cai Z, Cui K, et al. Robust Multiscale-Oriented Thermoresponsive Fibrous Hydrogels with Rapid Self-Recovery and Ultrafast Response Underwater. ACS Appl Mater Interfac. 2020;12:33152–62.
Zou M, Li S, Hu X, Leng X, Wang R, Zhou X, et al. Progresses in Tensile, Torsional, and Multifunctional Soft Actuators. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31:2007437.
Ilami M, Bagheri H, Ahmed R, Skowronek EO, Marvi H. Materials, Actuators, and Sensors for Soft Bioinspired Robots. Adv Mater. 2021;33:e2003139.
Zhu QL, Du C, Dai Y, Daab M, Matejdes M, Breu J, et al. Light-steered locomotion of muscle-like hydrogel by self-coordinated shape change and friction modulation. Nat Commun. 2020;11:5166.
Li C, Iscen A, Sai H, Sato K, Sather NA, Chin SM, et al. Supramolecular–covalent hybrid polymers for light-activated mechanical actuation. Nat Mater. 2020;19:900–9.
Ma C, Lu W, Yang X, He J, Le X, Wang L, et al. Bioinspired Anisotropic Hydrogel Actuators with On–Off Switchable and Color-Tunable Fluorescence Behaviors. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28:1704568.
Downs FG, Lunn DJ, Booth MJ, Sauer JB, Ramsay WJ, Klemperer RG. C. J. Hawker and H. Bayley. Nat Chem. 2020;12:363–71.
Yuk H, Lu B, Zhao X. Hydrogel bioelectronics. Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48:1642–67.
Liu Y, Li J, Song S, Kang J, Tsao Y, Chen S, et al. Morphing electronics enable neuromodulation in growing tissue. Nat Biotechnol. 2020;38:1031–6.
Liu J, Zhang X, Liu Y, Rodrigo M, Loftus PD, Aparicio-Valenzuela J, et al. Intrinsically stretchable electrode array enabled in vivo electrophysiological mapping of atrial fibrillation at cellular resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117:14769–78.
Feig VR, Tran H, Lee M, Liu K, Huang Z, Beker L, et al. An Electrochemical Gelation Method for Patterning Conductive PEDOT:PSS Hydrogels. Adv Mater. 2019;31:e1902869.
Li P, Wang Y, Gupta U, Liu J, Zhang L, Du D, et al. Transparent Soft Robots for Effective Camouflage. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29:1901908.
Xia S, Zhang Q, Song S, Duan L, Gao G. Feruloylated Oligosaccharides Alleviate Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Vivo. Chem Mater. 2019;31:9522–31.
Jolhe PD, Bhanvase BA, Patil VS, Sonawance SH. Sonocchemical synthesis of peracetic acid in a continuous flow micro-structured reactor. Chem Eng J. 2015;276:91–6.
Liu J, Xu W, Kuang Z, Dong P, Yao Y, Wu H, et al. Gradient porous PNIPAM-based hydrogel actuators with rapid response and flexibly controllable deformation. J Mater Chem C. 2020;8:12092–9.
Tan Y, Wang D, Xu H, Yang Y, Wang XL, Tian F, et al. Rapid Recovery Hydrogel Actuators in Air with Bionic Large-Ranged Gradient Structure. ACS Appl Mater Interfac. 2018;10:40125–31.
Geng H, Xu Q, Wu M, Ma H, Zhang P, Gao T, et al. Plant leaves inspired sunlight-driven purifier for high-efficiency clean water production. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1512.
Guo J, Yu Y, Wang H, Zhang H, Zhang X, Zhao Y. Conductive Polymer Hydrogel Microfibers from Multiflow Microfluidics. Small. 2019;15:e1805162.
Kim YS, Cho K, Lee HJ, Chang S, Lee H, Kim JH, et al. Highly conductive and hydrated PEG-based hydrogels for the potential application of a tissue engineering scaffold. React Funct Polym. 2016;109:15–22.
Bhat MA, Rather RA, Shalla AH. PEDOT and PEDOT:PSS conducting polymeric hydrogels: A report on their emerging applications. Synth Met. 2021;273:116709.
Han J, Cui Y, Han X, Liang C, Liu W, Luo D, et al. Super‐Soft DNA/Dopamine‐Grafted‐Dextran Hydrogel as Dynamic Wire for Electric Circuits Switched by a Microbial Metabolism Process. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7:2000684.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support of State Graduate Student Innovation Award No. KYCY20_1832, State Advanced Research for Industry Innovation Grant No. BE2017069, and the Fundamental Research Fund for Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, M., Zhang, J. Thermoresponsive PEDOT:PSS/PNIPAM conductive hydrogels as wearable resistive sensors for breathing pattern detection. Polym J 54, 793–801 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-022-00626-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-022-00626-y