Abstract
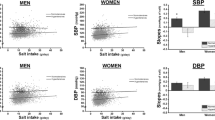
Excessive salt intake causes hypertension and heart diseases. B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a surrogate marker of heart disease, and a slightly elevated BNP level is associated with a poor prognosis. Our previous cross-sectional study demonstrated that plasma BNP has a significant positive association with daily salt intake in the general population. However, the relationship between changes in salt intake and changes in plasma BNP remains unknown. We recruited 3051 participants without hypertension or electrocardiogram abnormalities who underwent annual health check-ups for two consecutive years. Clinical parameters, including plasma BNP, were obtained, and daily salt intake was evaluated using urinary samples. Annual changes in these parameters were calculated. The median plasma BNP level was 12.9 pg/mL, and the daily salt intake was 8.73 ± 1.89 g. The annual changes in plasma BNP and daily salt intake were 4.79 ± 36.38% and 2.01 ± 21.80%, respectively. Participants in the highest quartile of annual changes in daily salt intake showed the largest annual changes in plasma BNP. Annual changes in plasma BNP indicated a significant positive association with daily salt intake. Moreover, multiple linear regression analyses revealed that annual changes in plasma BNP showed a significant positive association with daily salt intake after adjustments. Our study showed a significant positive relationship between annual changes in plasma BNP and annual changes in daily salt intake. The suppression of plasma BNP is therefore induced by salt intake restriction. The monitoring of plasma BNP while reducing salt intake may therefore prevent heart diseases and lead to improved prognoses in the general population without heart diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Graudal NA, Hubeck-Graudal T, Jurgens G. Effects of low sodium diet versus high sodium diet on blood pressure, renin, aldosterone, catecholamines, cholesterol, and triglyceride. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;4:CD004022. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004022.pub4.
Aburto NJ, Ziolkovska A, Hooper L, Elliott P, Cappuccio FP, Meerpohl JJ. Effect of lower sodium intake on health: systematic review and meta-analyses. BMJ. 2013;346:f1326. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f1326.
Mukoyama M, Nakao K, Hosoda K, Suga S, Saito Y, Ogawa Y, et al. Brain natriuretic peptide as a novel cardiac hormone in humans. Evidence for an exquisite dual natriuretic peptide system, atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide. J Clin Invest. 1991;87:1402–12.
Takase H, Toriyama T, Sugiura T, Ueda R, Dohi Y. Brain natriuretic peptide in the prediction of recurrence of angina pectoris. Eur J Clin Invest. 2004;34:79–84.
Takase H, Dohi Y, Sonoda H, Kimura G. Prediction of atrial fibrillation by B-type natriuretic peptide. J Atr Fibrillation. 2013;5:674. https://doi.org/10.4022/jafib.674.
Santaguida PL, Don-Wauchope AC, Oremus M, McKelvie R, Ali U, Hill SA, et al. BNP and NT-proBNP as prognostic markers in persons with acute decompensated heart failure: a systematic review. Heart Fail Rev. 2014;19:453–70.
Oremus M, Don-Wauchope A, McKelvie R, Santaguida PL, Hill S, Balion C, et al. BNP and NT-proBNP as prognostic markers in persons with chronic stable heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 2014;19:471–505.
McDonagh TA, Robb SD, Murdoch DR, Morton JJ, Ford I, Morrison CE, et al. Biochemical detection of left-ventricular systolic dysfunction. Lancet. 1998;351:9–13.
Ohashi N, Takase H, Aoki T, Matsuyama T, Ishigaki S, Isobe S, et al. Salt intake causes B-type natriuretic peptide elevation independently of blood pressure elevation in the general population without hypertension and heart disease. Med (Baltim). 2021;100:e25931. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000025931.
Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, Yasuda Y, Tomita K, Nitta K, et al. Collaborators developing the Japanese equation for estimated GFR. Collaborators developing the Japanese equation for estimated GFR. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:982–92.
Tanaka T, Okamura T, Miura K, Kadowaki T, Ueshima H, Nakagawa H, et al. A simple method to estimate populational 24-h urinary sodium and potassium excretion using a casual urine specimen. J Hum Hypertens. 2002;16:97–103.
Hashimoto T, Takase H, Okado T, Sugiura T, Yamashita S, Kimura G, et al. Significance of adjusting salt intake by body weight in the evaluation of dietary salt and blood pressure. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2016;10:647–55.e3.
Mino T, Kimura S, Kitaura A, Iwamoto T, Yuasa H, Chiba Y, et al. Can left ventricular hypertrophy on electrocardiography detect severe aortic valve stenosis? PLoS One. 2020;15:e0241591. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0241591.
Takase H, Dohi Y. Kidney function crucially affects B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), N-terminal proBNP and their relationship. Eur J Clin Invest. 2014;44:303–8.
Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, Benjamin EJ, Leip EP, Omland T, et al. Plasma natriuretic peptide levels and the risk of cardiovascular events and death. N. Engl J Med. 2004;350:655–63.
Damgaard M, Goetze JP, Norsk P, Gadsbøll N. Altered sodium intake affects plasma concentrations of BNP but not proBNP in healthy individuals and patients with compensated heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:2726–31.
Wambach G, Koch J. BNP plasma levels during acute volume expansion and chronic sodium loading in normal men. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1995;17:619–29.
Wen W, Wan Z, Ren K, Zhou D, Gao Q, Wu Y, et al. Potassium supplementation inhibits IL-17A production induced by salt loading in human T lymphocytes via p38/MAPK-SGK1 pathway. Exp Mol Pathol. 2016;100:370–7.
Yi B, Titze J, Rykova M, Feuerecker M, Vassilieva G, Nichiporuk I, et al. Effects of dietary salt levels on monocytic cells and immune responses in healthy human subjects: a longitudinal study. Transl Res. 2015;166:103–10.
Koshikawa M, Harada M, Noyama S, Kiyono K, Motoike Y, Nomura Y, et al. Association between inflammation and skeletal muscle proteolysis, skeletal mass and strength in elderly heart failure patients and their prognostic implications. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020;20:228. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-020-01514-0.
Brown IJ, Tzoulaki I, Candeias V, Elliott P. Salt intakes around the world: implications for public health. Int J Epidemiol. 2009;38:791–813.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohashi, N., Takase, H., Aoki, T. et al. Positive relationships between annual changes in salt intake and plasma B-type natriuretic peptide levels in the general population without hypertension and heart diseases. Hypertens Res 45, 944–953 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-022-00914-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-022-00914-3