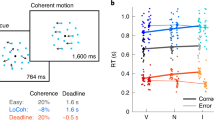
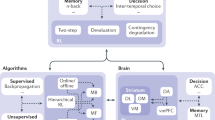
Abstract
The outcome of a decision is often uncertain, and outcomes can vary over repeated decisions. Whether decision outcomes should substantially affect behaviour and learning depends on whether they are representative of a typically experienced range of outcomes or signal a change in the reward environment. Successful learning and decision-making therefore require the ability to estimate expected uncertainty (related to the variability of outcomes) and unexpected uncertainty (related to the variability of the environment). Understanding the bases and effects of these two types of uncertainty and the interactions between them — at the computational and the neural level — is crucial for understanding adaptive learning. Here, we examine computational models and experimental findings to distil computational principles and neural mechanisms for adaptive learning under uncertainty.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doya, K. Modulators of decision making. Nat. Neurosci. 11, 410–416 (2008).
Farashahi, S. et al. Metaplasticity as a neural substrate for adaptive learning and choice under uncertainty. Neuron 94, 401–414 (2017).
Iigaya, K. Adaptive learning and decision-making under uncertainty by metaplastic synapses guided by a surprise detection system. eLife 5, e18073 (2016).
Khorsand, P. & Soltani, A. Optimal structure of metaplasticity for adaptive learning. PLOS Comput. Biol. 13, e1005630 (2017).
Dayan, P., Kakade, S. & Montague, P. R. Learning and selective attention. Nat. Neurosci. 3, S1218–S1223 (2000).
Courville, A. C., Daw, N. D. & Touretzky, D. S. Bayesian theories of conditioning in a changing world. Trends Cogn. Sci. 10, 294–300 (2006).
Bach, D. R. & Dolan, R. J. Knowing how much you don’t know: a neural organization of uncertainty estimates. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 13, 572–586 (2012).
McDannald, M. A. et al. Model-based learning and the contribution of the orbitofrontal cortex to the model-free world. Eur. J. Neurosci. 35, 991–996 (2012).
Langdon, A. J. et al. Model-based predictions for dopamine. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 49, 1–7 (2018).
Tobler, P. N. et al. Reward value coding distinct from risk attitude-related uncertainty coding in human reward systems. J. Neurophysiol. 97, 1621–1632 (2007).
O’Reilly, J. X. Making predictions in a changing world-inference, uncertainty, and learning. Front. Neurosci. 7, 105 (2013).
Preuschoff, K. & Bossaerts, P. Adding prediction risk to the theory of reward learning. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1104, 135–146 (2007).
Diederen, K. M. & Schultz, W. Scaling prediction errors to reward variability benefits error-driven learning in humans. J. Neurophysiol. 114, 1628–1640 (2015).
Yu, A. J. & Dayan, P. Uncertainty, neuromodulation, and attention. Neuron 46, 681–692 (2005).
Payzan-LeNestour, E. & Bossaerts, P. Risk, unexpected uncertainty, and estimation uncertainty: Bayesian learning in unstable settings. PLOS Comput. Biol. 7, e1001048 (2011).
Faraji, M., Preuschoff, K. & Gerstner, W. Balancing new against old information: the role of puzzlement surprise in learning. Neural Comput. 30, 34–83 (2018).
Jang, A. I. et al. The role of frontal cortical and medial-temporal lobe brain areas in learning a Bayesian prior belief on reversals. J. Neurosci. 35, 11751–11760 (2015).
Chen, W. J. & Krajbich, I. Computational modeling of epiphany learning. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, 4637–4642 (2017).
Nassar, M. R. et al. An approximately Bayesian delta-rule model explains the dynamics of belief updating in a changing environment. J. Neurosci. 30, 12366–12378 (2010).
Behrens, T. E. et al. Learning the value of information in an uncertain world. Nat. Neurosci. 10, 1214–1221 (2007).
Costa, V. D. et al. Reversal learning and dopamine: a Bayesian perspective. J. Neurosci. 35, 2407–2416 (2015).
Mathys, C. et al. A bayesian foundation for individual learning under uncertainty. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 5, 39 (2011).
Funamizu, A. et al. Uncertainty in action-value estimation affects both action choice and learning rate of the choice behaviors of rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 35, 1180–1189 (2012).
Payzan-LeNestour, E. et al. The neural representation of unexpected uncertainty during value-based decision making. Neuron 79, 191–201 (2013).
Wilson, R. C., Nassar, M. R. & Gold, J. I. A mixture of delta-rules approximation to bayesian inference in change-point problems. PLOS Comput. Biol. 9, e1003150 (2013).
McGuire, J. T. et al. Functionally dissociable influences on learning rate in a dynamic environment. Neuron 84, 870–881 (2014).
Sutton, R. S. & Barto, A. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction (MIT Press, 1998).
Pearce, J. M. & Hall, G. A model for Pavlovian learning: variations in the effectiveness of conditioned but not of unconditioned stimuli. Psychol. Rev. 87, 532–552 (1980).
Roesch, M. R. et al. Surprise! Neural correlates of Pearce–Hall and Rescorla–Wagner coexist within the brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 35, 1190–1200 (2012).
Krugel, L. K. et al. Genetic variation in dopaminergic neuromodulation influences the ability to rapidly and flexibly adapt decisions. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 17951–17956 (2009).
Dayan, P. & Long, T. in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 10: Proceedings of the 1997 Conference (eds Jordan, M. I., Kearns, M. J. & Solla, S. A.) 117–123 (MIT Press, 1998).
Schultz, W., Dayan, P. & Montague, P. R. A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 275, 1593–1599 (1997).
Soltani, A. C., W. & Wang, X. J. in Decision Neuroscience: An Integrative Perspective (eds Dreher, J.-C. & Tremblay, L.) 163–222 (Elsevier Academic Press, 2017).
Berridge, K. C. & Robinson, T. E. What is the role of dopamine in reward: hedonic impact, reward learning, or incentive salience? Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 28, 309–369 (1998).
Salamone, J. D. et al. Beyond the reward hypothesis: alternative functions of nucleus accumbens dopamine. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 5, 34–41 (2005).
Redgrave, P. & Gurney, K. The short-latency dopamine signal: a role in discovering novel actions? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 7, 967–975 (2006).
Abraham, W. C. Metaplasticity: tuning synapses and networks for plasticity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 387 (2008).
Walton, M. E. et al. Separable learning systems in the macaque brain and the role of orbitofrontal cortex in contingent learning. Neuron 65, 927–939 (2010).
Grupe, D. W. & Nitschke, J. B. Uncertainty and anticipation in anxiety: an integrated neurobiological and psychological perspective. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 14, 488–501 (2013).
Niv, Y., Duff, M. O. & Dayan, P. Dopamine, uncertainty and TD learning. Behav. Brain Funct. 1, 6 (2005).
Gershman, S. J. Dopamine, inference, and uncertainty. Neural Comput. 29, 3311–3326 (2017).
Rogers, R. D. The roles of dopamine and serotonin in decision making: evidence from pharmacological experiments in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 36, 114–132 (2011).
Rushworth, M. F. & Behrens, T. E. Choice, uncertainty and value in prefrontal and cingulate cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 11, 389–397 (2008).
Hayden, B. Y. et al. Surprise signals in anterior cingulate cortex: neuronal encoding of unsigned reward prediction errors driving adjustment in behavior. J. Neurosci. 31, 4178–4187 (2011).
Monosov, I. E. Anterior cingulate is a source of valence-specific information about value and uncertainty. Nat. Commun. 8, 134 (2017).
Seo, H. & Lee, D. Temporal filtering of reward signals in the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex during a mixed-strategy game. J. Neurosci. 27, 8366–8377 (2007).
Hyman, J. M., Holroyd, C. B. & Seamans, J. K. A. Novel neural prediction error found in anterior cingulate cortex ensembles. Neuron 95, 447–456 (2017).
Amiez, C., Joseph, J. P. & Procyk, E. Anterior cingulate error-related activity is modulated by predicted reward. Eur. J. Neurosci. 21, 3447–3452 (2005).
Sul, J. H. et al. Distinct roles of rodent orbitofrontal and medial prefrontal cortex in decision making. Neuron 66, 449–460 (2010).
Stalnaker, T. A. et al. Orbitofrontal neurons signal reward predictions, not reward prediction errors. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 153, 137–143 (2018).
Stalnaker, T. A., Cooch, N. K. & Schoenbaum, G. What the orbitofrontal cortex does not do. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 620–627 (2015).
Riceberg, J. S. & Shapiro, M. L. Orbitofrontal cortex signals expected outcomes with predictive codes when stable contingencies promote the integration of reward history. J. Neurosci. 37, 2010–2021 (2017).
Jo, S. & Jung, M. W. Differential coding of uncertain reward in rat insular and orbitofrontal cortex. Sci. Rep. 6, 24085 (2016).
Riceberg, J. S. & Shapiro, M. L. Reward stability determines the contribution of orbitofrontal cortex to adaptive behavior. J. Neurosci. 32, 16402–16409 (2012).
Izquierdo, A. Functional heterogeneity within rat orbitofrontal cortex in reward learning and decision making. J. Neurosci. 37, 10529–10540 (2017).
Wallis, J. D. Cross-species studies of orbitofrontal cortex and value-based decision-making. Nat. Neurosci. 15, 13–19 (2011).
Rich, E. L. & Wallis, J. D. Decoding subjective decisions from orbitofrontal cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 19, 973–980 (2016).
O’Neill, M. & Schultz, W. Coding of reward risk by orbitofrontal neurons is mostly distinct from coding of reward value. Neuron 68, 789–800 (2010).
Saez, R. A. et al. Distinct roles for the amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex in representing the relative amount of expected reward. Neuron 95, 70–77 (2017).
Massi, B., Donahue, C. H. & Lee, D. Volatility facilitates value updating in the prefrontal cortex. Neuron 99, 598–608 (2018).
Paus, T. Primate anterior cingulate cortex: where motor control, drive and cognition interface. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 417–424 (2001).
Heilbronner, S. R. & Hayden, B. Y. Dorsal anterior cingulate cortex: a bottom-up view. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 39, 149–170 (2016).
Rushworth, M. F. et al. Frontal cortex and reward-guided learning and decision-making. Neuron 70, 1054–1069 (2011).
Shenhav, A., Botvinick, M. M. & Cohen, J. D. The expected value of control: an integrative theory of anterior cingulate cortex function. Neuron 79, 217–240 (2013).
Kennerley, S. W. et al. Optimal decision making and the anterior cingulate cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 940–947 (2006).
Winstanley, C. A. & Floresco, S. B. Deciphering decision making: variation in animal models of effort- and uncertainty-based choice reveals distinct neural circuitries underlying core cognitive processes. J. Neurosci. 36, 12069–12079 (2016).
Mobini, S. et al. Effects of lesions of the orbitofrontal cortex on sensitivity to delayed and probabilistic reinforcement. Psychopharmacology 160, 290–298 (2002).
Stolyarova, A. & Izquierdo, A. Complementary contributions of basolateral amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex to value learning under uncertainty. eLife 6, e27483 (2017).
Dalton, G. L. et al. Multifaceted contributions by different regions of the orbitofrontal and medial prefrontal cortex to probabilistic reversal learning. J. Neurosci. 36, 1996–2006 (2016).
Bradfield, L. A. et al. Medial orbitofrontal cortex mediates outcome retrieval in partially observable task situations. Neuron 88, 1268–1280 (2015).
Rudebeck, P. H. et al. Specialized representations of value in the orbital and ventrolateral prefrontal cortex: desirability versus availability of outcomes. Neuron 95, 1208–1220 (2017).
Noonan, M. P. et al. Separate value comparison and learning mechanisms in macaque medial and lateral orbitofrontal cortex. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 20547–20552 (2010).
Meder, D. et al. Simultaneous representation of a spectrum of dynamically changing value estimates during decision making. Nat. Commun. 8, 1942 (2017).
Heilbronner, S. R. et al. Circuit-based corticostriatal homologies between rat and primate. Biol. Psychiatry 80, 509–521 (2016).
Vogt, B. A. & Paxinos, G. Cytoarchitecture of mouse and rat cingulate cortex with human homologies. Brain Struct. Funct. 219, 185–192 (2014).
Hoover, W. B. & Vertes, R. P. Projections of the medial orbital and ventral orbital cortex in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 519, 3766–3801 (2011).
Hunt, L. T. et al. Triple dissociation of attention and decision computations across prefrontal cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 21, 1471–1481 (2018).
White, J. K. & Monosov, I. E. Neurons in the primate dorsal striatum signal the uncertainty of object-reward associations. Nat. Commun. 7, 12735 (2016).
Costa, V. D. et al. Amygdala and ventral striatum make distinct contributions to reinforcement learning. Neuron 92, 505–517 (2016).
St Onge, J. R. et al. Separate prefrontal-subcortical circuits mediate different components of risk-based decision making. J. Neurosci. 32, 2886–2899 (2012).
Averbeck, B. B. & Costa, V. D. Motivational neural circuits underlying reinforcement learning. Nat. Neurosci. 20, 505–512 (2017).
Monosov, I. E. & Hikosaka, O. Selective and graded coding of reward uncertainty by neurons in the primate anterodorsal septal region. Nat. Neurosci. 16, 756–762 (2013).
Unal, G. et al. Synaptic targets of medial septal projections in the hippocampus and extrahippocampal cortices of the mouse. J. Neurosci. 35, 15812–15826 (2015).
Kumaran, D. & Maguire, E. A. An unexpected sequence of events: mismatch detection in the human hippocampus. PLOS Biol. 4, e424 (2006).
Vanni-Mercier, G. et al. The hippocampus codes the uncertainty of cue-outcome associations: an intracranial electrophysiological study in humans. J. Neurosci. 29, 5287–5294 (2009).
Wikenheiser, A. M. & Schoenbaum, G. Over the river, through the woods: cognitive maps in the hippocampus and orbitofrontal cortex. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 513–523 (2016).
Wikenheiser, A. M. & Redish, A. D. Decoding the cognitive map: ensemble hippocampal sequences and decision making. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 32, 8–15 (2015).
Morrison, S. E. et al. Different time courses for learning-related changes in amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex. Neuron 71, 1127–1140 (2011).
Rudebeck, P. H. et al. Amygdala contributions to stimulus-reward encoding in the macaque medial and orbital frontal cortex during learning. J. Neurosci. 37, 2186–2202 (2017).
Saez, A. et al. Abstract context representations in primate amygdala and prefrontal cortex. Neuron 87, 869–881 (2015).
Wassum, K. M. & Izquierdo, A. The basolateral amygdala in reward learning and addiction. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 57, 271–283 (2015).
Roesch, M. R. et al. Neural correlates of variations in event processing during learning in basolateral amygdala. J. Neurosci. 30, 2464–2471 (2010).
Cassell, M. D. & Wright, D. J. Topography of projections from the medial prefrontal cortex to the amygdala in the rat. Brain Res. Bull. 17, 321–333 (1986).
Amaral, D. G. & Price, J. L. Amygdalo-cortical projections in the monkey (Macaca fascicularis). J. Comp. Neurol. 230, 465–496 (1984).
Sharpe, M. J. & Schoenbaum, G. Back to basics: making predictions in the orbitofrontal-amygdala circuit. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 131, 201–206 (2016).
Lucantonio, F. et al. Neural estimates of imagined outcomes in basolateral amygdala depend on orbitofrontal cortex. J. Neurosci. 35, 16521–16530 (2015).
Stopper, C. M. et al. Overriding phasic dopamine signals redirects action selection during risk/reward decision making. Neuron 84, 177–189 (2014).
Mitchell, A. S., Baxter, M. G. & Gaffan, D. Dissociable performance on scene learning and strategy implementation after lesions to magnocellular mediodorsal thalamic nucleus. J. Neurosci. 27, 11888–11895 (2007).
Izquierdo, A. & Murray, E. A. Functional interaction of medial mediodorsal thalamic nucleus but not nucleus accumbens with amygdala and orbital prefrontal cortex is essential for adaptive response selection after reinforcer devaluation. J. Neurosci. 30, 661–669 (2010).
Mitchell, A. S. et al. Advances in understanding mechanisms of thalamic relays in cognition and behavior. J. Neurosci. 34, 15340–15346 (2014).
Chakraborty, S. et al. Critical role for the mediodorsal thalamus in permitting rapid reward-guided updating in stochastic reward environments. eLife 5, e13588 (2016).
Parnaudeau, S. et al. Mediodorsal thalamus hypofunction impairs flexible goal-directed behavior. Biol. Psychiatry 77, 445–453 (2015).
Wolff, M. & Vann, S. D. The cognitive thalamus as a gateway to mental representations. J. Neurosci. 39, 3–14 (2019).
Voon, V. et al. Model-based control in dimensional psychiatry. Biol. Psychiatry 82, 391–400 (2017).
Vaghi, M. M. et al. Compulsivity reveals a novel dissociation between action and confidence. Neuron 96, 348–354 (2017).
Soltani, A. & Wang, X. J. A biophysically based neural model of matching law behavior: melioration by stochastic synapses. J. Neurosci. 26, 3731–3744 (2006).
Soltani, A. & Wang, X. J. From biophysics to cognition: reward-dependent adaptive choice behavior. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 18, 209–216 (2008).
Izquierdo, A. et al. The neural basis of reversal learning: an updated perspective. Neuroscience 345, 12–26 (2017).
Cardinal, R. N. Neural systems implicated in delayed and probabilistic reinforcement. Neural Netw. 19, 1277–1301 (2006).
Cardinal, R. N. & Howes, N. J. Effects of lesions of the nucleus accumbens core on choice between small certain rewards and large uncertain rewards in rats. BMC Neurosci. 6, 37 (2005).
Ghods-Sharifi, S., St Onge, J. R. & Floresco, S. B. Fundamental contribution by the basolateral amygdala to different forms of decision making. J. Neurosci. 29, 5251–5259 (2009).
Li, Y. & Dudman, J. T. Mice infer probabilistic models for timing. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 110, 17154–17159 (2013).
Dalton, G. L., Phillips, A. G. & Floresco, S. B. Preferential involvement by nucleus accumbens shell in mediating probabilistic learning and reversal shifts. J. Neurosci. 34, 4618–4626 (2014).
Donahue, C. H. & Lee, D. Dynamic routing of task-relevant signals for decision making in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 295–301 (2015).
Amodeo, L. R., McMurray, M. S. & Roitman, J. D. Orbitofrontal cortex reflects changes in response-outcome contingencies during probabilistic reversal learning. Neuroscience 345, 27–37 (2017).
Daw, N. D. et al. Cortical substrates for exploratory decisions in humans. Nature 441, 876–879 (2006).
Averbeck, B. B. Theory of choice in bandit, information sampling and foraging tasks. PLOS Comput. Biol. 11, e1004164 (2015).
Groman, S. M. et al. Chronic exposure to methamphetamine disrupts reinforcement-based decision making in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 43, 770–780 (2018).
Groman, S. M. et al. Dopamine D3 receptor availability is associated with inflexible decision making. J. Neurosci. 36, 6732–6741 (2016).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank D. Lee, P. Rudebeck and A. Wikenheiser for helpful feedback. The authors acknowledge support from the US National Institutes of Health Grant R01DA047870 (A.S. and A.I.), a University of California–Los Angeles (UCLA) Division of Life Sciences Recruitment and Retention Fund (A.I.) and a UCLA Academic Senate Grant (A.I.).
Reviewer information
Nature Reviews Neuroscience thanks S. B. Floresco and K. Preuschoff, and the other anonymous reviewer(s), for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors researched data for the article, made substantial contributions to discussion of the content, wrote the article and reviewed or edited the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soltani, A., Izquierdo, A. Adaptive learning under expected and unexpected uncertainty. Nat Rev Neurosci 20, 635–644 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-019-0180-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-019-0180-y
This article is cited by
-
Longitudinal trajectories of anterior cingulate glutamate and subclinical psychotic experiences in early adolescence: the impact of bullying victimization
Molecular Psychiatry (2024)
-
Goal-directed learning in adolescence: neurocognitive development and contextual influences
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2024)
-
Assumed shared belief about conspiracy theories in social networks protects paranoid individuals against distress
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
The rat frontal orienting field dynamically encodes value for economic decisions under risk
Nature Neuroscience (2023)
-
Reinforcement Learning Under Uncertainty: Expected Versus Unexpected Uncertainty and State Versus Reward Uncertainty
Computational Brain & Behavior (2023)