Volume 17
-
No. 12 December 2011
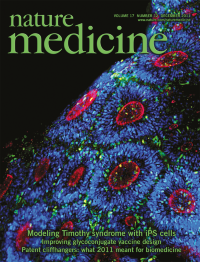
In this issue (p 1657), Ricardo Dolmetsch and his colleagues show that a mutation that causes Timothy syndrome, a condition characterized by autistic features, epilepsy and other non-neurological phenotypes, affects neuronal fate in the cerebral cortex. The cover depicts clusters of human neural progenitors derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. Image courtesy of R. Dolmetsch (Stanford University).
-
No. 11 November 2011
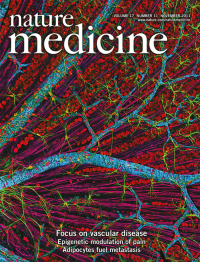
In this issue, we feature a collection of review articles on different aspects of vascular disease to accompany our recent meeting 'Vascular Disease 2011: From Bench to Bedside'. The image shows a quadruple multiphoton fluorescence image of mouse retina stained to reveal GFAP in astrocytes (green), neurofilaments in the retinal ganglion axons (magenta), actin in the vascular endothelial cells (red) and RNA and DNA (cyan). Image courtesy of T. Deerinck and M. Ellisman, the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research, UCSD.
Focus
-
No. 10 October 2011
Biomedical research is on the rise in Brazil. Our special news focus (p 1169) examines the strengths of the country's translational science and the many challenges Brazil faces to become a world leader in drug development.
-
No. 9 September 2011
In this issue, Liu et al. (p 1116) uncover new mechanisms of mammary tumor resistance to PI3K-targeted therapy. The artwork on the cover is by Haiming Cheng, sister of one of the authors, entitled The Promise and the Challenge of PI3K-Targeted Therapy in Breast Cancer. Also in this issue, Korpal et al. (p 1101) reveal a new role for miR-200 in metastatic colonization of breast cancer, and Lyons et al. (p 1109) uncover molecular pathways responsible for the increased risk and malignancy of postpartum breast cancer.
-
No. 8 August 2011
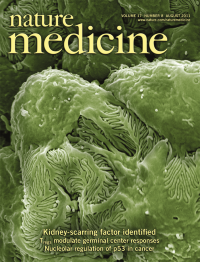
In this issue, Wei et al. (p 952) have identified soluble urokinase receptor as the long-sought-after soluble serum factor that can cause focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. The cover shows a scanning electron micrograph of mouse glomerular podocytes. Magnification, ×15,000. Image courtesy of Björn Hartleben, Martin Helmstädter and Tobias B. Huber, University Hospital Freiburg.
-
No. 7 July 2011
Cholinergic signaling is vital for pancreatic beta cell function. In this issue, Rodriguez-Diaz et al. (p. 888) show that alpha cells of human pancreatic islets provide cholinergic input to beta cells, sensitizing them to increases in glucose concentration. The cover shows a three-dimensional rendering of a human islet in which glucagon-labeled alpha cells (red; nuclei in blue) express the vesicular acetylcholine transporter (green). Image courtesy of Rayner Rodriguez-Diaz and Midhat H. Abdulreda, University of Miami.
-
No. 6 June 2011
Mutations in LDL receptorrelated protein 5 (LRP5) affect bone formation. In this issue, Cui et al. (p 684) show that high- and low-bone-mass phenotypes resulting from different Lrp5 mutations occur within the bone tissue. The cover shows an undemineralized section through the ulna (top) and radius (bottom) of an adult mouse. Image courtesy of Alexander G. Robling, Indiana University School of Medicine.
-
No. 5 May 2011
Fragile X mental retardation syndrome is caused by mutations in FMRP. In this issue, Weixiang Guo et al. (p 559) examine the role of stem cell FMRP in driving disease. The cover shows a mouse hippocampus, courtesy of Tom Deerinck, NCMIR, UCSD.
-
No. 4 April 2011
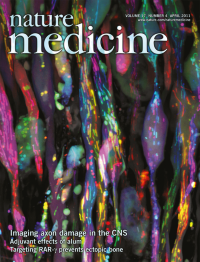
In multiple sclerosis, axonal damage leads to permanent neurologic deficits. In this issue, Ivana Nikić et al. (p 495) report that axonal damage is characterized by distinct morphologic stages and is reversible. The cover shows a confocal microscopy image of injured axons (white) and damaged axonal mitochondria (color coded for depth) in the spinal cord of a mouse with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
-
No. 3 March 2011
Huntington's disease is characterized by mitochondrial dysfunction and neuron death. In this issue, Ella Bossy-Wetzel and her colleagues report that the aberrant interaction of mutant huntingtin protein with the mitochondrial fission protein DRP1 results in DRP1 activation and neuron death. The cover image shows the cristae inside a portion of a mitochondrion.
Focus
-
No. 2 February 2011
In this issue (p 223), Barretto et al. use fluorescence microendoscopy to image deep brain areas in vivo. The cover shows a dual-color image of CA1 pyramidal neurons expressing green fluorescence protein and the surrounding microvasculature (of Texas-red-dextran) labeled by intravascular injection in a live mouse. Image courtesy of Yaniv Ziv and Mark Schnitzer, Stanford University.
-
No. 1 January 2011
Reliable imaging of metastatic tumor cells would have a major impact on cancer diagnosis and treatment. In this issue (p 123), Martin Pomper and his coworkers develop a technology to detect micrometastases using systemic in vivo delivery of a reporter imaging gene in tumor-bearing mice. The cover image shows concurrent computed tomography (CT, top and bottom rows) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT, middle and bottom rows) images of mouse lungs for detection of reporter gene-expressing tumor cells.