Featured
-
-
Outlook |
 Diagnostics: The new risk predictors
Diagnostics: The new risk predictors
New imaging methods and biomarkers may help identify people who are at risk for heart disease but are overlooked by standard risk assessments.
- Peter Gwynne
-
Article |
 Functional screening identifies miRNAs inducing cardiac regeneration
Functional screening identifies miRNAs inducing cardiac regeneration
The human heart regenerates poorly, causing insufficient healing after injury; here, microRNAs screened for the ability to induce cardiomyocyte proliferation are shown to stimulate cardiac regeneration and almost complete recovery of the heart after infarction.
- Ana Eulalio
- , Miguel Mano
- & Mauro Giacca
-
Letter |
 Mammalian heart renewal by pre-existing cardiomyocytes
Mammalian heart renewal by pre-existing cardiomyocytes
During normal ageing a low rate of division of pre-existing cardiomyocytes, rather than progenitor cells, is responsible for cardiomyocyte genesis; this process is increased fourfold during myocardial infarction.
- Samuel E. Senyo
- , Matthew L. Steinhauser
- & Richard T. Lee
-
Research Highlights |
Nanofibres foster blood vessels
-
News & Views |
 Bad matters made worse
Bad matters made worse
Heart attacks occur when lipoprotein-driven inflammation called atherosclerosis triggers blood clotting in the arteries. It seems that the attacks can, in turn, accelerate atherosclerosis by fanning the inflammation. See Letter p.325
- Ira Tabas
-
Article |
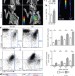 Myocardial infarction accelerates atherosclerosis
Myocardial infarction accelerates atherosclerosis
Myocardial infarction accelerates atherosclerosis through activation of the sympathetic nervous system, and the consequent release of haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.
- Partha Dutta
- , Gabriel Courties
- & Matthias Nahrendorf
-
Article |
 Heart repair by reprogramming non-myocytes with cardiac transcription factors
Heart repair by reprogramming non-myocytes with cardiac transcription factors
A combination of four transcription factors, GATA4, HAND2, MEF2C and TBX5, can reprogram fibroblasts into cardiac-like myocytes in vitro and in vivo; expression of these factors ameliorated cardiac function in mice that had suffered myocardial infarction.
- Kunhua Song
- , Young-Jae Nam
- & Eric N. Olson
-
Research Highlights |
Restore my beating heart
-
Research Highlights |
Heart attack hits bone marrow
-
Letter |
 De novo cardiomyocytes from within the activated adult heart after injury
De novo cardiomyocytes from within the activated adult heart after injury
- Nicola Smart
- , Sveva Bollini
- & Paul R. Riley
-
Research Highlights |
 Fooling the heart into repair
Fooling the heart into repair
-
Article |
 From noncoding variant to phenotype via SORT1 at the 1p13 cholesterol locus
From noncoding variant to phenotype via SORT1 at the 1p13 cholesterol locus
A non-coding polymorphism at a locus associated with myocardial infarction in humans creates a CCAAT/enhancer binding protein transcription factor binding site and alters the hepatic expression of the SORT1 gene. These authors show that modulating Sort1 levels in mouse liver alters levels of plasma low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and very low-density lipoprotein, potentially explaining why polymorphisms at this locus are associated with heart disease.
- Kiran Musunuru
- , Alanna Strong
- & Daniel J. Rader

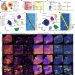 Spatial multi-omic map of human myocardial infarction
Spatial multi-omic map of human myocardial infarction