Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Photosynthesis re-wired on the pico-second timescale
Photosynthesis re-wired on the pico-second timescale
By using in vivo ultrafast TA spectroscopy, extraction of electrons directly from photoexcited PSI and PSII in cyanobacterial cells using exogenous electron mediators is demonstrated.
- Tomi K. Baikie
- , Laura T. Wey
- & Jenny Z. Zhang
-
Article |
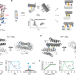 Overcoming universal restrictions on metal selectivity by protein design
Overcoming universal restrictions on metal selectivity by protein design
An alternative approach to metalloprotein design shows that it is possible to overcome the restrictions of the Irving–Williams series and achieve both flexibility and specificity in the binding of metal ions.
- Tae Su Choi
- & F. Akif Tezcan
-
Article |
 Few-fs resolution of a photoactive protein traversing a conical intersection
Few-fs resolution of a photoactive protein traversing a conical intersection
Serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) has provided significant understanding of time-resolved processes of various systems in biology, for example, rhodopsin, which underlies our vision. The approach involves femtosecond-length X-ray pulses directed at protein crystals and has been used to study various photoactive proteins. However, the function of proteins such as rhodopsin requires trans–cis isomerization of a chromophore, which involves crossing of a conical intersection—a funnel separating potential energy surfaces—at timescales faster than what can be achieved experimentally. Here, Ourmazd and colleagues report a machine learning analysis of SFX data of photoactive yellow protein, which resolves the protein passing through a conical intersection, providing information about the potential energy surfaces involved and achieving time resolution of less than 10 fs. This approach offers an opportunity to understand some of the fastest processes in biology by extracting even more information from SFX datasets.
- A. Hosseinizadeh
- , N. Breckwoldt
- & A. Ourmazd
-
Article |
 Intracellular pH controls WNT downstream of glycolysis in amniote embryos
Intracellular pH controls WNT downstream of glycolysis in amniote embryos
The authors show that metabolic activity leads to an increase in the intracellular pH of neuromesodermal precursors, and that this increase in pH, by allowing post-translational modification of β-catenin, is required for the activation of WNT signalling and mesodermal fate acquisition.
- Masayuki Oginuma
- , Yukiko Harima
- & Olivier Pourquié
-
Article |
 Crystal structure of the natural anion-conducting channelrhodopsin GtACR1
Crystal structure of the natural anion-conducting channelrhodopsin GtACR1
The crystal structure of anion channelrhodopsin-1 (ACR1) from the algae Guillardia theta provides insights into the basis of anion conductance.
- Yoon Seok Kim
- , Hideaki E. Kato
- & Karl Deisseroth
-
Letter |
 Molecular nucleation mechanisms and control strategies for crystal polymorph selection
Molecular nucleation mechanisms and control strategies for crystal polymorph selection
Cryo-transmission electron microscopy reveals the initiation of glucose isomerase crystals and their growth into different crystalline or gel polymorphs, and shows that mutating specific amino acids controls which polymorph grows.
- Alexander E. S. Van Driessche
- , Nani Van Gerven
- & Mike Sleutel
-
Article |
 Extreme disorder in an ultrahigh-affinity protein complex
Extreme disorder in an ultrahigh-affinity protein complex
A high-affinity complex of histone H1 and prothymosin-α reveals an unexpected interaction mechanism, where the large opposite net charge enables the two proteins to remain highly disordered even in the complex.
- Alessandro Borgia
- , Madeleine B. Borgia
- & Benjamin Schuler
-
Article |
 Dynamic basis for dG•dT misincorporation via tautomerization and ionization
Dynamic basis for dG•dT misincorporation via tautomerization and ionization
A kinetic model is proposed to predict the probability of dG•dT misincorporation across different polymerases, and provides mechanisms for sequence-dependent misincorporation.
- Isaac J. Kimsey
- , Eric S. Szymanski
- & Hashim M. Al-Hashimi
-
Letter |
 Liquid droplet formation by HP1α suggests a role for phase separation in heterochromatin
Liquid droplet formation by HP1α suggests a role for phase separation in heterochromatin
Phosphorylation or DNA binding promotes the physical partitioning of HP1α out of a soluble aqueous phase into droplets, suggesting that the repressive action of heterochromatin may in part be mediated by the phase separation of HP1.
- Adam G. Larson
- , Daniel Elnatan
- & Geeta J. Narlikar
-
Letter |
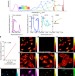 Super-multiplex vibrational imaging
Super-multiplex vibrational imaging
Stimulated Raman scattering under electronic pre-resonance conditions, combined with a new palette of probes, enables super-multiplex imaging of molecular targets in living cells with very high vibrational selectivity and sensitivity.
- Lu Wei
- , Zhixing Chen
- & Wei Min
-
Letter |
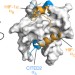 Hypersensitive termination of the hypoxic response by a disordered protein switch
Hypersensitive termination of the hypoxic response by a disordered protein switch
The intrinsically disordered CITED2 negative feedback regulator displaces the tightly bound hypoxia-inducible transcription factor HIF-1α from their common target TAZ1 through the formation of an intermediate ternary complex and thereby attenuates the hypoxic response.
- Rebecca B. Berlow
- , H. Jane Dyson
- & Peter E. Wright
-
Letter |
 Structure of photosystem II and substrate binding at room temperature
Structure of photosystem II and substrate binding at room temperature
The structures of three intermediate states of photosystem II, which is crucial for photosynthesis, have been solved at room temperature, shedding new light on this process.
- Iris D. Young
- , Mohamed Ibrahim
- & Junko Yano
-
Letter |
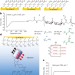 Modulation of hydrophobic interactions by proximally immobilized ions
Modulation of hydrophobic interactions by proximally immobilized ions
Chemical force microscopy measurements show that the immobilization of specific cationic groups near non-polar domains produces pronounced changes in the domains’ hydrophobic interaction strengths: charged ammonium groups double interaction strengths, whereas guanidinium groups eliminate measurable interactions.
- C. Derek Ma
- , Chenxuan Wang
- & Nicholas L. Abbott
-
Article |
 Structure of the DDB1–CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase in complex with thalidomide
Structure of the DDB1–CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase in complex with thalidomide
The crystal structures of thalidomide and its derivatives bound to the E3 ligase subcomplex DDB1–CRBN are shown; these drugs are found to have dual functions, interfering with the binding of certain cellular substrates to the E3 ligase but promoting the binding of others, thereby modulating the degradation of cellular proteins.
- Eric S. Fischer
- , Kerstin Böhm
- & Nicolas H. Thomä
-
Article |
 DNA interrogation by the CRISPR RNA-guided endonuclease Cas9
DNA interrogation by the CRISPR RNA-guided endonuclease Cas9
This study defines how a short DNA sequence, known as the PAM, is critical for target DNA interrogation by the CRISPR-associated enzyme Cas9 — DNA melting and heteroduplex formation initiate near the PAM and extend directionally through the remaining target sequence, and the PAM is also required to activate the catalytic activity of Cas9.
- Samuel H. Sternberg
- , Sy Redding
- & Jennifer A. Doudna
-
Letter |
 Responsive biomimetic networks from polyisocyanopeptide hydrogels
Responsive biomimetic networks from polyisocyanopeptide hydrogels
Thermal transitions of polyisocyanide single molecules to polymer bundles and finally networks lead to hydrogels mimicking the properties of biopolymer intermediate-filament networks; their analysis shows that bundling and chain stiffness are crucial design parameters for hydrogels.
- Paul H. J. Kouwer
- , Matthieu Koepf
- & Alan E. Rowan
-
Letter |
 Ubiquitin chain conformation regulates recognition and activity of interacting proteins
Ubiquitin chain conformation regulates recognition and activity of interacting proteins
Single-molecule FRET assays used to probe the conformational dynamics of ubiquitin chains reveal that conformational selection is an important mechanism of ubiquitin chain recognition.
- Yu Ye
- , Georg Blaser
- & David Komander

 m1A in CAG repeat RNA binds to TDP-43 and induces neurodegeneration
m1A in CAG repeat RNA binds to TDP-43 and induces neurodegeneration