Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Outlook |
 Epidemiology: The complexities of epilepsy
Epidemiology: The complexities of epilepsy
An estimated 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy. But research funding is low, treatment can fail and the mechanisms of the disease are a mystery. By Neil Savage.
- Neil Savage
-
-
Outlook |
 Technology: Dressed to detect
Technology: Dressed to detect
Wearable devices that monitor seizures promise improvements in epilepsy treatments and research.
- Elie Dolgin
-
Outlook |
 Sociology: Shedding the shame
Sociology: Shedding the shame
Plagued by a history of fear and stigma, epilepsy has languished when it comes to research funding.
- Lauren Gravitz
-
Outlook |
 Drug development: Illuminated targets
Drug development: Illuminated targets
The development of effective antiepilepsy drugs is moving on from trial-and-error approaches to sophisticated molecular solutions.
- Megan Cully
-
Outlook |
 Perspective: The surgical solution
Perspective: The surgical solution
Not enough doctors and patients opt for surgery to treat epilepsy, despite clinical evidence of the benefits, says Samuel Wiebe.
- Samuel Wiebe
-
Outlook |
 Food science: Fat chance
Food science: Fat chance
For children with epilepsy whose condition is resistant to medication, a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet may help bring their seizures under control.
- Rachel Brazil
-
Outlook |
 Genetics: Complex expressions
Genetics: Complex expressions
Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological disorders to affect the human brain. Many genetic aspects of the disease have been identified, but mechanisms remains elusive.
- Charvy Narain
-
Outlook |
 Neurobiology: Unrestrained excitement
Neurobiology: Unrestrained excitement
Epilepsy arises from natural mechanisms in the brain that go awry. Researchers are trying to unravel its complexities.
- Michael Eisenstein
-
-
Letter |
 Purkinje neuron synchrony elicits time-locked spiking in the cerebellar nuclei
Purkinje neuron synchrony elicits time-locked spiking in the cerebellar nuclei
Through a combination of intrinsic and synaptic properties, synchronous activation of a small number of Purkinje cells can set the spike timing of target neurons in the cerebellar nuclei.
- Abigail L. Person
- & Indira M. Raman
-
Letter |
 Energetics and the evolution of human brain size
Energetics and the evolution of human brain size
- Ana Navarrete
- , Carel P. van Schaik
- & Karin Isler
-
Letter |
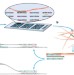 Somatic retrotransposition alters the genetic landscape of the human brain
Somatic retrotransposition alters the genetic landscape of the human brain
- J. Kenneth Baillie
- , Mark W. Barnett
- & Geoffrey J. Faulkner
-
News Feature |
 Tissue-bank shortage: Brain child
Tissue-bank shortage: Brain child
Asking parents to donate a child's brain to research is emotionally fraught. Some researchers say that it is time to put aside the taboos.
- Alison Abbott
-
Article |
 Spatio-temporal transcriptome of the human brain
Spatio-temporal transcriptome of the human brain
- Hyo Jung Kang
- , Yuka Imamura Kawasawa
- & Nenad Šestan
-
Research Highlights |
Placenta protects the brain
-
News & Views |
 Sleepy neurons?
Sleepy neurons?
A study in rats suggests that individual neurons take a nap when the brain is forced to stay awake, and that the basic unit of sleep is the electrical activity of single cortical neurons. See Article p.443
- Christopher S. Colwell
-
Books & Arts |
 Neuroscience: Browsing and the brain
Neuroscience: Browsing and the brain
Two books reach opposite verdicts on how the Internet affects us, find Daphne Bavelier and C. Shawn Green
- Daphne Bavelier
- & C. Shawn Green
-
News Feature |
 Neuroscience: Thought experiment
Neuroscience: Thought experiment
Japanese hospitals are using near-infrared imaging to help diagnose psychiatric disorders. But critics are not sure the technique is ready for the clinic.
- David Cyranoski
-
News |
 Amygdala at the centre of your social network
Amygdala at the centre of your social network
A larger emotion-processing brain centre is linked to a bigger circle of friends.
- Janelle Weaver
-
Review Article |
 Glial and neuronal control of brain blood flow
Glial and neuronal control of brain blood flow
- David Attwell
- , Alastair M. Buchan
- & Eric A. Newman
-
Review Article |
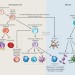 The myeloid cells of the central nervous system parenchyma
The myeloid cells of the central nervous system parenchyma
- Richard M. Ransohoff
- & Astrid E. Cardona
-
Letter |
 Pericytes are required for blood–brain barrier integrity during embryogenesis
Pericytes are required for blood–brain barrier integrity during embryogenesis
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is made up of vascular endothelial cells and was thought to have formed postnatally from astrocytes. Two independent studies demonstrate that this barrier forms during embryogenesis, with pericyte/endothelial cell interactions being critical to regulate the BBB during development. A better understanding of the relationship among pericytes, neuroendothelial cells and astrocytes in BBB function will contribute to our understanding of BBB breakdown during central nervous system injury and disease.
- Richard Daneman
- , Lu Zhou
- & Ben A. Barres
-
Letter |
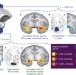 Amygdalar and hippocampal substrates of anxious temperament differ in their heritability
Amygdalar and hippocampal substrates of anxious temperament differ in their heritability
Anxious temperament in both humans and monkeys is an important early predictor of psychopathology and is known to be heritable. These authors characterize the neural circuitry associated with this trait and the extent to which its function is heritable. A scan of related monkeys after exposure to mild stress showed that activation in both the amygdala and hippocampus was predictive of anxious temperament, but that heritability of activity in hippocampus was greater than that in amygdala.
- Jonathan A. Oler
- , Andrew S. Fox
- & Ned H. Kalin
-
News |
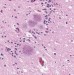 'Spontaneous generation' of prions observed
'Spontaneous generation' of prions observed
Metal wires 'catalyse' appearance of rogue proteins from healthy brain tissue.
- Daniel Cressey
-
Article |
 Start/stop signals emerge in nigrostriatal circuits during sequence learning
Start/stop signals emerge in nigrostriatal circuits during sequence learning
The appropriate initiation and termination of behavioural action sequences is imperative, but the neural mechanisms underlying the learning and execution of fixed behavioural patterns are poorly understood. Here the authors reveal start/stop neuronal activity in basal ganglia circuits that emerge during task training in mice. Genetically altering these circuits disrupted the activity and impaired performance, providing evidence for a causal relationship between the specific neuronal activity and task learning.
- Xin Jin
- & Rui M. Costa
-
Letter |
 Subcapsular sinus macrophages prevent CNS invasion on peripheral infection with a neurotropic virus
Subcapsular sinus macrophages prevent CNS invasion on peripheral infection with a neurotropic virus
Macrophages that populate the lymph nodes are known to clear viruses from the lymph and to initiate antiviral humoral immune responses. It is now shown that these macrophages also have another function: they prevent lymph-borne neurotropic viruses from entering the central nervous system. The mechanism is dependent on the production of type I interferon.
- Matteo Iannacone
- , E. Ashley Moseman
- & Ulrich H. von Andrian
-
Article |
 Neurogenic radial glia in the outer subventricular zone of human neocortex
Neurogenic radial glia in the outer subventricular zone of human neocortex
In the mammalian brain, the subventricular zone (SVZ) produces neural progenitor cells that migrate into the cortex to populate the upper layers. In humans this region is massively expanded, producing an outer SVZ (OSVZ). Here, live-cell imaging of developing human tissue was used to show that the OSVZ has similar characteristics to the SVZ, with progenitor cells proliferating in a way that depends on the Notch protein. The findings have implications for our understanding of how the complex human brain evolved.
- David V. Hansen
- , Jan H. Lui
- & Arnold R. Kriegstein

 Compartmentalized ocular lymphatic system mediates eye–brain immunity
Compartmentalized ocular lymphatic system mediates eye–brain immunity Epilepsy
Epilepsy Central nervous system control of metabolism
Central nervous system control of metabolism