Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access The economic commitment of climate change
The economic commitment of climate change
Analysis of projected sub-national damages from temperature and precipitation show an income reduction of 19% of the world economy within the next 26 years independent of future emission choices.
- Maximilian Kotz
- , Anders Levermann
- & Leonie Wenz
-
Article |
 Drought triggers and sustains overnight fires in North America
Drought triggers and sustains overnight fires in North America
By examining the hourly diurnal cycle of 23,557 fires in North America during 2017–2020, 1,095 overnight burning events were identified, mostly associated with extreme fires and driven by long-term drought conditions.
- Kaiwei Luo
- , Xianli Wang
- & Mike Flannigan
-
Article |
 Fertilizer management for global ammonia emission reduction
Fertilizer management for global ammonia emission reduction
A machine learning model for generating crop-specific and spatially explicit NH3 emission factors globally shows that global NH3 emissions in 2018 were lower than previous estimates that did not fully consider fertilizer management practices.
- Peng Xu
- , Geng Li
- & Benjamin Z. Houlton
-
Article |
 Global population profile of tropical cyclone exposure from 2002 to 2019
Global population profile of tropical cyclone exposure from 2002 to 2019
A global profile of tropical cyclone population exposure for the period 2002–2019 shows a steady increase, with approximately 560 million people exposed yearly and a disproportionate exposure among those with lower socioeconomic status.
- Renzhi Jing
- , Sam Heft-Neal
- & Zachary Wagner
-
Article
| Open Access Unequal climate impacts on global values of natural capital
Unequal climate impacts on global values of natural capital
Country-level changes in economic production and the value of non-market ecosystem benefits show unequal impacts on the global values of natural capital resulting from climate-change-induced shifts in terrestrial vegetation cover.
- B. A. Bastien-Olvera
- , M. N. Conte
- & F. C. Moore
-
Article
| Open Access Overshooting the critical threshold for the Greenland ice sheet
Overshooting the critical threshold for the Greenland ice sheet
Simulations using two state-of-the-art ice-sheet models show that abrupt melting of the Greenland ice sheet following overshooting of the global mean temperature critical threshold can be mitigated by subsequent cooling to below 1.5 °C.
- Nils Bochow
- , Anna Poltronieri
- & Niklas Boers
-
Article |
 Global evidence of rapid urban growth in flood zones since 1985
Global evidence of rapid urban growth in flood zones since 1985
Analysis of high-resolution annual data shows that global human settlements have expanded continuously and rapidly into flood zones, with those in the most hazardous zones increasing by 122% from 1985 to 2015.
- Jun Rentschler
- , Paolo Avner
- & Stéphane Hallegatte
-
Article
| Open Access Seasonal advance of intense tropical cyclones in a warming climate
Seasonal advance of intense tropical cyclones in a warming climate
We identify a seasonal advance of intense tropical cyclones that is closely related to the seasonal advance of rapid intensification events, favoured by the observed earlier onset of favourable oceanic conditions.
- Kaiyue Shan
- , Yanluan Lin
- & Fengfei Song
-
Article
| Open Access Global population exposure to landscape fire air pollution from 2000 to 2019
Global population exposure to landscape fire air pollution from 2000 to 2019
The global population is increasingly exposed to daily landscape fire-sourced air pollution but there are socioeconomic disparities, with this pollution four times higher in low-income countries than in high-income countries during the period 2000–2019.
- Rongbin Xu
- , Tingting Ye
- & Shanshan Li
-
Article |
 Marine heatwaves are not a dominant driver of change in demersal fishes
Marine heatwaves are not a dominant driver of change in demersal fishes
Of 248 marine heatwaves between 1993 and 2019 in North American and European seas, the effects on fish biomass were often minimal, and the heatwaves were not consistently associated with tropicalization or deborealization.
- Alexa L. Fredston
- , William W. L. Cheung
- & Malin L. Pinsky
-
Article
| Open Access Widespread retreat of coastal habitat is likely at warming levels above 1.5 °C
Widespread retreat of coastal habitat is likely at warming levels above 1.5 °C
Without mitigation, relative sea-level rises under current climate change projections will exceed the capacity of coastal habitats such as mangroves and tidal marshes to adjust, leading to instability and profound changes to coastal ecosystems.
- Neil Saintilan
- , Benjamin Horton
- & Glenn Guntenspergen
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerating the energy transition towards photovoltaic and wind in China
Accelerating the energy transition towards photovoltaic and wind in China
To meet China’s goal of carbon neutrality by 2060, substantial investment in upgrading power systems needs to be made to optimize the deployment of new photovoltaic and wind power plants.
- Yijing Wang
- , Rong Wang
- & Renhe Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Net greenhouse gas balance of fibre wood plantation on peat in Indonesia
Net greenhouse gas balance of fibre wood plantation on peat in Indonesia
Measurements of the net ecosystem exchanges of CO2, CH4 and soil N2O from Acacia plantation, degraded forest and intact forest enable presentation of the peatland wood plantation rotation greenhouse gas flux balance.
- Chandra S. Deshmukh
- , Ari P. Susanto
- & Chris D. Evans
-
Article
| Open Access Oceanic climate changes threaten the sustainability of Asia’s water tower
Oceanic climate changes threaten the sustainability of Asia’s water tower
Weakening blocking effect of the High Mountain Asia on the westerlies-carried deficit in precipitation minus evaporation from the southeast North Atlantic is demonstrated, leading to persistent northward expansion of terrestrial water storage deficit in the Tibet Plateau.
- Qiang Zhang
- , Zexi Shen
- & Gang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Global hotspots of salt marsh change and carbon emissions
Global hotspots of salt marsh change and carbon emissions
Analysis of Landsat imagery from the past two decades allows quantification of the changes in salt marsh ecosystems, as well as associated carbon emissions resulting from net global losses.
- Anthony D. Campbell
- , Lola Fatoyinbo
- & David Lagomasino
-
Perspective |
 The missing risks of climate change
The missing risks of climate change
The unquantified, poorly understood and uncertain risks of climate change in economic valuations are identified and classified, and an integrated approach is proposed to include these missing risks in future valuations and decision-making processes.
- James Rising
- , Marco Tedesco
- & David A. Stainforth
-
Article
| Open Access Comprehensive evidence implies a higher social cost of CO2
Comprehensive evidence implies a higher social cost of CO2
Coupling advances in socioeconomic projections, climate models, damage functions and discounting methods yields an estimate of the social cost of carbon of US$185 per tonne of CO2—triple the widely used value published by the US government.
- Kevin Rennert
- , Frank Errickson
- & David Anthoff
-
Article
| Open Access Sufficient conditions for rapid range expansion of a boreal conifer
Sufficient conditions for rapid range expansion of a boreal conifer
A boreal conifer is advancing northwards into Arctic tundra, with this treeline advance facilitated by climate warming together with winter winds, deeper snow and increased soil nutrient availability.
- Roman J. Dial
- , Colin T. Maher
- & Patrick F. Sullivan
-
Article
| Open Access Increasing the resilience of plant immunity to a warming climate
Increasing the resilience of plant immunity to a warming climate
Suppression of salicylic acid production in Arabidopsis thaliana at high temperature is caused by decreased recruitment of GUANYLATE BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE 3 defence-associated condensates on promoter sites of master immune regulatory genes.
- Jong Hum Kim
- , Christian Danve M. Castroverde
- & Sheng Yang He
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced silica export in a future ocean triggers global diatom decline
Enhanced silica export in a future ocean triggers global diatom decline
Mesocosm experiments in different biomes show that future ocean acidification will slow down the dissolution of biogenic silica, decreasing silicic acid availability in the surface ocean and triggering a global decline of diatoms as revealed by Earth system model simulations.
- Jan Taucher
- , Lennart T. Bach
- & Ulf Riebesell
-
Article |
 Climate change increases cross-species viral transmission risk
Climate change increases cross-species viral transmission risk
Changes in climate and land use will lead to species aggregating in new combinations at high elevations, in biodiversity hotspots and in areas of high human population density in Asia and Africa, driving the cross-species transmission of animal-associated viruses.
- Colin J. Carlson
- , Gregory F. Albery
- & Shweta Bansal
-
Article |
 Expanding ocean food production under climate change
Expanding ocean food production under climate change
Sustainable mariculture could increase seafood production under almost all climate-change scenarios analysed, but this would require substantial fisheries reforms, continued advances in feed technology and the establishment of effective mariculture governance and best practices.
- Christopher M. Free
- , Reniel B. Cabral
- & Steven D. Gaines
-
Article |
 Warming weakens the night-time barrier to global fire
Warming weakens the night-time barrier to global fire
An analysis of satellite observations and climate data shows that night-time fire intensity has increased over the past two decades owing to hotter and drier nights under anthropogenic climate change.
- Jennifer K. Balch
- , John T. Abatzoglou
- & A. Park Williams
-
Article |
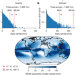 The effect of rainfall changes on economic production
The effect of rainfall changes on economic production
A global assessment shows that increases in the number of wet days and extreme daily rainfall adversely affect economic growth, particularly in high-income nations and via the services and manufacturing sectors.
- Maximilian Kotz
- , Anders Levermann
- & Leonie Wenz
-
Article |
 Estimating a social cost of carbon for global energy consumption
Estimating a social cost of carbon for global energy consumption
Using global data, econometrics and climate science to estimate the damages induced by the emission of one ton of carbon dioxide, climate change is projected to increase electricity spending but reduce overall end-use energy expenditure.
- Ashwin Rode
- , Tamma Carleton
- & Jiacan Yuan
-
Article |
 The Paris Climate Agreement and future sea-level rise from Antarctica
The Paris Climate Agreement and future sea-level rise from Antarctica
An observationally calibrated ice sheet–shelf model suggests that global warming of 3 °C will trigger rapid Antarctic ice loss, contributing about 0.5 cm per year of sea-level rise by 2100.
- Robert M. DeConto
- , David Pollard
- & Andrea Dutton
-
Matters Arising |
 Concerns about reported harvests in European forests
Concerns about reported harvests in European forests
- Marc Palahí
- , Rubén Valbuena
- & Gert-Jan Nabuurs
-
Article |
 Accelerated global glacier mass loss in the early twenty-first century
Accelerated global glacier mass loss in the early twenty-first century
Analysis of satellite stereo imagery uncovers two decades of mass change for all of Earth’s glaciers, revealing accelerated glacier shrinkage and regionally contrasting changes consistent with decadal climate variability.
- Romain Hugonnet
- , Robert McNabb
- & Andreas Kääb
-
Article |
 Equity is more important for the social cost of methane than climate uncertainty
Equity is more important for the social cost of methane than climate uncertainty
Accounting for equity influences the social cost of methane more than climate model uncertainty does and produces results that differ by over an order of magnitude between low- and high-income regions.
- Frank C. Errickson
- , Klaus Keller
- & David Anthoff
-
Article |
 Unveiling African rainforest composition and vulnerability to global change
Unveiling African rainforest composition and vulnerability to global change
A large dataset of 6 million trees from 193 taxa is used to map the floristic and functional composition of central African forests and predict their vulnerability to climate change.
- Maxime Réjou-Méchain
- , Frédéric Mortier
- & Sylvie Gourlet-Fleury
-
Review Article |
 Towards a rigorous understanding of societal responses to climate change
Towards a rigorous understanding of societal responses to climate change
This Review proposes an interdisciplinary framework for researching climate–society interactions that focuses on the mechanisms through which climate change has influenced societies, and the uncertainties of discerning this influence across different spatiotemporal scales.
- Dagomar Degroot
- , Kevin Anchukaitis
- & Natale Zappia
-
Article |
 Lake heatwaves under climate change
Lake heatwaves under climate change
Modelling and remote sensing show that by the end of the twenty-first century, lake heatwaves will be several degrees Celsius warmer and some will be months longer, with potentially major adverse consequences for lake ecosystems.
- R. Iestyn Woolway
- , Eleanor Jennings
- & Stephen C. Maberly
-
Article |
 Slower decay of landfalling hurricanes in a warming world
Slower decay of landfalling hurricanes in a warming world
North Atlantic landfalling hurricanes are weakening more slowly than in the past because warming oceans are increasing the moisture carried by the storm until it hits land, and this storm moisture acts as an ongoing heat source post-landfall.
- Lin Li
- & Pinaki Chakraborty
-
Article |
 Thermal displacement by marine heatwaves
Thermal displacement by marine heatwaves
Ocean heatwaves displace surface isotherms by tens to thousands of kilometres—comparable to shifts associated with long-term warming trends—potentially driving rapid redistributions of marine species.
- Michael G. Jacox
- , Michael A. Alexander
- & James D. Scott
-
Article |
 Asynchronous carbon sink saturation in African and Amazonian tropical forests
Asynchronous carbon sink saturation in African and Amazonian tropical forests
Unlike Amazonian forests, African forests have maintained their carbon sink until recently but by 2030 the African carbon sink will have shrunk by 14 per cent and the Amazonian sink will reach almost zero.
- Wannes Hubau
- , Simon L. Lewis
- & Lise Zemagho
-
Article |
 The past and future of global river ice
The past and future of global river ice
An analysis based on Landsat imagery shows that the extent of river ice has declined extensively over past decades and that this trend will continue under future global warming.
- Xiao Yang
- , Tamlin M. Pavelsky
- & George H. Allen
-
Article |
 Twofold expansion of the Indo-Pacific warm pool warps the MJO life cycle
Twofold expansion of the Indo-Pacific warm pool warps the MJO life cycle
Since the 1980s, rapid warming of the Indo-Pacific warm pool has altered global rainfall pattern by changing the residence time of the Madden–Julian Oscillation, decreasing it by 3–4 days over the Indian Ocean and increasing it over the Indo-Pacific by 5–6 days.
- M. K. Roxy
- , Panini Dasgupta
- & Daehyun Kim
-
Analysis |
 Climate as a risk factor for armed conflict
Climate as a risk factor for armed conflict
Climate has affected organized armed conflict within countries, and intensifying climate change is estimated to increase future risks of conflict, although other drivers are substantially more influential and the mechanisms of climate–conflict linkages remain uncertain.
- Katharine J. Mach
- , Caroline M. Kraan
- & Nina von Uexkull
-
Article |
 Change in future climate due to Antarctic meltwater
Change in future climate due to Antarctic meltwater
Accounting for meltwater from the Antarctic Ice Sheet in simulations of global climate leads to substantial changes in future climate projections and identifies a potential feedback mechanism that exacerbates melting.
- Ben Bronselaer
- , Michael Winton
- & Joellen L. Russell
-
Letter |
 Future response of global coastal wetlands to sea-level rise
Future response of global coastal wetlands to sea-level rise
A global modelling approach shows that in response to rises in global sea level, gains of up to 60% in coastal wetland areas are possible, if appropriate coastal management solutions are developed to help support wetland resilience.
- Mark Schuerch
- , Tom Spencer
- & Sally Brown
-
Letter |
 Globally rising soil heterotrophic respiration over recent decades
Globally rising soil heterotrophic respiration over recent decades
Global soil respiration is rising, probably in response to environmental changes, suggesting that climate-driven losses of soil carbon are occurring worldwide.
- Ben Bond-Lamberty
- , Vanessa L. Bailey
- & Rodrigo Vargas
-
Letter |
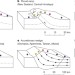 Spatial correlation bias in late-Cenozoic erosion histories derived from thermochronology
Spatial correlation bias in late-Cenozoic erosion histories derived from thermochronology
Reported acceleration of erosion in mountainous landscapes during the late Cenozoic is the result of combining thermochronology data with disparate exhumation histories, thereby converting spatial variations in erosion rates into temporal increases.
- Taylor F. Schildgen
- , Pieter A. van der Beek
- & Rasmus C. Thiede
-
Perspective |
 Choosing the future of Antarctica
Choosing the future of Antarctica
The future of Antarctica and the Southern Ocean by 2070 is described under two scenarios, one in which action is taken to limit greenhouse gas emissions, and one in which no action is taken.
- S. R. Rintoul
- , S. L. Chown
- & J. C. Xavier
-
Analysis |
 Mass balance of the Antarctic Ice Sheet from 1992 to 2017
Mass balance of the Antarctic Ice Sheet from 1992 to 2017
- Andrew Shepherd
- , Erik Ivins
- & Bert Wouters
-
Letter |
 A global slowdown of tropical-cyclone translation speed
A global slowdown of tropical-cyclone translation speed
The translation speed of tropical cyclones has decreased globally by 10% over the past 70 years, compounding the increases in cyclone-related local rainfall that have resulted from anthropogenic warming.
- James P. Kossin
-
Perspective |
 The many possible climates from the Paris Agreement’s aim of 1.5 °C warming
The many possible climates from the Paris Agreement’s aim of 1.5 °C warming
The results of efforts to limit global mean warming to below 1.5 °C may include many possible future world climates.
- Sonia I. Seneviratne
- , Joeri Rogelj
- & Rachel F. Warren
-
Letter |
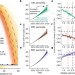 Large potential reduction in economic damages under UN mitigation targets
Large potential reduction in economic damages under UN mitigation targets
If the world can meet the target of limiting global warming to 1.5 °C, economic damage will probably be greatly reduced, especially in poorer countries.
- Marshall Burke
- , W. Matthew Davis
- & Noah S. Diffenbaugh
-
Letter |
 Accelerated increase in plant species richness on mountain summits is linked to warming
Accelerated increase in plant species richness on mountain summits is linked to warming
Analysis of changes in plant species richness on mountain summits over the past 145 years suggests that increased climatic warming has led to an acceleration in species richness increase.
- Manuel J. Steinbauer
- , John-Arvid Grytnes
- & Sonja Wipf
-
Outlook |
 Sea change
Sea change
The increasing acidity of our seas is a threat to marine life that for many species may be impossible to overcome.
- Sarah DeWeerdt

 Frequent disturbances enhanced the resilience of past human populations
Frequent disturbances enhanced the resilience of past human populations