Featured
-
-
Article |
 Rapid unleashing of macrophage efferocytic capacity via transcriptional pause release
Rapid unleashing of macrophage efferocytic capacity via transcriptional pause release
Macrophages are revealed to adopt a polymerase II pause/release process to effectively deal with ingested apoptotic corpses and for continuous efferocytosis.
- Turan Tufan
- , Gamze Comertpay
- & Kodi S. Ravichandran
-
Article
| Open Access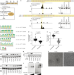 FOXP3 recognizes microsatellites and bridges DNA through multimerization
FOXP3 recognizes microsatellites and bridges DNA through multimerization
FOXP3 uses the forkhead domain to form a higher-order multimer after binding to TnG repeat microsatellites.
- Wenxiang Zhang
- , Fangwei Leng
- & Sun Hur
-
Article |
 IL-1β+ macrophages fuel pathogenic inflammation in pancreatic cancer
IL-1β+ macrophages fuel pathogenic inflammation in pancreatic cancer
Single-cell and spatial gene expression analyses of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma uncover a population of interleukin-1β-expressing macrophages that drive inflammatory reprogramming of neighboring tumour cells leading to disease progression and poor prognosis for patients.
- Nicoletta Caronni
- , Federica La Terza
- & Renato Ostuni
-
Article |
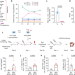 Reductive carboxylation epigenetically instructs T cell differentiation
Reductive carboxylation epigenetically instructs T cell differentiation
Reductive carboxylation of glutamine by isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2) has a role in determining the fate of T cells, and inhibiting this enzyme promotes the differentiation of memory T cells.
- Alison Jaccard
- , Tania Wyss
- & Mathias Wenes
-
Article |
 Thymic mimetic cells function beyond self-tolerance
Thymic mimetic cells function beyond self-tolerance
Multiomic analyses of mouse thymic epithelial cells identify several unconventional subsets that are mimetics of various populations of terminally differentiated parenchymal cells and provide insights into their development, molecular features and function.
- Tal Givony
- , Dena Leshkowitz
- & Jakub Abramson
-
Article
| Open Access Dissecting human population variation in single-cell responses to SARS-CoV-2
Dissecting human population variation in single-cell responses to SARS-CoV-2
Population differences in immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 can be explained by environmental exposures, but also by local adaptation acting through genetic variants acquired after admixture with archaic hominin forms.
- Yann Aquino
- , Aurélie Bisiaux
- & Lluis Quintana-Murci
-
Article |
 Pre-T cell receptor self-MHC sampling restricts thymocyte dedifferentiation
Pre-T cell receptor self-MHC sampling restricts thymocyte dedifferentiation
Aberrant thymocyte developmental programming results when interactions between thymic stroma and pre-T cell receptors occur in the absence of major histocompatibility complex bound to antigen peptide.
- Jonathan S. Duke-Cohan
- , Aoi Akitsu
- & Ellis L. Reinherz
-
Article
| Open Access MYB orchestrates T cell exhaustion and response to checkpoint inhibition
MYB orchestrates T cell exhaustion and response to checkpoint inhibition
CD62L+ precursors of exhausted T cells retain long-term proliferative potential, multipotency and repopulation capacity, and the transcription factor MYB is essential for the development and function of this population of cells.
- Carlson Tsui
- , Lorenz Kretschmer
- & Axel Kallies
-
Article
| Open Access DOCK2 is involved in the host genetics and biology of severe COVID-19
DOCK2 is involved in the host genetics and biology of severe COVID-19
A genome-wide association study highlights a variant in DOCK2, which is common in East Asian populations but rare in Europeans, as a host genetic risk factor for severe COVID-19.
- Ho Namkoong
- , Ryuya Edahiro
- & Yukinori Okada
-
Article |
 ZBTB46 defines and regulates ILC3s that protect the intestine
ZBTB46 defines and regulates ILC3s that protect the intestine
A subset of group 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3s) expresses the transcription factor ZBTB46—which was previously thought to be restricted to conventional dendritic cells—and these ILC3s have a role in regulating intestinal health.
- Wenqing Zhou
- , Lei Zhou
- & Gregory F. Sonnenberg
-
Article |
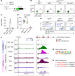 Ablation of cDC2 development by triple mutations within the Zeb2 enhancer
Ablation of cDC2 development by triple mutations within the Zeb2 enhancer
The transcription factor NFIL3 acts antagonistically to C/EBP proteins by binding the Zeb2 enhancer to prevent Zeb2 expression and the development of the conventional type 2 dendritic cell lineage.
- Tian-Tian Liu
- , Sunkyung Kim
- & Kenneth M. Murphy
-
Article |
 Self-guarding of MORC3 enables virulence factor-triggered immunity
Self-guarding of MORC3 enables virulence factor-triggered immunity
MORC3 is revealed as an essential negative regulator of the anti-viral interferon response that functions in an innate immune pathway that detects viral virulence factors.
- Moritz M. Gaidt
- , Alyssa Morrow
- & Russell E. Vance
-
Article |
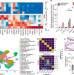 A myeloid–stromal niche and gp130 rescue in NOD2-driven Crohn’s disease
A myeloid–stromal niche and gp130 rescue in NOD2-driven Crohn’s disease
NOD2 deficiency drives fibrosis and stricturing complications in Crohn’s disease through dysregulated homeostasis of activated fibroblasts and macrophages, which is ameliorated by gp130 blockade in human cell and zebrafish models.
- Shikha Nayar
- , Joshua K. Morrison
- & Judy H. Cho
-
Article |
 H1 histones control the epigenetic landscape by local chromatin compaction
H1 histones control the epigenetic landscape by local chromatin compaction
Experiments using a conditional triple-knockout mouse strain show that histone H1 regulates the activity of chromatin domains by controlling chromatin compaction, genome architecture and histone methylation.
- Michael A. Willcockson
- , Sean E. Healton
- & Arthur I. Skoultchi
-
Article |
 Dichotomous engagement of HDAC3 activity governs inflammatory responses
Dichotomous engagement of HDAC3 activity governs inflammatory responses
During the activation of mouse macrophages by lipopolysaccharides, histone deacetylase 3 controls inflammatory responses by both repressing and activating gene transcription depending on its differential association with transcription factors.
- Hoang C. B. Nguyen
- , Marine Adlanmerini
- & Mitchell A. Lazar
-
Article |
 Histone H3.3 phosphorylation amplifies stimulation-induced transcription
Histone H3.3 phosphorylation amplifies stimulation-induced transcription
The histone variant H3.3 is phosphorylated at Ser31 in induced genes, and this selective mark stimulates the histone methyltransferase SETD2 and ejects the ZMYND11 repressor, thus revealing a role for histone phosphorylation in amplifying de novo transcription.
- Anja Armache
- , Shuang Yang
- & Steven Z. Josefowicz
-
Article |
 A distal enhancer at risk locus 11q13.5 promotes suppression of colitis by Treg cells
A distal enhancer at risk locus 11q13.5 promotes suppression of colitis by Treg cells
Shared synteny guides loss-of-function analysis of human enhancer homologues in mice, identifying a distal enhancer at the autoimmune and allergic disease risk locus at chromosome 11q13.5 whose function in regulatory T cells provides a mechanistic basis for its role in disease.
- Rabab Nasrallah
- , Charlotte J. Imianowski
- & Rahul Roychoudhuri
-
Article |
 CRISPR screen in regulatory T cells reveals modulators of Foxp3
CRISPR screen in regulatory T cells reveals modulators of Foxp3
A CRISPR-based screening platform was used to identify previously uncharacterized genes that regulate the regulatory T cell-specific master transcription factor Foxp3, indicating that this screening method may be broadly applicable for the discovery of other genes involved in autoimmunity and immune responses to cancer.
- Jessica T. Cortez
- , Elena Montauti
- & Deyu Fang
-
Article |
 Sex-specific adipose tissue imprinting of regulatory T cells
Sex-specific adipose tissue imprinting of regulatory T cells
Visceral adipose tissue contains populations of regulatory T cells that exhibit sexual dimorphism, determined by the surrounding niche, and differ between male and female mice in terms of cell number, phenotype, transcriptional landscape and chromatin accessibility.
- Ajithkumar Vasanthakumar
- , David Chisanga
- & Axel Kallies
-
Article |
 TOX transcriptionally and epigenetically programs CD8+ T cell exhaustion
TOX transcriptionally and epigenetically programs CD8+ T cell exhaustion
The transcription factor TOX is a central regulator of the transcriptional and epigenetic development of exhausted T cells.
- Omar Khan
- , Josephine R. Giles
- & E. John Wherry
-
Letter |
 NR4A transcription factors limit CAR T cell function in solid tumours
NR4A transcription factors limit CAR T cell function in solid tumours
Transfer of NR4A-deficient T cells expressing chimeric antigen receptors is shown to reduce tumour burden and increase survival by shifting T cell transcriptional programs away from exhaustion and towards increased effector function.
- Joyce Chen
- , Isaac F. López-Moyado
- & Anjana Rao
-
Letter |
 Mitochondrial complex III is essential for suppressive function of regulatory T cells
Mitochondrial complex III is essential for suppressive function of regulatory T cells
Specific ablation of mitochondrial complex III subunits in Treg cells in mice results in inflammatory disease, altered Treg gene expression and defective Treg function, indicating a key functional role for mitochondrial complex III in Treg cells.
- Samuel E. Weinberg
- , Benjamin D. Singer
- & Navdeep S. Chandel
-
Letter |
 Induction and transcriptional regulation of the co-inhibitory gene module in T cells
Induction and transcriptional regulation of the co-inhibitory gene module in T cells
A module of co-inhibitory T cell receptors, driven by the cytokine IL-27, is identified in mice that is regulated by the transcription factors PRDM1 and c-MAF.
- Norio Chihara
- , Asaf Madi
- & Vijay K. Kuchroo
-
Letter |
 Survival of tissue-resident memory T cells requires exogenous lipid uptake and metabolism
Survival of tissue-resident memory T cells requires exogenous lipid uptake and metabolism
FABP4 and FABP5 are important for the maintenance, longevity and function of CD8+ tissue-resident memory T cells, which use oxidative metabolism of exogenous free fatty acids to persist in tissues and to mediate protective immunity.
- Youdong Pan
- , Tian Tian
- & Thomas S. Kupper
-
Letter |
 The long non-coding RNA Morrbid regulates Bim and short-lived myeloid cell lifespan
The long non-coding RNA Morrbid regulates Bim and short-lived myeloid cell lifespan
The long non-coding RNA Morrbid controls myeloid cell lifespan and regulates apoptosis by repressing the adjacent pro-apoptotic Bcl2l11 gene in cis.
- Jonathan J. Kotzin
- , Sean P. Spencer
- & Jorge Henao-Mejia
-
Article |
 DDX5 and its associated lncRNA Rmrp modulate TH17 cell effector functions
DDX5 and its associated lncRNA Rmrp modulate TH17 cell effector functions
The ability of the DEAD-box RNA helicase DDX5 to interact with master transcription factor RORγt is dependent on binding of the long noncoding RNA Rmrp; the DDX5–RORγt complex coordinates transcription of selective TH17 genes and is required for the pathogenicity of TH17 cells.
- Wendy Huang
- , Benjamin Thomas
- & Dan R. Littman
-
Article |
 Single-cell RNA-seq reveals dynamic paracrine control of cellular variation
Single-cell RNA-seq reveals dynamic paracrine control of cellular variation
Large-scale single-cell RNA-seq of stimulated primary mouse bone-marrow-derived dendritic cells highlights positive and negative intercellular signalling pathways that promote and restrain cellular variation.
- Alex K. Shalek
- , Rahul Satija
- & Aviv Regev
-
Letter |
 Clonal allelic predetermination of immunoglobulin-κ rearrangement
Clonal allelic predetermination of immunoglobulin-κ rearrangement
Immunoglobulin genes are expressed from either the maternal or paternal chromosome; it is now shown that in early haematopoietic stem cells, an individual cell can choose either of the two alleles, but as they develop they become committed to only one.
- Marganit Farago
- , Chaggai Rosenbluh
- & Yehudit Bergman
-
Letter |
 BATF–JUN is critical for IRF4-mediated transcription in T cells
BATF–JUN is critical for IRF4-mediated transcription in T cells
The pleiotropic transcription factor IRF4 is shown to regulate CD4+ T-cell differentiation and TH17 function through cooperative binding interactions with BATF and JUN family proteins via AP1–IRF4 composite elements (AICEs).
- Peng Li
- , Rosanne Spolski
- & Warren J. Leonard
-
Letter |
 Novel role of PKR in inflammasome activation and HMGB1 release
Novel role of PKR in inflammasome activation and HMGB1 release
Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) is shown to be a key regulator of the inflammasome; PKR is central for caspase-1 activation and the release of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-18 and high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) in response to a diverse range of stimuli.
- Ben Lu
- , Takahisa Nakamura
- & Kevin J. Tracey
-
Letter |
 An epigenetic silencing pathway controlling T helper 2 cell lineage commitment
An epigenetic silencing pathway controlling T helper 2 cell lineage commitment
The histone modification H3K9me3, the histone methyltransferase SUV39H1 and the H3K9me3-binding protein HP1α participate in maintaining the silent state of the two canonical T helper 1 cell signature genes (which encode interferon-γ and T-bet), ensuring T helper 2 lineage stability in vitro and in vivo; targeting this pathway has the potential to reduce asthma-related pathology.
- Rhys S. Allan
- , Elina Zueva
- & Sebastian Amigorena
-
Article |
 Biophysical mechanism of T-cell receptor triggering in a reconstituted system
Biophysical mechanism of T-cell receptor triggering in a reconstituted system
After introducing the T-cell receptor and other essential signalling genes, a non-immune cell is capable of displaying the early events of T-cell activation when placed in contact with antigen-presenting cells, and the initial signalling in this reconstituted system is shown to require the spatial reorganization of molecules at the cell interface.
- John R. James
- & Ronald D. Vale
-
Research Highlights |
Immune system master switch
-
Outlook |
 Morbidity: A personal response
Morbidity: A personal response
Some people get horribly sick from the flu, and even die. Others just rest for a few days. What's behind this fateful variation?
- Christine Junge
-
Letter |
 Natural killer cells act as rheostats modulating antiviral T cells
Natural killer cells act as rheostats modulating antiviral T cells
Natural killer cells can act as rheostats, or ‘master regulators’, controlling antiviral T-cell responses.
- Stephen N. Waggoner
- , Markus Cornberg
- & Raymond M. Welsh
-
Letter |
 Coronin 2A mediates actin-dependent de-repression of inflammatory response genes
Coronin 2A mediates actin-dependent de-repression of inflammatory response genes
Activation of inflammatory gene expression by toll-like receptor (TLR) signalling pathways involves the removal of gene repression complexes such as NCoR. Here, coronin 2A, a component of the NCoR complex, is shown to mediate TLR-induced NCoR turnover and de-repression of inflammatory genes by a mechanism involving interaction with oligomeric nuclear actin.
- Wendy Huang
- , Serena Ghisletti
- & Christopher K. Glass
-
Letter |
 Generation of pathogenic TH17 cells in the absence of TGF-β signalling
Generation of pathogenic TH17 cells in the absence of TGF-β signalling
CD4+ T cells that selectively produce interleukin (IL)-17 (TH17 cells) are essential for host defence and autoimmunity. It has been thought that IL-6 and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 are the factors responsible for initiating the specification of TH17 cells. Here, however, it is shown that TH17 differentiation can occur in the absence of TGF-β signalling. IL-6, IL-23 and IL-1β effectively induced IL-17 production in naive precursors. These data reveal an alternative mode for TH17 differentiation and the importance of IL-23.
- Kamran Ghoreschi
- , Arian Laurence
- & John J. O’Shea

 AIRE relies on Z-DNA to flag gene targets for thymic T cell tolerization
AIRE relies on Z-DNA to flag gene targets for thymic T cell tolerization