Analysis
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide characterization of circulating metabolic biomarkers
Genome-wide characterization of circulating metabolic biomarkers
A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for 233 circulating metabolites from 33 cohorts reveals more than 400 loci and suggests probable causal genes, providing insights into metabolic pathways and disease aetiology.
- Minna K. Karjalainen
- , Savita Karthikeyan
- & Johannes Kettunen
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic drivers of heterogeneity in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology
Genetic drivers of heterogeneity in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology
A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of type 2 diabetes (T2D) identifies more than 600 T2D-associated loci; integrating physiological trait and single-cell chromatin accessibility data at these loci sheds light on heterogeneity within the T2D phenotype.
- Ken Suzuki
- , Konstantinos Hatzikotoulas
- & Eleftheria Zeggini
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic data in the All of Us Research Program
Genomic data in the All of Us Research Program
A study describes the release of clinical-grade whole-genome sequence data for 245,388 diverse participants by the All of Us Research Program and characterizes the properties of the dataset.
- Alexander G. Bick
- , Ginger A. Metcalf
- & Joshua C. Denny
-
Article |
 The Born in Guangzhou Cohort Study enables generational genetic discoveries
The Born in Guangzhou Cohort Study enables generational genetic discoveries
Analysis of data from the Born in Guangzhou Cohort Study comprising mainly of trios and mother–infant pairs reveals novel East Asian-specific genetic associations with maternal bile acid, gestational weight gain and infant cord blood traits.
- Shujia Huang
- , Siyang Liu
- & Xiu Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale plasma proteomics comparisons through genetics and disease associations
Large-scale plasma proteomics comparisons through genetics and disease associations
Comparisons of phenotypic and genetic association with protein levels from Icelandic and UK Biobank cohorts show that using multiple analysis platforms and stratifying populations by ancestry improves the detection of associations and allows the refinement of their location within the genome.
- Grimur Hjorleifsson Eldjarn
- , Egil Ferkingstad
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Plasma proteomic associations with genetics and health in the UK Biobank
Plasma proteomic associations with genetics and health in the UK Biobank
The Pharma Proteomics Project generates the largest open-access plasma proteomics dataset to date, offering insights into trans protein quantitative trait loci across multiple biological domains, and highlighting genetic influences on ligand–receptor interactions and pathway perturbations across a diverse collection of cytokines and complement networks.
- Benjamin B. Sun
- , Joshua Chiou
- & Christopher D. Whelan
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access A second update on mapping the human genetic architecture of COVID-19
A second update on mapping the human genetic architecture of COVID-19
- Masahiro Kanai
- , Shea J. Andrews
- & Matthew Solomonson
-
Review Article |
 From target discovery to clinical drug development with human genetics
From target discovery to clinical drug development with human genetics
This Review provides a perspective on the development of non-cancer therapies based on human genetics studies and suggests measures that can be taken to streamline the pipeline from initial genetic discovery to approved therapy.
- Katerina Trajanoska
- , Claude Bhérer
- & Vincent Mooser
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear genetic control of mtDNA copy number and heteroplasmy in humans
Nuclear genetic control of mtDNA copy number and heteroplasmy in humans
We quantify mitochondrial DNA copy number and heteroplasmy levels and study their association with nuclear genetic loci in population-scale biobanks.
- Rahul Gupta
- , Masahiro Kanai
- & Vamsi K. Mootha
-
Article |
 Africa-specific human genetic variation near CHD1L associates with HIV-1 load
Africa-specific human genetic variation near CHD1L associates with HIV-1 load
Africa-specific genetic variation on chromosome 1 near CHD1L is associated with HIV replication in vivo.
- Paul J. McLaren
- , Immacolata Porreca
- & Jacques Fellay
-
Article |
 Locus for severity implicates CNS resilience in progression of multiple sclerosis
Locus for severity implicates CNS resilience in progression of multiple sclerosis
A genome-wide association study including 22,389 cases of multiple sclerosis finds an association with disease progression at the DYSF–ZNF638 and DNM3–PIGC loci and identifies a potential of higher educational attainment in slowing disease progression.
- Adil Harroud
- , Pernilla Stridh
- & Kári Stefánsson
-
Article
| Open Access Polygenic scoring accuracy varies across the genetic ancestry continuum
Polygenic scoring accuracy varies across the genetic ancestry continuum
Using two large biobank datasets, a study shows that the accuracy of polygenic scores decreases as a function of relatedness at the individual level when modelling genetic ancestry as a continuum.
- Yi Ding
- , Kangcheng Hou
- & Bogdan Pasaniuc
-
Article
| Open Access GWAS and meta-analysis identifies 49 genetic variants underlying critical COVID-19
GWAS and meta-analysis identifies 49 genetic variants underlying critical COVID-19
An analysis of 24,202 critical cases of COVID-19 identifies potentially druggable targets in inflammatory signalling (JAK1), monocyte–macrophage activation and endothelial permeability (PDE4A), immunometabolism (SLC2A5 and AK5), and host factors required for viral entry and replication (TMPRSS2 and RAB2A).
- Erola Pairo-Castineira
- , Konrad Rawlik
- & J. Kenneth Baillie
-
Article |
 Clonal haematopoiesis and risk of chronic liver disease
Clonal haematopoiesis and risk of chronic liver disease
A study shows that clonal haematopoiesis of indeterminate potential is associated with an increased risk of chronic liver disease specifically through the promotion of liver inflammation and injury.
- Waihay J. Wong
- , Connor Emdin
- & Pradeep Natarajan
-
Article |
 An atlas of genetic scores to predict multi-omic traits
An atlas of genetic scores to predict multi-omic traits
A machine learning approach is used to analyse multi-omics (proteomics, metabolomics and transcriptomics) data, producing genetic scores for more than 17,000 biomolecular traits in human blood, and identifying possible associations with disease.
- Yu Xu
- , Scott C. Ritchie
- & Michael Inouye
-
Article |
 Polygenic architecture of rare coding variation across 394,783 exomes
Polygenic architecture of rare coding variation across 394,783 exomes
An analysis of rare coding variants across 22 common traits and diseases indicates that these variants will contribute substantially to biological insights but modestly to population risk stratification.
- Daniel J. Weiner
- , Ajay Nadig
- & Luke J. O’Connor
-
Article
| Open Access Mono- and biallelic variant effects on disease at biobank scale
Mono- and biallelic variant effects on disease at biobank scale
An analysis of biobank data from the FinnGen project examines dosage effects of genetic variants on disease, andidentifies a benefit when considering more complex inheritance in the genetics of common as well as Mendelian diseases.
- H. O. Heyne
- , J. Karjalainen
- & M. J. Daly
-
Article
| Open Access FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population
FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population
Genome-wide association studies of individuals from an isolated population (data from the Finnish biobank study FinnGen) and consequent meta-analyses facilitate the identification of previously unknown coding variant associations for both rare and common diseases.
- Mitja I. Kurki
- , Juha Karjalainen
- & Aarno Palotie
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic diversity fuels gene discovery for tobacco and alcohol use
Genetic diversity fuels gene discovery for tobacco and alcohol use
A multi-ancestry meta-regression study analyses diverse genome-wide association studies and genome loci associated with tobacco and alcohol use.
- Gretchen R. B. Saunders
- , Xingyan Wang
- & Scott Vrieze
-
Article |
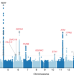 Common and rare variant associations with clonal haematopoiesis phenotypes
Common and rare variant associations with clonal haematopoiesis phenotypes
Exome sequence data from 628,388 individuals was used to identify 24 risk loci in 40,208 carriers of clonal haematopoiesis of indeterminate potential and link them to other conditions including COVID-19, cardiovascular disease and cancer.
- Michael D. Kessler
- , Amy Damask
- & Eric Jorgenson
-
Article
| Open Access A saturated map of common genetic variants associated with human height
A saturated map of common genetic variants associated with human height
A large genome-wide association study of more than 5 million individuals reveals that 12,111 single-nucleotide polymorphisms account for nearly all the heritability of height attributable to common genetic variants.
- Loïc Yengo
- , Sailaja Vedantam
- & Joel N. Hirschhorn
-
Article
| Open Access Stroke genetics informs drug discovery and risk prediction across ancestries
Stroke genetics informs drug discovery and risk prediction across ancestries
A cross-ancestry meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies association signals for stroke and its subtypes at 89 (61 new) independent loci, reveals putative causal genes, highlighting F11, KLKB1, PROC, GP1BA, LAMC2 and VCAM1 as potential drug targets, and provides cross-ancestry integrative risk prediction.
- Aniket Mishra
- , Rainer Malik
- & Stephanie Debette
-
Article
| Open Access DOCK2 is involved in the host genetics and biology of severe COVID-19
DOCK2 is involved in the host genetics and biology of severe COVID-19
A genome-wide association study highlights a variant in DOCK2, which is common in East Asian populations but rare in Europeans, as a host genetic risk factor for severe COVID-19.
- Ho Namkoong
- , Ryuya Edahiro
- & Yukinori Okada
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access A first update on mapping the human genetic architecture of COVID-19
A first update on mapping the human genetic architecture of COVID-19
- Gita A. Pathak
- , Juha Karjalainen
- & J. Kenneth Baillie
-
Article
| Open Access The sequences of 150,119 genomes in the UK Biobank
The sequences of 150,119 genomes in the UK Biobank
To measure selection on variants, whole-genome sequencing of approximately 150,000 individuals from the UK Biobank is used to rank sequence variants by their level of depletion.
- Bjarni V. Halldorsson
- , Hannes P. Eggertsson
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Graph pangenome captures missing heritability and empowers tomato breeding
Graph pangenome captures missing heritability and empowers tomato breeding
A precise catalogue of more than 19 million variants from 838 tomato genomes, including 32 new reference-level genome assemblies, advances the understanding of the heritability of complex traits and demonstrates the power of the graph pangenome in crop breeding.
- Yao Zhou
- , Zhiyang Zhang
- & Sanwen Huang
-
Article |
 ABO genotype alters the gut microbiota by regulating GalNAc levels in pigs
ABO genotype alters the gut microbiota by regulating GalNAc levels in pigs
The host blood-type-associated ABO genotype affects the abundance of specific bacteria in the pig intestine.
- Hui Yang
- , Jinyuan Wu
- & Lusheng Huang
-
Article |
 Rare coding variants in ten genes confer substantial risk for schizophrenia
Rare coding variants in ten genes confer substantial risk for schizophrenia
Whole-exome sequencing identifies ten risk genes for schizophrenia implicated by rare protein-coding variants, a subset of which overlap with risk genes in other neurodevelopmental disorders.
- Tarjinder Singh
- , Timothy Poterba
- & Mark J. Daly
-
Article |
 Mapping genomic loci implicates genes and synaptic biology in schizophrenia
Mapping genomic loci implicates genes and synaptic biology in schizophrenia
A genome-wide association study including over 76,000 individuals with schizophrenia and over 243,000 control individuals identifies common variant associations at 287 genomic loci, and further fine-mapping analyses highlight the importance of genes involved in synaptic processes.
- Vassily Trubetskoy
- , Antonio F. Pardiñas
- & Jim van Os
-
Article
| Open Access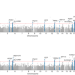 Whole-genome sequencing reveals host factors underlying critical COVID-19
Whole-genome sequencing reveals host factors underlying critical COVID-19
Whole-genome sequencing, transcriptome-wide association and fine-mapping analyses in over 7,000 individuals with critical COVID-19 are used to identify 16 independent variants that are associated with severe illness in COVID-19.
- Athanasios Kousathanas
- , Erola Pairo-Castineira
- & J. Kenneth Baillie
-
Perspective |
 An open science study of ageing in companion dogs
An open science study of ageing in companion dogs
The Dog Aging Project is an open-data, community science study to identify genetic, environmental and lifestyle factors associated with canine healthy lifespan, generating knowledge that could readily translate to human ageing.
- Kate E. Creevy
- , Joshua M. Akey
- & Benjamin S. Wilfond
-
Article |
 The power of genetic diversity in genome-wide association studies of lipids
The power of genetic diversity in genome-wide association studies of lipids
A genome-wide association meta-analysis study of blood lipid levels in roughly 1.6 million individuals demonstrates the gain of power attained when diverse ancestries are included to improve fine-mapping and polygenic score generation, with gains in locus discovery related to sample size.
- Sarah E. Graham
- , Shoa L. Clarke
- & Cristen J. Willer
-
Article
| Open Access Exome sequencing and analysis of 454,787 UK Biobank participants
Exome sequencing and analysis of 454,787 UK Biobank participants
Whole-exome sequencing analysis of 454,787 individuals in the UK Biobank is used to examine the association of protein-coding variants with nearly 4,000 health-related traits, identifying 564 distinct genes with significant trait associations.
- Joshua D. Backman
- , Alexander H. Li
- & Manuel A. R. Ferreira
-
Article
| Open Access Rare variant contribution to human disease in 281,104 UK Biobank exomes
Rare variant contribution to human disease in 281,104 UK Biobank exomes
The authors analyse rare protein-coding genetic variants for association with 18,780 traits in the UK Biobank cohort.
- Quanli Wang
- , Ryan S. Dhindsa
- & Slavé Petrovski
-
Article |
 Genetic insights into biological mechanisms governing human ovarian ageing
Genetic insights into biological mechanisms governing human ovarian ageing
Hundreds of genetic loci associated with age at menopause, combined with experimental evidence in mice, highlight mechanisms of reproductive ageing across the lifespan.
- Katherine S. Ruth
- , Felix R. Day
- & John R. B. Perry
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping the human genetic architecture of COVID-19
Mapping the human genetic architecture of COVID-19
A global network of researchers was formed to investigate the role of human genetics in SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 severity; this paper reports 13 genome-wide significant loci and potentially actionable mechanisms in response to infection.
- Mari E. K. Niemi
- , Juha Karjalainen
- & Chloe Donohue
-
Article |
 Enhancer release and retargeting activates disease-susceptibility genes
Enhancer release and retargeting activates disease-susceptibility genes
Disruption of a promoter can release its partner enhancer to activate other promoters in the same contact domain, and this process, named ‘enhancer release and retargeting’, can often lead to gene alterations that cause disease.
- Soohwan Oh
- , Jiaofang Shao
- & Michael G. Rosenfeld
-
Article |
 Interpreting type 1 diabetes risk with genetics and single-cell epigenomics
Interpreting type 1 diabetes risk with genetics and single-cell epigenomics
A genome-wide association study combined with single-cell epigenomics identifies risk loci for type 1 diabetes.
- Joshua Chiou
- , Ryan J. Geusz
- & Kyle J. Gaulton
-
Article |
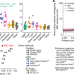 Genome-wide enhancer maps link risk variants to disease genes
Genome-wide enhancer maps link risk variants to disease genes
Mapping enhancer regulation across human cell types and tissues illuminates genome function and provides a resource to connect risk variants for common diseases to their molecular and cellular functions.
- Joseph Nasser
- , Drew T. Bergman
- & Jesse M. Engreitz
-
Article
| Open Access Regulatory genomic circuitry of human disease loci by integrative epigenomics
Regulatory genomic circuitry of human disease loci by integrative epigenomics
The authors present EpiMap, a compendium that comprises 10,000 epigenomic maps across more than 800 biosamples for the annotation of genome-wide association study circuitry.
- Carles A. Boix
- , Benjamin T. James
- & Manolis Kellis
-
Article |
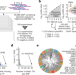 Systematic analysis of binding of transcription factors to noncoding variants
Systematic analysis of binding of transcription factors to noncoding variants
An ultra-high-throughput multiplex protein–DNA binding assay is used to assess binding of 270 human transcription factors to 95,886 noncoding variants in the human genome, providing data to improve prediction of the effects of noncoding variants on transcription factor binding and thereby increase understanding of molecular pathways involved in diverse human traits and genetic diseases.
- Jian Yan
- , Yunjiang Qiu
- & Bing Ren
-
Article |
 Genetic mechanisms of critical illness in COVID-19
Genetic mechanisms of critical illness in COVID-19
A genome-wide association study of critically ill patients with COVID-19 identifies genetic signals that relate to important host antiviral defence mechanisms and mediators of inflammatory organ damage that may be targeted by repurposing drug treatments.
- Erola Pairo-Castineira
- , Sara Clohisey
- & J. Kenneth Baillie
-
Article |
 Inherited causes of clonal haematopoiesis in 97,691 whole genomes
Inherited causes of clonal haematopoiesis in 97,691 whole genomes
Analysis of 97,691 high-coverage human blood DNA-derived whole-genome sequences enabled simultaneous identification of germline and somatic mutations that predispose individuals to clonal expansion of haematopoietic stem cells, indicating that both inherited and acquired mutations are linked to age-related cancers and coronary heart disease.
- Alexander G. Bick
- , Joshua S. Weinstock
- & Pradeep Natarajan
-
Article |
 Inherited myeloproliferative neoplasm risk affects haematopoietic stem cells
Inherited myeloproliferative neoplasm risk affects haematopoietic stem cells
A genome-wide association study identifies 17 genetic loci that are associated with the risk of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), and shows that the modulation of haematopoietic stem cell function drives MPN risk.
- Erik L. Bao
- , Satish K. Nandakumar
- & Vijay G. Sankaran
-
Article |
 Genetic and functional insights into the fractal structure of the heart
Genetic and functional insights into the fractal structure of the heart
A genome-wide association study shows that myocardial trabeculae are an important determinant of cardiac performance in the adult heart, identifies conserved pathways that regulate structural complexity and reveals the influence of trabeculae on the susceptibility to cardiovascular disease.
- Hannah V. Meyer
- , Timothy J. W. Dawes
- & Declan P. O’Regan
-
Article |
 Massive haplotypes underlie ecotypic differentiation in sunflowers
Massive haplotypes underlie ecotypic differentiation in sunflowers
Resequencing analyses of three species of wild sunflower identify large non-recombining haplotype blocks that correlate with ecologically relevant traits, soil and climate characteristics, and that differentiate species ecotypes.
- Marco Todesco
- , Gregory L. Owens
- & Loren H. Rieseberg
-
Article |
 FLT3 stop mutation increases FLT3 ligand level and risk of autoimmune thyroid disease
FLT3 stop mutation increases FLT3 ligand level and risk of autoimmune thyroid disease
A predicted loss-of-function germline mutation in FLT3 causes a reduction in full-length FLT3, with a compensatory increase in the levels of FLT3 ligand, leading to increased risk of autoimmune thyroid disease.
- Saedis Saevarsdottir
- , Thorunn A. Olafsdottir
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article |
 Monogenic and polygenic inheritance become instruments for clonal selection
Monogenic and polygenic inheritance become instruments for clonal selection
Analysis of blood-derived DNA from participants in the UK Biobank demonstrates that clonal expansions of acquired copy-neutral loss of heterozygosity mutations act on inherited alleles along a chromosome arm by modifying their allelic dosages.
- Po-Ru Loh
- , Giulio Genovese
- & Steven A. McCarroll
-
Article |
 Chromosomal alterations among age-related haematopoietic clones in Japan
Chromosomal alterations among age-related haematopoietic clones in Japan
Population-specific patterns of genomic mutations and selection of haematopoietic clones in Japanese and European participants predict the divergent rates of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and T cell leukaemia in these populations.
- Chikashi Terao
- , Akari Suzuki
- & Yoichiro Kamatani

 Refining the impact of genetic evidence on clinical success
Refining the impact of genetic evidence on clinical success