Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Subaerial weathering drove stabilization of continents
Subaerial weathering drove stabilization of continents
The geological histories of Archaean regions indicate that stabilization of the Earth’s continents and the formation of cratons was driven by continental emergence and subaerial weathering.
- Jesse R. Reimink
- & Andrew J. Smye
-
Article |
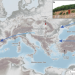 East-to-west human dispersal into Europe 1.4 million years ago
East-to-west human dispersal into Europe 1.4 million years ago
Burial-dating methods using cosmogenic nuclides indicate that the oldest stone tools at Korolevo archaeological site in western Ukraine date to around 1.4 million years ago, providing evidence of early human dispersal into Europe from the east.
- R. Garba
- , V. Usyk
- & J. D. Jansen
-
News |
 The world has warmed 1.5 °C, according to 300-year-old sponges
The world has warmed 1.5 °C, according to 300-year-old sponges
By the time that official temperature records began, global temperatures had already risen by half a degree.
- Bianca Nogrady
-
Nature Podcast |
 Toxic red mud could be turned into ‘green’ steel
Toxic red mud could be turned into ‘green’ steel
Researchers extract useful metal from industrial waste, and how analysis of blood proteins could help unravel the mystery of long COVID.
- Benjamin Thompson
- & Shamini Bundell
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for a liquid silicate layer atop the Martian core
Evidence for a liquid silicate layer atop the Martian core
Using multiply diffracted P waves and first-principles computations of the thermoelastic properties of liquid iron-rich alloys, we show that the core of Mars is smaller and denser than previously thought.
- A. Khan
- , D. Huang
- & M. Murakami
-
Article |
 Highest terrestrial 3He/4He credibly from the core
Highest terrestrial 3He/4He credibly from the core
Olivines from Baffin Island lavas have the highest magmatic 3He/4He ratio measured so far in terrestrial igneous rocks, indicating that the helium in these lavas might derive from Earth’s core.
- F. Horton
- , P. D. Asimow
- & X. M. Boyes
-
Article
| Open Access Sublithospheric diamond ages and the supercontinent cycle
Sublithospheric diamond ages and the supercontinent cycle
The ages and geochemical compositions of inclusions of sublithospheric diamonds indicate additions to the mantle keel of Gondwana by the underplating of buoyant subducted material, originating from 300–700-km depth, which may have contributed to supercontinent stability during long-distance migration.
- Suzette Timmerman
- , Thomas Stachel
- & D. Graham Pearson
-
Nature Index |
 Three scientists on the front line of climate and conservation research
Three scientists on the front line of climate and conservation research
By bearing firsthand witness to how the climate crisis is affecting life and livelihoods, their fieldwork directly informs policy to protect vulnerable sites.
- Sandy Ong
- & Andy Tay
-
Article
| Open Access Rock organic carbon oxidation CO2 release offsets silicate weathering sink
Rock organic carbon oxidation CO2 release offsets silicate weathering sink
Silicate weathering of uplifted rock depletes atmospheric CO2, but oxidation of revealed rock organic carbon supplies CO2, offsetting depletion to a degree dependent on regional geological history.
- Jesse R. Zondervan
- , Robert G. Hilton
- & Mateja Ogrič
-
Article |
 Earth’s early continental crust formed from wet and oxidizing arc magmas
Earth’s early continental crust formed from wet and oxidizing arc magmas
The use of two zircon oxybarometers to simultaneously determine fO2 and H2O contents shows that Archaean granitoids were mostly formed from relatively oxidizing and H2O-rich magmas, probably at ancient subduction zones.
- Rong-Feng Ge
- , Simon A. Wilde
- & Xiao-Lei Wang
-
Article |
 Sustained wet–dry cycling on early Mars
Sustained wet–dry cycling on early Mars
Observations by the Curiosity rover at Gale Crater on Mars indicate that high-frequency wet–dry cycling occurred on the early Martian surface, indicating a possible seasonal climate conducive to prebiotic evolution on early Mars.
- W. Rapin
- , G. Dromart
- & N. L. Lanza
-
Article |
 Carbonate-rich crust subduction drives the deep carbon and chlorine cycles
Carbonate-rich crust subduction drives the deep carbon and chlorine cycles
New experiments show that most carbonates in carbonate-rich crustal rocks survive devolatilization and hydrous melting in cold and warm subduction zones, demonstrating their role in driving the deep carbon and chlorine cycles since the Mesoproterozoic.
- Chunfei Chen
- , Michael W. Förster
- & Svyatoslav S. Shcheka
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term organic carbon preservation enhanced by iron and manganese
Long-term organic carbon preservation enhanced by iron and manganese
Catalysis of simple organic carbon molecules into complex macromolecules by Fe and Mn may play a fundamental role in organic carbon preservation, to a degree that could substantially affect the Earth’s carbon and oxygen cycles.
- Oliver W. Moore
- , Lisa Curti
- & Caroline L. Peacock
-
Article
| Open Access Earth’s evolving geodynamic regime recorded by titanium isotopes
Earth’s evolving geodynamic regime recorded by titanium isotopes
Titanium isotope measurements for chondrites, ancient terrestrial mantle-derived lavas and modern ocean island basalts imply the preservation of a primordial lower-mantle reservoir for most of Earth’s geologic history.
- Zhengbin Deng
- , Martin Schiller
- & Martin Bizzarro
-
Article
| Open Access Rift-induced disruption of cratonic keels drives kimberlite volcanism
Rift-induced disruption of cratonic keels drives kimberlite volcanism
Most kimberlites erupting in the past billion years on Earth did so about 30 million years after continental breakup, with dynamical and analytical models suggesting a control from rifting-related mantle delamination.
- Thomas M. Gernon
- , Stephen M. Jones
- & Anne Glerum
-
Research Briefing |
 An in situ search for organic molecules in Mars’s Jezero Crater
An in situ search for organic molecules in Mars’s Jezero Crater
Samples from the surface of Jezero Crater on Mars have been analysed by the SHERLOC instrument aboard NASA’s Perseverance rover. Signatures from these samples are consistent with the presence of organic molecules and, together with earlier measurements, could constitute the first in situ detection of organic molecules on another planet.
-
Article
| Open Access Diverse organic-mineral associations in Jezero crater, Mars
Diverse organic-mineral associations in Jezero crater, Mars
Raman and fluorescence spectra, consistent with several species of aromatic organic molecules, are reported in the Crater Floor sequences of Jezero crater, Mars, suggesting multiple mechanisms of organic synthesis, transport, or preservation.
- Sunanda Sharma
- , Ryan D. Roppel
- & Anastasia Yanchilina
-
News |
 Mars mission snaps striking ultraviolet view — image of the week
Mars mission snaps striking ultraviolet view — image of the week
The spacecraft is boosting understanding of the Martian surface and atmosphere.
-
News & Views |
 Phosphate discovery hints at geochemistry and origin of Enceladus
Phosphate discovery hints at geochemistry and origin of Enceladus
Evidence of phosphates in the subsurface ocean of Enceladus, an icy moon of Saturn, confirms that the water is alkaline. The finding provides clues about the geochemistry and origin of this moon and its ability to support life.
- Mikhail Yu. Zolotov
-
Article
| Open Access Silicon isotope constraints on terrestrial planet accretion
Silicon isotope constraints on terrestrial planet accretion
The nucleosynthetic composition of silicon in meteorites indicates that material akin to early-formed differentiated asteroids must represent a major constituent of terrestrial planets such as Earth and Mars.
- Isaac J. Onyett
- , Martin Schiller
- & Martin Bizzarro
-
Article
| Open Access Detection of phosphates originating from Enceladus’s ocean
Detection of phosphates originating from Enceladus’s ocean
Cassini’s Cosmic Dust Analyzer mass spectra of ice grains emitted by Enceladus show the presence of sodium phosphates, suggesting that phosphorus is readily available in Enceladus’s ocean in the form of orthophosphates.
- Frank Postberg
- , Yasuhito Sekine
- & Shuya Tan
-
Article |
 Uncovering the Ediacaran phosphorus cycle
Uncovering the Ediacaran phosphorus cycle
Reconstruction of oceanic phosphorus concentrations during a large negative carbon-isotope excursion co-occurring with global oceanic oxygenation and evolution of some of Earth’s earliest animals suggests that decoupled phosphorus and ocean anoxia cycles during the Ediacaran may have prolonged the rise of atmospheric oxygen.
- Matthew S. Dodd
- , Wei Shi
- & Timothy W. Lyons
-
Article |
 Bipolar impact and phasing of Heinrich-type climate variability
Bipolar impact and phasing of Heinrich-type climate variability
Ice-core data show that extreme iceberg discharge events in the North Atlantic had no detectable impact on Greenland temperatures but are synchronous with abrupt acceleration of Antarctic warming.
- Kaden C. Martin
- , Christo Buizert
- & Todd A. Sowers
-
Article |
 Degassing of early-formed planetesimals restricted water delivery to Earth
Degassing of early-formed planetesimals restricted water delivery to Earth
The very low water contents of minerals in achondrite meteorites from the early Solar System show that substantial amounts of water could only have been delivered to Earth by means of unmelted material.
- M. E. Newcombe
- , S. G. Nielsen
- & A. J. Irving
-
Article |
 Deep, ultra-hot-melting residues as cradles of mantle diamond
Deep, ultra-hot-melting residues as cradles of mantle diamond
New thermodynamic and geochemical modelling of melting shows that the observed composition of the cratonic mantle can be reproduced by deep and very hot melting, obviating the need for shallow melting and lithospheric stacking.
- Carl Walsh
- , Balz S. Kamber
- & Emma L. Tomlinson
-
Article |
 Primary N2–He gas field formation in intracratonic sedimentary basins
Primary N2–He gas field formation in intracratonic sedimentary basins
A modelling study shows that crustal nitrogen from the crystalline basement can reach sufficient concentrations in some sedimentary basins to form a free gas phase, into which helium partitions.
- Anran Cheng
- , Barbara Sherwood Lollar
- & Chris J. Ballentine
-
Article |
 Core origin of seismic velocity anomalies at Earth’s core–mantle boundary
Core origin of seismic velocity anomalies at Earth’s core–mantle boundary
Investigations of the crystallization of FeSi in Fe–Si–H melt under high pressure−temperature conditions provide evidence of a new process that explains geochemical and geophysical observations at the core–mantle boundary.
- Suyu Fu
- , Stella Chariton
- & Sang-Heon Shim
-
News |
 Scientists made a new kind of ice that might exist on distant moons
Scientists made a new kind of ice that might exist on distant moons
The 'amorphous' solid is denser and could be water ‘frozen in time’.
- Jonathan O'Callaghan
-
Matters Arising |
 Triassic sauropodomorph eggshell might not be soft
Triassic sauropodomorph eggshell might not be soft
- Seung Choi
- , Tzu-Ruei Yang
- & Noe-Heon Kim
-
Article |
 Nd isotope variation between the Earth–Moon system and enstatite chondrites
Nd isotope variation between the Earth–Moon system and enstatite chondrites
Isotopic analysis reveals that the samarium/neodymium ratio of the Earth–Moon system is higher than that of chondrites, and that the neodymium composition of Earth is similar to that of enstatite chondrites.
- Shelby Johnston
- , Alan Brandon
- & Peter Copeland
-
News |
 NASA’s Mars rover makes ‘fantastic’ find in search for past life
NASA’s Mars rover makes ‘fantastic’ find in search for past life
Perseverance has collected four rock samples from an ancient river delta where organisms might have thrived.
- Alexandra Witze
-
Research Briefing |
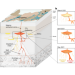 A glimpse into the deepest parts of the Fagradalsfjall volcanic system
A glimpse into the deepest parts of the Fagradalsfjall volcanic system
After around 780 years without volcanic activity, Iceland’s Reykjanes peninsula sprang to life in 2021, when magma breached the surface at the Fagradalsfjall volcano. Observed changes in the lava composition have provided an unprecedented record of the supply and mixing mechanics of deep magma at the base of the crust.
-
Article
| Open Access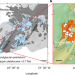 Rapid shifting of a deep magmatic source at Fagradalsfjall volcano, Iceland
Rapid shifting of a deep magmatic source at Fagradalsfjall volcano, Iceland
Primitive lavas of the Fagradalsfjall eruption present a window into the deep roots of a magmatic system previously inaccessible to near-real-time investigation, showing that eruptible batches of basaltic magma mix on a timescale of weeks.
- Sæmundur A. Halldórsson
- , Edward W. Marshall
- & Andri Stefánsson
-
News |
 Scientists have unearthed what could be the world’s oldest ice core
Scientists have unearthed what could be the world’s oldest ice core
Antarctic sample dated to between three million and five million years old extracted as international ice-drilling teams race to extend Earth’s climate record.
- McKenzie Prillaman
-
Article |
 Giant impacts and the origin and evolution of continents
Giant impacts and the origin and evolution of continents
Oxygen isotope compositions of dated magmatic zircon show that the Pilbara Craton in Western Australia, Earth’s best-preserved Archaean continental remnant, was built in three stages initiated by a giant meteorite impact.
- Tim E. Johnson
- , Christopher L. Kirkland
- & Michael I. H. Hartnady
-
Article |
 Hadean isotopic fractionation of xenon retained in deep silicates
Hadean isotopic fractionation of xenon retained in deep silicates
An explanation of the Earth’s ‘missing Xe’ problem that involves multiple magma ocean stages combined with atmospheric loss is proposed.
- Igor Rzeplinski
- , Chrystèle Sanloup
- & Denis Horlait
-
Review Article |
 Evolution of Earth’s tectonic carbon conveyor belt
Evolution of Earth’s tectonic carbon conveyor belt
Oceanic plate carbon reservoirs are reconstructed and the fate of subducted carbon is tracked using thermodynamic modelling, challenging previous views and providing boundary conditions for future carbon cycle models.
- R. Dietmar Müller
- , Ben Mather
- & Sabin Zahirovic
-
Article |
 Assembly of the basal mantle structure beneath Africa
Assembly of the basal mantle structure beneath Africa
Reconstruction of one billion years of mantle flow shows that mobile basal mantle structures are just as consistent with the Earth’s volcanic history as are fixed mantle structures.
- Nicolas Flament
- , Ömer F. Bodur
- & Andrew S. Merdith
-
News |
 A year on Mars: How NASA’s Perseverance hit a geological jackpot
A year on Mars: How NASA’s Perseverance hit a geological jackpot
The rover collected exciting rock samples on the first leg of its epic journey. Next, it will turn towards an ancient river delta to look for past life.
- Alexandra Witze
-
Research Highlight |
 How a space rock became King Tut’s dagger
How a space rock became King Tut’s dagger
An X-ray scan helps to show how the pharaoh’s knife was forged — and suggests a prestigious pedigree.
-
Article
| Open Access Age of the oldest known Homo sapiens from eastern Africa
Age of the oldest known Homo sapiens from eastern Africa
Geochemical analyses correlating the stratum that overlies the sediments containing the Omo fossils with material from a volcanic eruption suggest that these fossils (the oldest known modern human fossils in eastern Africa) are over 200,000 years old.
- Céline M. Vidal
- , Christine S. Lane
- & Clive Oppenheimer
-
Article |
 Deep-mantle krypton reveals Earth’s early accretion of carbonaceous matter
Deep-mantle krypton reveals Earth’s early accretion of carbonaceous matter
The krypton isotopic pattern of Earth’s deep mantle indicates that volatile-rich material from the outer Solar System was delivered early in Earth’s accretion history.
- Sandrine Péron
- , Sujoy Mukhopadhyay
- & David W. Graham
-
Article |
 A large West Antarctic Ice Sheet explains early Neogene sea-level amplitude
A large West Antarctic Ice Sheet explains early Neogene sea-level amplitude
Variations in Miocene sea level can be explained by a large marine-based West Antarctic Ice Sheet.
- J. W. Marschalek
- , L. Zurli
- & Zhifang Xiong
-
News & Views |
 Robotic sample return reveals lunar secrets
Robotic sample return reveals lunar secrets
A mission to unexplored lunar territory has returned the youngest volcanic samples collected so far. The rocks highlight the need to make revisions to models of the thermal evolution of the Moon.
- Richard W. Carlson
-
News Round-Up |
 New mineral, FDA chief and the pandemic’s toll on research
New mineral, FDA chief and the pandemic’s toll on research
The latest science news, in brief.
-
News |
 Diamond delivers long-sought mineral from the deep Earth
Diamond delivers long-sought mineral from the deep Earth
Davemaoite is a vehicle for radioactive isotopes that help to heat the planet’s mantle.
- Alexandra Witze
-
-
Article
| Open Access Non-KREEP origin for Chang’e-5 basalts in the Procellarum KREEP Terrane
Non-KREEP origin for Chang’e-5 basalts in the Procellarum KREEP Terrane
Isotopic analysis of basalt clasts returned from the Moon by the Chang’e-5 mission indicates that the rocks were derived from a mantle source that lacked potassium, rare-earth elements and phosphorus.
- Heng-Ci Tian
- , Hao Wang
- & Fu-Yuan Wu
-
Article
| Open Access A dry lunar mantle reservoir for young mare basalts of Chang’e-5
A dry lunar mantle reservoir for young mare basalts of Chang’e-5
Water abundance and hydrogen isotope compositions of two-billion-year-old basalt samples returned from the Moon by the Chang’e-5 mission suggest that the samples came from a relatively dry mantle source.
- Sen Hu
- , Huicun He
- & Ziyuan Ouyang

 Did atmospheric weathering help Earth’s earliest continents to survive?
Did atmospheric weathering help Earth’s earliest continents to survive?