Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Stress granules plug and stabilize damaged endolysosomal membranes
Stress granules plug and stabilize damaged endolysosomal membranes
Stress granules function at sites of intracellular membrane damage by forming on and stabilizing the ruptured membrane and promoting membrane repair.
- Claudio Bussi
- , Agustín Mangiarotti
- & Maximiliano G. Gutierrez
-
Article |
 A pentameric TRPV3 channel with a dilated pore
A pentameric TRPV3 channel with a dilated pore
High-speed atomic force microscopy single-molecule imaging and cryo-EM analysis discover and reveal the structure of a TRPV3 pentamer, providing evidence for a non-canonical pentameric TRP-channel assembly, laying the foundation for new directions in TRP channel research.
- Shifra Lansky
- , John Michael Betancourt
- & Simon Scheuring
-
Article |
 Bestrophin-2 and glutamine synthetase form a complex for glutamate release
Bestrophin-2 and glutamine synthetase form a complex for glutamate release
Electrophysiological, structural and biochemical studies on the bestrophin-2 anion channel reveal asymmetric permeability to glutamate and show that it forms a cooperative machinery in complex with glutamine synthetase for glutamate release.
- Aaron P. Owji
- , Kuai Yu
- & Tingting Yang
-
Article |
 Autoantibody mimicry of hormone action at the thyrotropin receptor
Autoantibody mimicry of hormone action at the thyrotropin receptor
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the thyrotropin receptor reveal the basis for the activation of the receptor by autoantibodies in patients with Graves’ disease.
- Bryan Faust
- , Christian B. Billesbølle
- & Aashish Manglik
-
Article |
 Mitochondrial uncouplers induce proton leak by activating AAC and UCP1
Mitochondrial uncouplers induce proton leak by activating AAC and UCP1
Common protonophores—previously known as protein-independent proton translocators—activate mitochondrial heat production due to H+ leak through the ADP/ATP carrier and uncoupling protein 1.
- Ambre M. Bertholet
- , Andrew M. Natale
- & Yuriy Kirichok
-
Article
| Open Access Capturing a rhodopsin receptor signalling cascade across a native membrane
Capturing a rhodopsin receptor signalling cascade across a native membrane
The rhodopsin signalling cascade, initiated by light, is captured using mass spectrometry of a native membrane.
- Siyun Chen
- , Tamar Getter
- & Carol V. Robinson
-
Article |
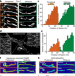 Distinct fission signatures predict mitochondrial degradation or biogenesis
Distinct fission signatures predict mitochondrial degradation or biogenesis
Mitochondrial fission at the organelle periphery generates small daughter mitochondria that are removed by mitophagy whereas fission at the midzone leads to proliferation.
- Tatjana Kleele
- , Timo Rey
- & Suliana Manley
-
Article |
 Visualization of the mechanosensitive ion channel MscS under membrane tension
Visualization of the mechanosensitive ion channel MscS under membrane tension
The authors report the structural characterization of the mechanically activated channel MscS in different membrane environments and show how the mechanosensation of MscS can be visualized.
- Yixiao Zhang
- , Csaba Daday
- & Thomas Walz
-
Article |
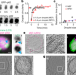 Wetting regulates autophagy of phase-separated compartments and the cytosol
Wetting regulates autophagy of phase-separated compartments and the cytosol
A theoretical model, in vitro reconstitution and in vivo experimentation show that competition between droplet surface tension and membrane sheet instability dictates the form and function of autophagosomal membranes.
- Jaime Agudo-Canalejo
- , Sebastian W. Schultz
- & Roland L. Knorr
-
Review Article |
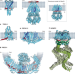 Discoveries in structure and physiology of mechanically activated ion channels
Discoveries in structure and physiology of mechanically activated ion channels
This Review summarizes developments in the field of mechanically activated ion channels, which have been driven by the increasing breadth of structural studies.
- J. M. Kefauver
- , A. B. Ward
- & A. Patapoutian
-
Article |
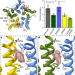 Shared structural mechanisms of general anaesthetics and benzodiazepines
Shared structural mechanisms of general anaesthetics and benzodiazepines
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of GABAA receptors bound to intravenous anaesthetics and benzodiazepines reveal both common and distinct transmembrane binding sites, and show that the mechanisms of action of anaesthetics partially overlap with those of benzodiazepines.
- Jeong Joo Kim
- , Anant Gharpure
- & Ryan E. Hibbs
-
Article |
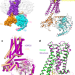 Structure of a D2 dopamine receptor–G-protein complex in a lipid membrane
Structure of a D2 dopamine receptor–G-protein complex in a lipid membrane
The structure of the D2 dopamine receptor in complex with its G protein reveals how dopamine receptors are activated and, importantly, how a G-protein-coupled receptor can interact with its G protein in a phospholipid membrane.
- Jie Yin
- , Kuang-Yui M. Chen
- & Daniel M. Rosenbaum
-
Article |
 Electromechanical coupling in the hyperpolarization-activated K+ channel KAT1
Electromechanical coupling in the hyperpolarization-activated K+ channel KAT1
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of the hyperpolarization-activated K+ channel KAT1 points to a direct-coupling mechanism between S4 movement and the reorientation of the C-linker.
- Michael David Clark
- , Gustavo F. Contreras
- & Eduardo Perozo
-
Article |
 Femtosecond-to-millisecond structural changes in a light-driven sodium pump
Femtosecond-to-millisecond structural changes in a light-driven sodium pump
Crystallographic ‘snapshots’ taken at intervals of femtoseconds to milliseconds after activation show how a light-activated sodium pump carries sodium ions across the cell membrane.
- Petr Skopintsev
- , David Ehrenberg
- & Jörg Standfuss
-
Article |
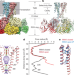 Ball-and-chain inactivation in a calcium-gated potassium channel
Ball-and-chain inactivation in a calcium-gated potassium channel
Cryo-electron microscopy structures and molecular dynamics simulations of the calcium-activated potassium channel MthK from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum are used to show that gating of this channel involves a ball-and-chain inactivation mechanism mediated by a previously unresolved N-terminal peptide.
- Chen Fan
- , Nattakan Sukomon
- & Crina M. Nimigean
-
Article |
 Mechanism of adrenergic CaV1.2 stimulation revealed by proximity proteomics
Mechanism of adrenergic CaV1.2 stimulation revealed by proximity proteomics
An in vivo approach to identify proteins whose enrichment near cardiac CaV1.2 channels changes upon β-adrenergic stimulation finds the G protein Rad, which is phosphorylated by protein kinase A, thereby relieving channel inhibition by Rad and causing an increased Ca2+ current.
- Guoxia Liu
- , Arianne Papa
- & Steven O. Marx
-
Article |
 Quantifying secondary transport at single-molecule resolution
Quantifying secondary transport at single-molecule resolution
Imaging of substrate transport by individual MhsT transporters, members of the neurotransmitter:sodium symporter family of secondary transporters, at single- and multi-turnover resolution reveals that the rate-limiting step varies with the identity of the transported substrate.
- Gabriel A. Fitzgerald
- , Daniel S. Terry
- & Scott C. Blanchard
-
Article |
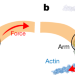 Force-induced conformational changes in PIEZO1
Force-induced conformational changes in PIEZO1
Cryo-electron microscopy and high-speed atomic force microscopy reveal that PIEZO1 can reversibly deform its shape towards a planar structure, which may explain how the PIEZO1 channel is gated in response to mechanical stimulation.
- Yi-Chih Lin
- , Yusong R. Guo
- & Simon Scheuring
-
Article |
 H+ transport is an integral function of the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier
H+ transport is an integral function of the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier
The mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier mediates the proton leak in mitochondria from all tissues that lack UCP1, thereby linking coupled (ATP production) and uncoupled (thermogenesis) energy conversion.
- Ambre M. Bertholet
- , Edward T. Chouchani
- & Yuriy Kirichok
-
Letter |
 Structure and assembly of the mitochondrial membrane remodelling GTPase Mgm1
Structure and assembly of the mitochondrial membrane remodelling GTPase Mgm1
Crystal and electron cryo-tomography structures of Mgm1 from Chaetomium thermophilum reveal that Mgm1 forms bent tetramers, which further assemble into helical filaments on both positively and negatively curved membranes.
- Katja Faelber
- , Lea Dietrich
- & Oliver Daumke
-
Letter |
 A potassium channel β-subunit couples mitochondrial electron transport to sleep
A potassium channel β-subunit couples mitochondrial electron transport to sleep
Sleep deprivation in Drosophila elevates reactive oxygen species in sleep-promoting neurons, leading to changes in potassium currents and spiking activity and thereby connecting energy metabolism, oxidative stress, and sleep.
- Anissa Kempf
- , Seoho M. Song
- & Gero Miesenböck
-
Letter |
 Structural basis for KCTD-mediated rapid desensitization of GABAB signalling
Structural basis for KCTD-mediated rapid desensitization of GABAB signalling
X-ray crystallography, electron microscopy and functional experiments reveal the details of how KCTD proteins interact with GABAB receptors and desensitize G-protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels.
- Sanduo Zheng
- , Nohely Abreu
- & Andrew C. Kruse
-
Article |
 Structure of native lens connexin 46/50 intercellular channels by cryo-EM
Structure of native lens connexin 46/50 intercellular channels by cryo-EM
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of connexin channels composed of connexin 46 and connexin 50 in an open-state reveal features that govern permselectivity and the location of mutated residues linked to herediatry cataracts.
- Janette B. Myers
- , Bassam G. Haddad
- & Steve L. Reichow
-
Article |
 Structural mechanisms of selectivity and gating in anion channelrhodopsins
Structural mechanisms of selectivity and gating in anion channelrhodopsins
Crystal structures and molecular simulations of the designed anion-conducting channelrhodopsin iC++ provide molecular insights that enable structure-based design of channelrhodopsins with desirable properties for use as optogenetic tools.
- Hideaki E. Kato
- , Yoon Seok Kim
- & Karl Deisseroth
-
Article |
 Cryo-EM structures of fungal and metazoan mitochondrial calcium uniporters
Cryo-EM structures of fungal and metazoan mitochondrial calcium uniporters
Structures of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter from fungal and metazoan organisms reveal a tetrameric architecture and shed light on the function of the channel.
- Rozbeh Baradaran
- , Chongyuan Wang
- & Stephen Barstow Long
-
Article |
 Structure of a volume-regulated anion channel of the LRRC8 family
Structure of a volume-regulated anion channel of the LRRC8 family
The structure of a homomeric channel of subunit A of leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 8 (LRRC8) determined by cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography reveals the basis for anion selectivity.
- Dawid Deneka
- , Marta Sawicka
- & Raimund Dutzler
-
Letter |
 Structural insights into the voltage and phospholipid activation of the mammalian TPC1 channel
Structural insights into the voltage and phospholipid activation of the mammalian TPC1 channel
Structures of the voltage-gated and phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate-activated mouse two-pore channel TPC1 in apo and ligand-bound states provide insights into the selectivity and gating mechanisms of mammalian two-pore channels.
- Ji She
- , Jiangtao Guo
- & Xiao-chen Bai
-
Letter |
 Architecture of a channel-forming O-antigen polysaccharide ABC transporter
Architecture of a channel-forming O-antigen polysaccharide ABC transporter
The crystal structure of a channel-forming O-antigen polysaccharide ABC transporter suggests a novel biopolymer translocation mechanism.
- Yunchen Bi
- , Evan Mann
- & Jochen Zimmer
-
Letter |
 Cryo-EM structures of the TMEM16A calcium-activated chloride channel
Cryo-EM structures of the TMEM16A calcium-activated chloride channel
Electron cryo-microscopy density maps of mouse TMEM16A reconstituted in nanodiscs or solubilized in detergent reveal two functional states of calcium-activated chloride channels.
- Shangyu Dang
- , Shengjie Feng
- & Lily Yeh Jan
-
Letter |
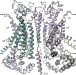 Activation mechanism of the calcium-activated chloride channel TMEM16A revealed by cryo-EM
Activation mechanism of the calcium-activated chloride channel TMEM16A revealed by cryo-EM
Cryo-electron microscopy mapping of the calcium-activated chloride channel TMEM16A combined with functional experiments reveals that calcium ions interact directly with the pore to activate the channel.
- Cristina Paulino
- , Valeria Kalienkova
- & Raimund Dutzler
-
Article |
 Structures of the calcium-activated, non-selective cation channel TRPM4
Structures of the calcium-activated, non-selective cation channel TRPM4
Electron cryo-microscopy structures of mouse TRPM4, a calcium-activated, non-selective cation channel, in the apo and ATP-bound states.
- Jiangtao Guo
- , Ji She
- & Youxing Jiang
-
Article |
 Protein–phospholipid interplay revealed with crystals of a calcium pump
Protein–phospholipid interplay revealed with crystals of a calcium pump
Solvent contrast modulation reveals how the lipid bilayer actively participates in the conformational switches of Ca2+-ATPase through the actions of tryptophan, arginine and lysine residues, which function as membrane floats and anchors.
- Yoshiyuki Norimatsu
- , Kazuya Hasegawa
- & Chikashi Toyoshima
-
Letter |
 The role of interfacial lipids in stabilizing membrane protein oligomers
The role of interfacial lipids in stabilizing membrane protein oligomers
Membrane lipids such as cardiolipin act as molecular glue to preserve the oligomeric states of membrane proteins with low oligomeric stability.
- Kallol Gupta
- , Joseph A. C. Donlan
- & Carol V. Robinson
-
Letter |
 Structural basis for nutrient acquisition by dominant members of the human gut microbiota
Structural basis for nutrient acquisition by dominant members of the human gut microbiota
The authors present structures of nutrient transport complexes of the commensal bacterium Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron and the mechanism by which it imports glycans.
- Amy J. Glenwright
- , Karunakar R. Pothula
- & Bert van den Berg
-
Article |
 Cryo-EM structure of the open high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel
Cryo-EM structure of the open high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel
Two complementary studies present the full-length high-resolution structure of a Slo1 channel in the presence or absence of Ca2+ ions, in which an unconventional allosteric voltage-sensing mechanism regulates the Ca2+ sensor in addition to the voltage sensor’s direct action on the pore.
- Xiao Tao
- , Richard K. Hite
- & Roderick MacKinnon
-
Article |
 Structural basis for gating the high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel
Structural basis for gating the high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel
Two complementary studies present the full-length high-resolution structure of a Slo1 channel in the presence or absence of Ca2+ ions, in which an unconventional allosteric voltage-sensing mechanism regulates the Ca2+ sensor in addition to the voltage sensor’s direct action on the pore.
- Richard K. Hite
- , Xiao Tao
- & Roderick MacKinnon
-
Letter |
 High-resolution crystal structure of the human CB1 cannabinoid receptor
High-resolution crystal structure of the human CB1 cannabinoid receptor
The authors report a 2.6 Å resolution crystal structure of the human CB1 cannabinoid receptor trapped in the inactive conformation and bound to the antagonist taranabant.
- Zhenhua Shao
- , Jie Yin
- & Daniel M. Rosenbaum
-
Letter |
 An endosomal tether undergoes an entropic collapse to bring vesicles together
An endosomal tether undergoes an entropic collapse to bring vesicles together
A new endosomal tethering mechanism involving a mechanochemical cycle of the dimeric coiled-coil protein EEA1 regulated by Rab5:GTP binding and GTP hydrolysis.
- David H. Murray
- , Marcus Jahnel
- & Marino Zerial
-
Letter |
 Hemi-fused structure mediates and controls fusion and fission in live cells
Hemi-fused structure mediates and controls fusion and fission in live cells
Super-resolution imaging provides direct evidence in live cells that membrane fusion and fission are mediated through an intermediate hemi-fused structure, where fusion and calcium/dynamin-dependent fission mechanisms compete to determine the transition of the intermediate to fusion or fission.
- Wei-Dong Zhao
- , Edaeni Hamid
- & Ling-Gang Wu
-
Letter |
 Backbone NMR reveals allosteric signal transduction networks in the β1-adrenergic receptor
Backbone NMR reveals allosteric signal transduction networks in the β1-adrenergic receptor
Although several X-ray crystal structures of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have been reported, relatively little is known about the conformational dynamics of these important membrane proteins; here, the authors used NMR spectroscopy to monitor the conformational changes that occur in the turkey β1-adrenergic receptor in the presence of antagonists, partial agonists, and full agonists.
- Shin Isogai
- , Xavier Deupi
- & Stephan Grzesiek
-
Letter |
 Supramolecular assemblies underpin turnover of outer membrane proteins in bacteria
Supramolecular assemblies underpin turnover of outer membrane proteins in bacteria
Fluorescent labelling is used to show that in E. coli, outer membrane protein (OMP) turnover is passive and binary in nature, and OMPs cluster to form islands in which diffusion of individual proteins is restricted owing to lateral interactions with other OMPs; new OMPs are inserted mostly at mid-cell, meaning that old OMP islands are displaced to the poles of growing cells.
- Patrice Rassam
- , Nikki A. Copeland
- & Colin Kleanthous
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter and CaMKII in heart
Mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter and CaMKII in heart
- Francesca Fieni
- , Derrick E. Johnson
- & Yuriy Kirichok
-
Brief Communications Arising |
Joiner et al. reply
- Mei-ling A. Joiner
- , Olha M. Koval
- & Mark E. Anderson
-
Article |
 The cancer glycocalyx mechanically primes integrin-mediated growth and survival
The cancer glycocalyx mechanically primes integrin-mediated growth and survival
Metastatic cancer cells are shown to have a tendency towards forming a bulky glycocalyx owing to the production of large glycoproteins, and this cancer-associated glycocalyx has a mechanical effect on the spatial organization of integrins — by funnelling integrins into adhesions, integrin clustering and signalling is promoted, which leads to enhanced cell survival and proliferation.
- Matthew J. Paszek
- , Christopher C. DuFort
- & Valerie M. Weaver
-
Article |
 X-ray structure of the mammalian GIRK2–βγ G-protein complex
X-ray structure of the mammalian GIRK2–βγ G-protein complex
An X-ray structure and electrophysiological analysis of mammalian G-protein-gated inward rectifier potassium channel GIRK2 in complex with βγ reveals a pre-open channel structure consistent with channel activation by membrane delimited G-protein subunits.
- Matthew R. Whorton
- & Roderick MacKinnon
-
Letter |
 Structural basis for alternating access of a eukaryotic calcium/proton exchanger
Structural basis for alternating access of a eukaryotic calcium/proton exchanger
The X-ray crystal structure of a member of the Ca2+/H+ (CAX) antiporter family from Saccharomyces cerevisiae in a cytosol-facing, substrate-bound conformation is solved; using the structure, a mechanism by which members of the Ca2+:cation (CaCA) superfamily facilitate Ca2+ transport across cellular membranes is proposed.
- Andrew B. Waight
- , Bjørn Panyella Pedersen
- & Robert M. Stroud
-
Letter |
 Structure of a bacterial energy-coupling factor transporter
Structure of a bacterial energy-coupling factor transporter
The crystal structure of a nucleotide-free energy-coupling factor transporter from Lactobacillus brevis at a resolution of 3.5 Å suggests a plausible working model for the transport cycle of such transporters.
- Tingliang Wang
- , Guobin Fu
- & Yigong Shi
-
Letter |
 Crystal structure of a eukaryotic phosphate transporter
Crystal structure of a eukaryotic phosphate transporter
The X-ray crystal structure of a high-affinity phosphate importer in an inward-facing, occluded state in the presence of phosphate is reported; this is the first structure of a membrane protein involved in inorganic phosphate uptake and the first crystal structure of a eukaryotic MFS transporter.
- Bjørn P. Pedersen
- , Hemant Kumar
- & Robert M. Stroud
-
Letter |
 Structure and mechanism of a bacterial sodium-dependent dicarboxylate transporter
Structure and mechanism of a bacterial sodium-dependent dicarboxylate transporter
The cytosolic concentration of citrate partially depends on its direct import across the plasma membrane by the Na+-dependent citrate transporter (NaCT); here the X-ray crystal structure of a bacterial homologue of NaCT is reported, which, along with transport-activity studies, suggests how specific conformational changes facilitate substrate translocation across the cellular membrane.
- Romina Mancusso
- , G. Glenn Gregorio
- & Da-Neng Wang

 Motion of VAPB molecules reveals ER–mitochondria contact site subdomains
Motion of VAPB molecules reveals ER–mitochondria contact site subdomains