Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Metals strengthen with increasing temperature at extreme strain rates
Metals strengthen with increasing temperature at extreme strain rates
Microballistic impact testing at strain rates greater than 106 s−1 shows that pure metals, including copper, gold and titanium, become stronger with increasing temperature.
- Ian Dowding
- & Christopher A. Schuh
-
Article |
 High fatigue resistance in a titanium alloy via near-void-free 3D printing
High fatigue resistance in a titanium alloy via near-void-free 3D printing
We successfully rebuild an approximate void-free additive manufacturing microstructure in Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy by the development of a void-free additive manufacturing processing technique through an understanding of the asynchronism of phase transformation and grain growth.
- Zhan Qu
- , Zhenjun Zhang
- & Zhefeng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Green steel from red mud through climate-neutral hydrogen plasma reduction
Green steel from red mud through climate-neutral hydrogen plasma reduction
Red mud is shown to yield green steel through fossil-free hydrogen-plasma-based reduction, a simple and fast method involving rapid liquid-state reduction, chemical partitioning, and density-driven and viscosity-driven separation.
- Matic Jovičević-Klug
- , Isnaldi R. Souza Filho
- & Dierk Raabe
-
Article |
 Negative mixing enthalpy solid solutions deliver high strength and ductility
Negative mixing enthalpy solid solutions deliver high strength and ductility
A HfNbTiVAl10 alloy shows tensile ductility and ultrahigh yield strength from the addition of aluminium to a HfNbTiV alloy, resulting in a negative mixing enthalpy solid solution, which promotes strength and favours formation of hierarchical chemical fluctuations.
- Zibing An
- , Ang Li
- & Xiaodong Han
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional atomic structure and local chemical order of medium- and high-entropy nanoalloys
Three-dimensional atomic structure and local chemical order of medium- and high-entropy nanoalloys
Atomic electron tomography is used to determine the 3D atomic positions and chemical species of medium- and high-entropy alloy nanoparticles and quantitatively characterize the local lattice distortion, strain tensor, twin boundaries, dislocation cores and chemical short-range order.
- Saman Moniri
- , Yao Yang
- & Jianwei Miao
-
Article |
 A stable atmospheric-pressure plasma for extreme-temperature synthesis
A stable atmospheric-pressure plasma for extreme-temperature synthesis
A plasma set-up consisting of a pair of carbon-fibre-tip-enhanced electrodes enables the generation of a uniform, ultra-high temperature and stable plasma (up to 8,000 K) at atmospheric pressure using a combination of vertically oriented long and short carbon fibres.
- Hua Xie
- , Ning Liu
- & Liangbing Hu
-
Article |
 On the origin of diffuse intensities in fcc electron diffraction patterns
On the origin of diffuse intensities in fcc electron diffraction patterns
Some of the diffuse intensities observed in electron diffraction patterns of face-centred cubic multi-principal element alloys are due to reflections from higher-order Laue zones.
- Francisco Gil Coury
- , Cody Miller
- & Michael Kaufman
-
Article |
 Autonomous healing of fatigue cracks via cold welding
Autonomous healing of fatigue cracks via cold welding
We report that fatigue cracks in pure metals can undergo intrinsic self-healing; they were observed to heal by crack flank cold welding induced by local stress state and grain boundary migration.
- Christopher M. Barr
- , Ta Duong
- & Brad L. Boyce
-
Article
| Open Access Strong and ductile titanium–oxygen–iron alloys by additive manufacturing
Strong and ductile titanium–oxygen–iron alloys by additive manufacturing
Combining alloy design with additive manufacturing process design creates α–β titanium–oxygen–iron alloys that are both strong and ductile, with the potential to revitalize off-grade sponge titanium and thereby reduce the carbon footprint of the titanium industry.
- Tingting Song
- , Zibin Chen
- & Ma Qian
-
Article
| Open Access A 3D printable alloy designed for extreme environments
A 3D printable alloy designed for extreme environments
The authors develop a new oxide-dispersion-strengthened NiCoCr-based alloy using a model-driven alloy design approach and laser-based additive manufacturing, showing how such designs can provide superior compositions using far fewer resources than previous methods.
- Timothy M. Smith
- , Christopher A. Kantzos
- & John W. Lawson
-
Article |
 Additive manufacturing of micro-architected metals via hydrogel infusion
Additive manufacturing of micro-architected metals via hydrogel infusion
An additive manufacturing technique that infuses 3D printed hydrogels with metallic precursors leads to metallic micromaterials, providing new opportunities for the fabrication of energy materials, micro-electromechanical systems and biomedical devices.
- Max A. Saccone
- , Rebecca A. Gallivan
- & Julia R. Greer
-
Article |
 Anomalous slip in body-centred cubic metals
Anomalous slip in body-centred cubic metals
Observations by transmission electron microscopy of deforming niobium and tungsten at low temperature shows that anomalous slip in body-centred cubic metals arises from the unusually high mobility of multi-junctions, which is a source of softening.
- Daniel Caillard
- , Baptiste Bienvenu
- & Emmanuel Clouet
-
Article |
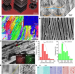 Strong yet ductile nanolamellar high-entropy alloys by additive manufacturing
Strong yet ductile nanolamellar high-entropy alloys by additive manufacturing
An additive manufacturing strategy is used to produce dual-phase nanolamellar high-entropy alloys that show a combination of enhanced high yield strength and high tensile ductility.
- Jie Ren
- , Yin Zhang
- & Wen Chen
-
Article |
 Dislocation-induced stop-and-go kinetics of interfacial transformations
Dislocation-induced stop-and-go kinetics of interfacial transformations
Environmental transmission electron microscopy is used to reveal that mismatch dislocations modulate the interfacial transformation of copper oxide to copper metal in an intermittent manner.
- Xianhu Sun
- , Dongxiang Wu
- & Guangwen Zhou
-
Article |
 Uniting tensile ductility with ultrahigh strength via composition undulation
Uniting tensile ductility with ultrahigh strength via composition undulation
A nanocrystalline metallic alloy with ultrahigh tensile strength and good ductility is achieved by introducing compositional undulation in a highly concentrated solid solution.
- Heng Li
- , Hongxiang Zong
- & Jun Sun
-
Article
| Open Access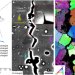 Hydrogen trapping and embrittlement in high-strength Al alloys
Hydrogen trapping and embrittlement in high-strength Al alloys
Atom-scale analysis of hydrogen and other elements at the grain boundaries of a 7xxx aluminium alloy shows that co-segregation of elements favours grain boundary decohesion, and that hydrogen embrittlement is prevented by strong partitioning into the second-phase particles.
- Huan Zhao
- , Poulami Chakraborty
- & Dierk Raabe
-
Article |
 A highly distorted ultraelastic chemically complex Elinvar alloy
A highly distorted ultraelastic chemically complex Elinvar alloy
A chemically complex alloy that exhibits a high elastic strain limit and low internal friction is described; it also has an Elinvar effect (invariant elastic modulus) over a large temperature range, up to 627 °C.
- Q. F. He
- , J. G. Wang
- & Y. Yang
-
Article |
 Selective sulfidation of metal compounds
Selective sulfidation of metal compounds
A framework for selective sulfidation is proposed for the practical separation and enrichment of numerous metallic elements, to enable environmentally and economically sustainable metal processing.
- Caspar Stinn
- & Antoine Allanore
-
Article |
 Bifunctional nanoprecipitates strengthen and ductilize a medium-entropy alloy
Bifunctional nanoprecipitates strengthen and ductilize a medium-entropy alloy
Increased strength and ductility in a medium-entropy alloy of Fe, Ni, Al and Ti is demonstrated using nanoprecipitates that simultaneously hinder phase transformation and block dislocation motion.
- Ying Yang
- , Tianyi Chen
- & Easo P. George
-
Article |
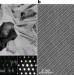 Direct observation of chemical short-range order in a medium-entropy alloy
Direct observation of chemical short-range order in a medium-entropy alloy
Direct experimental evidence of chemical short-range atomic-scale ordering (CSRO) in a VCoNi medium-entropy alloy is provided via diffraction and electron microscopy, analysed from specific crystallographic directions.
- Xuefei Chen
- , Qi Wang
- & En Ma
-
Article |
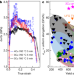 Facile route to bulk ultrafine-grain steels for high strength and ductility
Facile route to bulk ultrafine-grain steels for high strength and ductility
Bulk ultrafine-grained steel is prepared by an approach that involves the rapid production of coherent, disordered nanoprecipitates, which restrict grain growth but do not interfere with twinning or dislocation motion, resulting in high strength and ductility.
- Junheng Gao
- , Suihe Jiang
- & W. Mark Rainforth
-
Article |
 High-strength Damascus steel by additive manufacturing
High-strength Damascus steel by additive manufacturing
A Damascus-like steel consisting of alternating hard and soft layers is created by using a laser additive manufacturing technique and digital control of the processing parameters.
- Philipp Kürnsteiner
- , Markus Benjamin Wilms
- & Dierk Raabe
-
Article |
 Short-range order and its impact on the CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy
Short-range order and its impact on the CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy
Metal alloys consisting of three or more major elemental components show enhanced mechanical properties, which are now shown to be correlated with short-range order observed with electron microscopy.
- Ruopeng Zhang
- , Shiteng Zhao
- & Andrew M. Minor
-
Article |
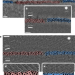 Observations of grain-boundary phase transformations in an elemental metal
Observations of grain-boundary phase transformations in an elemental metal
Atomic-resolution observations combined with simulations show that grain boundaries within elemental copper undergo temperature-induced solid-state phase transformation to different structures; grain boundary phases can also coexist and are kinetically trapped structures.
- Thorsten Meiners
- , Timofey Frolov
- & Christian H. Liebscher
-
Article |
 Strain-hardening and suppression of shear-banding in rejuvenated bulk metallic glass
Strain-hardening and suppression of shear-banding in rejuvenated bulk metallic glass
Bulk metallic glasses can acquire the ability to strain-harden through a mechanical rejuvenation treatment at room temperature that retains their non-crystalline structure.
- J. Pan
- , Yu. P. Ivanov
- & A. L. Greer
-
Article |
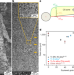 Additive manufacturing of ultrafine-grained high-strength titanium alloys
Additive manufacturing of ultrafine-grained high-strength titanium alloys
Titanium–copper alloys with fully equiaxed grains and a fine microstructure are realized via an additive manufacturing process that exploits high cooling rates and multiple thermal cycles.
- Duyao Zhang
- , Dong Qiu
- & Mark A. Easton
-
Review Article |
 Strategies for improving the sustainability of structural metals
Strategies for improving the sustainability of structural metals
Structural metals enable improved energy efficiency through their reduced mass, higher thermal stability and better mechanical properties; here, methods of improving the sustainability of structural metals, from recycling to contaminant tolerance, are described.
- Dierk Raabe
- , C. Cem Tasan
- & Elsa A. Olivetti
-
Letter |
 Tuning element distribution, structure and properties by composition in high-entropy alloys
Tuning element distribution, structure and properties by composition in high-entropy alloys
In high-entropy alloys, atomic-resolution chemical mapping shows that swapping some of the atoms for larger, more electronegative elements results in atomic-scale modulations that produce higher yield strength, excellent strain hardening and ductility.
- Qingqing Ding
- , Yin Zhang
- & Qian Yu
-
Letter |
 High-temperature bulk metallic glasses developed by combinatorial methods
High-temperature bulk metallic glasses developed by combinatorial methods
Bulk metallic glasses made from alloys of iridium, nickel, tantalum and boron are developed by combinatorial methods, with higher strength at high temperature than those previously produced.
- Ming-Xing Li
- , Shao-Fan Zhao
- & Wei-Hua Wang
-
Letter |
 Enhanced strength and ductility in a high-entropy alloy via ordered oxygen complexes
Enhanced strength and ductility in a high-entropy alloy via ordered oxygen complexes
Ordered oxygen complexes in high-entropy alloys enhance both strength and ductility in these compositionally complex solid solutions.
- Zhifeng Lei
- , Xiongjun Liu
- & Zhaoping Lu
-
Letter |
 History-independent cyclic response of nanotwinned metals
History-independent cyclic response of nanotwinned metals
In copper components containing highly oriented nanotwins, correlated ‘necklace’ dislocations moving back and forth offer an unusually fatigue-resistant response to engineering stress.
- Qingsong Pan
- , Haofei Zhou
- & Lei Lu
-
Letter |
 Probing the limits of metal plasticity with molecular dynamics simulations
Probing the limits of metal plasticity with molecular dynamics simulations
The limits of dislocation-mediated metal plasticity are studied by using in situ computational microscopy to reduce the enormous amount of data from fully dynamic atomistic simulations into a manageable form.
- Luis A. Zepeda-Ruiz
- , Alexander Stukowski
- & Vasily V. Bulatov
-
Letter |
 3D printing of high-strength aluminium alloys
3D printing of high-strength aluminium alloys
Zirconium nanoparticles introduced into aluminium alloy powders control solidification during 3D printing, enabling the production of crack-free materials with strengths comparable to the corresponding wrought material.
- John H. Martin
- , Brennan D. Yahata
- & Tresa M. Pollock
-
Letter |
 Ultrastrong steel via minimal lattice misfit and high-density nanoprecipitation
Ultrastrong steel via minimal lattice misfit and high-density nanoprecipitation
A method of producing superstrong yet ductile steels using cheaper and lighter alloying elements is described, based on minimization of the lattice misfit to achieve a maximal dispersion of nanoprecipitates, leading to ultimate precipitation strengthening.
- Suihe Jiang
- , Hui Wang
- & Zhaoping Lu
-
Letter |
 Dual-phase nanostructuring as a route to high-strength magnesium alloys
Dual-phase nanostructuring as a route to high-strength magnesium alloys
Combining the benefits of nanocrystals with those of amorphous metallic glasses leads to a dual-phase material—comprising sub-10-nanometre-sized nanocrystalline grains embedded in amorphous glassy shells—that exhibits a strength approaching the ideal theoretical limit.
- Ge Wu
- , Ka-Cheung Chan
- & Jian Lu
-
Letter |
 Extreme creep resistance in a microstructurally stable nanocrystalline alloy
Extreme creep resistance in a microstructurally stable nanocrystalline alloy
A nanocrystalline copper–tantalum alloy with high strength and extremely high-temperature creep resistance is achieved via a processing method that creates clusters of atoms within the alloy that pin grain boundaries.
- K. A. Darling
- , M. Rajagopalan
- & K. N. Solanki
-
Letter |
 Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength–ductility trade-off
Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength–ductility trade-off
An alloy design strategy that aims for phase metastability, rather than phase stability, is described that will lead to the development of transformation-induced plasticity-assisted, dual-phase high-entropy alloys, which exhibit a rare combined increase in strength and ductility.
- Zhiming Li
- , Konda Gokuldoss Pradeep
- & Cemal Cem Tasan
-
Letter |
 Processing and properties of magnesium containing a dense uniform dispersion of nanoparticles
Processing and properties of magnesium containing a dense uniform dispersion of nanoparticles
Magnesium is light but not very strong; here the addition of silicon carbide nanoparticles uniformly dispersed to 14 per cent by volume, achieved through a nanoparticle self-stabilization mechanism in a molten metal alloy, yields improved strength, stiffness, plasticity and high-temperature stability.
- Lian-Yi Chen
- , Jia-Quan Xu
- & Xiao-Chun Li
-
Article |
 The origins of high hardening and low ductility in magnesium
The origins of high hardening and low ductility in magnesium
Practical applications of magnesium as a lightweight structural metal are limited by its high work hardening, low ductility and fracture at very low strains; now molecular dynamics simulations reveal the origins of these problems and offer a route to design magnesium alloys with improved mechanical properties.
- Zhaoxuan Wu
- & W. A. Curtin
-
Letter |
 Rejuvenation of metallic glasses by non-affine thermal strain
Rejuvenation of metallic glasses by non-affine thermal strain
This study shows that metallic glasses can be rejuvenated (taken to higher energy states with more plasticity) by thermally cycling them at relatively low temperatures (well below the glass transition temperature); this is attributed to the effect of intrinsic structural inhomogeneities in the glassy state, which translate into localized internal strains as the temperature is cycled and the different regions expand and contract by different amounts.
- S. V. Ketov
- , Y. H. Sun
- & A. L. Greer
-
Letter |
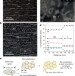 Brittle intermetallic compound makes ultrastrong low-density steel with large ductility
Brittle intermetallic compound makes ultrastrong low-density steel with large ductility
Alloying steel with aluminium improves the material’s strength-to-weight ratio, but the resulting formation of brittle intermetallic compounds within the steel matrix reduces its ductility; here the morphology and distribution of the intermetallic precipitates are controlled to alleviate this problem.
- Sang-Heon Kim
- , Hansoo Kim
- & Nack J. Kim
-
Letter |
 Enhanced reversibility and unusual microstructure of a phase-transforming material
Enhanced reversibility and unusual microstructure of a phase-transforming material
The enhanced reversibility (stable transition temperature even at high strain under a solid-to-solid phase transition), low hysteresis and unusual riverine microstructure (ranging through thermal cycles) of the martensitic material Zn45Au30Cu25 makes it attractive for applications from eco-friendly fridges to medical sensors.
- Yintao Song
- , Xian Chen
- & Richard D. James
-
Letter |
 A new anode material for oxygen evolution in molten oxide electrolysis
A new anode material for oxygen evolution in molten oxide electrolysis
Molten oxide electrolysis is considered a promising route for extractive metallurgy with much reduced carbon dioxide emissions relative to traditional routes; now a new chromium-based alloy has been developed for use as an oxygen evolving anode that remains stable in the high-temperature corrosive conditions found during iron production via electrolysis.
- Antoine Allanore
- , Lan Yin
- & Donald R. Sadoway
-
Outlook |
 Resources: Mine, all mine!
Resources: Mine, all mine!
Throughout history, gold has been prized around the world and eagerly sought. But where does it come from, and where does it all go? By Neil Savage.
- Neil Savage
-
Outlook |
 Perspective: A glint of the future
Perspective: A glint of the future
The same property that gives stained glass windows their sublime beauty is being crafted in the latest nanophotonic technologies, says Anatoly V. Zayats.
- Anatoly V. Zayats
-
Outlook |
 Photonics: Trick of the light
Photonics: Trick of the light
Invisibly small particles of gold can be used to manipulate the properties of light.
- Neil Savage
-
Outlook |
 Catalysis: The accelerator
Catalysis: The accelerator
Gold can speed up a multitude of chemical reactions — so why isn't it widely used in industry?
- Mark Peplow
-
Outlook |
 Microbiology: There's gold in them there bugs
Microbiology: There's gold in them there bugs
Microbial 'alchemy' could lead to new ways of detecting and producing the precious metal.
- Peter Gwynne
-
Outlook |
 Mining: Extreme prospects
Mining: Extreme prospects
High gold prices are making it worthwhile to look for gold in some unusual places.
- Brian Owens

 Work hardening in colloidal crystals
Work hardening in colloidal crystals