Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
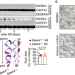 MARK4 controls ischaemic heart failure through microtubule detyrosination
MARK4 controls ischaemic heart failure through microtubule detyrosination
MARK4 regulates cardiomyocyte contractility by promoting MAP4 phosphorylation, which facilitates the access of VASH2 to microtubules for the detyrosination of α-tubulin; MARK4 deficiency after acute myocardial infarction limits the reduction in the left ventricular ejection fraction.
- Xian Yu
- , Xiao Chen
- & Xuan Li
-
Article |
 Insights into the assembly and activation of the microtubule nucleator γ-TuRC
Insights into the assembly and activation of the microtubule nucleator γ-TuRC
The cryo-EM structure of the γ-tubulin ring complex (γ-TuRC) from Xenopus laevis provides insights into the molecular organization of the complex, and shows that actin is a structural component that is functionally relevant to microtubule nucleation.
- Peng Liu
- , Erik Zupa
- & Elmar Schiebel
-
Article |
 Reconstitution reveals motor activation for intraflagellar transport
Reconstitution reveals motor activation for intraflagellar transport
Reconstitution of a functional intraflagellar transport complex in Caenorhabditis elegans provides insight into the recruitment and activation of the kinesin-2 motor protein.
- Mohamed A. A. Mohamed
- , Willi L. Stepp
- & Zeynep Ökten
-
Letter |
 Inhibition of cell expansion by rapid ABP1-mediated auxin effect on microtubules
Inhibition of cell expansion by rapid ABP1-mediated auxin effect on microtubules
In roots and dark-grown hypocotyls of Arabidopsis thaliana, ABP1-mediated auxin signalling induces swift re-orientation of the microtubule cytoskeleton from transverse to longitudinal, thus inhibiting cell expansion.
- Xu Chen
- , Laurie Grandont
- & Jiří Friml
-
Letter |
 Oncogene-like induction of cellular invasion from centrosome amplification
Oncogene-like induction of cellular invasion from centrosome amplification
Cancer cells often have extra centrosomes, a paradox considering the detrimental effect extra centrosomes usually have on cell division; a study of human cells reveals that extra centrosomes can promote cancer cell invasion phenotypes through a pathway involving increased microtubule nucleation and Rac1 activity.
- Susana A. Godinho
- , Remigio Picone
- & David Pellman
-
Letter |
 Centralspindlin links the mitotic spindle to the plasma membrane during cytokinesis
Centralspindlin links the mitotic spindle to the plasma membrane during cytokinesis
Structural and functional analysis of the centralspindlin complex shows that it connects the mitotic spindle to the plasma membrane during cytokinesis through interactions of the C1 domain of centralspindlin’s MgcRacGAP subunit with phosphoinositide lipids.
- Sergey Lekomtsev
- , Kuan-Chung Su
- & Mark Petronczki
-
News & Views |
 Swarming microtubules
Swarming microtubules
An artificial system of microtubules propelled by dynein motor proteins self-organizes into a pattern of whirling rings. This observation may provide insight into collective motion in biological systems. See Letter p.448
- Tamás Vicsek
-
Letter |
 Large-scale vortex lattice emerging from collectively moving microtubules
Large-scale vortex lattice emerging from collectively moving microtubules
Emergent collective behaviour is observed in dynein-driven microtubules and modelled by taking into account only local interactions and the reptation-like motion of individual microtubules.
- Yutaka Sumino
- , Ken H. Nagai
- & Kazuhiro Oiwa
-
Research Highlights |
The first microtubules
-
Research Highlights |
Microtubules beat in sync
-
Letter |
 Tension directly stabilizes reconstituted kinetochore-microtubule attachments
Tension directly stabilizes reconstituted kinetochore-microtubule attachments
The kinetochore is a large protein complex that assembles on centromeric DNA and captures microtubules to mediate chromosome separation. These authors report the first purification of functional kinetochores. They also show that kinetochore particles maintain load-bearing associations with assembling and disassembling ends of single microtubules and that tension increases the lifetimes of the attachments directly. These results provide evidence that tension selectively stabilises kinetochore–microtubule interactions.
- Bungo Akiyoshi
- , Krishna K. Sarangapani
- & Sue Biggins
-
Letter |
 Asterless is a scaffold for the onset of centriole assembly
Asterless is a scaffold for the onset of centriole assembly
Centrioles are essential for the formation of centrosomes, cilia and flagella. The centriolar protein Polo-like-kinase 4 (Plk4) is a key regulator of centriole biogenesis and for maintaining constant centriole number in cells. These authors show that the centriolar protein Asterless (CEP152 in humans) interacts with Plk4 and Sas-4. They find that Asl functions as a scaffold for Plk4 and Sas-4 that facilitates self-assembly and duplication of the centriole, and organization of pericentriolar material.
- Nikola S. Dzhindzhev
- , Quan D. Yu
- & David M. Glover
-
Letter |
 MEC-17 is an α-tubulin acetyltransferase
MEC-17 is an α-tubulin acetyltransferase
In eukaryotic cells, a subset of microtubules undergo post-translational modifications such as acetylation, which alters microtubule dynamics and trafficking of motors. These authors identify MEC-17 as the enzyme that directly acetylates α-tubulin in vitro and in vivo and in both invertebrates and vertebrates. This is the identification of the long-sought enzyme that acetylates microtubules.
- Jyothi S. Akella
- , Dorota Wloga
- & Jacek Gaertig
-
Letter |
 Microtubule nucleating γ-TuSC assembles structures with 13-fold microtubule-like symmetry
Microtubule nucleating γ-TuSC assembles structures with 13-fold microtubule-like symmetry
XXXMicrotubules are nucleated in vivo by γ-tubulin complexes and comprise 13 protofilaments. How this precise geometry is controlled remains unclear. These authors report the cryo-electron microscopic structure of the universally conserved, core microtubule nucleating complex, γ-tubulin small complex. The structure provides insight into how this complex establishes thirteen-fold tubulin symmetry.
- Justin M. Kollman
- , Jessica K. Polka
- & David A. Agard

 ER proteins decipher the tubulin code to regulate organelle distribution
ER proteins decipher the tubulin code to regulate organelle distribution