Featured
-
-
Article |
 Atomically precise photothermal nanomachines
Atomically precise photothermal nanomachines
Gold nanoclusters show promise as photothermal materials, but are often thermally unstable. Here ligand engineering is used to integrate molecular rotors with gold nanoclusters to dissipate thermal energy and improve photothermal therapy performance.
- Jing Chen
- , Peilin Gu
- & Chunhai Fan
-
Article |
 The exit of nanoparticles from solid tumours
The exit of nanoparticles from solid tumours
Nanoparticle retention inside tumours has been associated with lymphatic vessel collapse. It is now shown that nanoparticles exit from solid tumours through lymphatic vessels in or surrounding the tumour by a nanoparticle-size-dependent mechanism.
- Luan N. M. Nguyen
- , Zachary P. Lin
- & Warren C. W. Chan
-
Review Article |
 Hydrogels for RNA delivery
Hydrogels for RNA delivery
RNA-based therapeutics hold promise for the treatment of several diseases. This Review provides an overview of hydrogels for RNA delivery, discussing how the chemical nature and physical properties of hydrogels can be explored for tailored RNA loading and release, and highlighting the use of these materials in biomedical applications.
- Ruibo Zhong
- , Sepehr Talebian
- & Jinjun Shi
-
News & Views |
 Exploiting endothelial transcytosis to reach into the brain
Exploiting endothelial transcytosis to reach into the brain
Targeting P-selectin enables safer and more effective nanomedicine delivery through caveolin-1-mediated endothelial transcytosis in preclinical medulloblastoma tumour models.
- Lin Wang
- & Stefan Wilhelm
-
News & Views |
 Immunostimulatory nanoparticles go viral
Immunostimulatory nanoparticles go viral
A polymeric nanoparticle adjuvant containing a Toll-like receptor 7 agonist elicits broad protection against viral challenges.
- Jorge Huete-Carrasco
- & Ed C. Lavelle
-
Article
| Open Access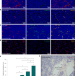 P-selectin-targeted nanocarriers induce active crossing of the blood–brain barrier via caveolin-1-dependent transcytosis
P-selectin-targeted nanocarriers induce active crossing of the blood–brain barrier via caveolin-1-dependent transcytosis
Targeting of tumour vasculature endothelial P-selectin promotes caveolin-1-mediated transcytosis for enhanced blood–brain barrier crossing of therapeutic nanoparticles against medulloblastoma.
- Daniel E. Tylawsky
- , Hiroto Kiguchi
- & Daniel A. Heller
-
Article
| Open Access A TLR7-nanoparticle adjuvant promotes a broad immune response against heterologous strains of influenza and SARS-CoV-2
A TLR7-nanoparticle adjuvant promotes a broad immune response against heterologous strains of influenza and SARS-CoV-2
A nanoparticle-based adjuvant incorporating a Toll-like receptor 7 agonist elicits cross-reactive antibodies for both dominant and subdominant epitopes and enhances immune responses against multiple variants of influenza and SARS-CoV-2.
- Qian Yin
- , Wei Luo
- & Mark M. Davis
-
Article |
 Nanoparticle-modified microrobots for in vivo antibiotic delivery to treat acute bacterial pneumonia
Nanoparticle-modified microrobots for in vivo antibiotic delivery to treat acute bacterial pneumonia
Biohybrid microrobots consisting of nanoparticle-modified microalgae are constructed for active drug delivery in the lungs. In an acute bacterial pneumonia model, the microrobots effectively reduce bacterial burden and lessen animal mortality.
- Fangyu Zhang
- , Jia Zhuang
- & Joseph Wang
-
Editorial |
 Materials at the heart of the COVID-19 pandemic
Materials at the heart of the COVID-19 pandemic
Materials scientists have played a key role in the global response to the COVID-19 pandemic from the development of vaccines and diagnostic tools to the rapid prototyping of ventilators.
-
News & Views |
 A ‘Swiss army knife’ probe for metastatic cancers
A ‘Swiss army knife’ probe for metastatic cancers
A nanosensor probe that combines a tumour-targeting peptide, a diagnostic reporter and an imaging contrast agent enables early diagnosis, precision imaging, disease stratification and downstream therapeutic response monitoring of metastatic cancer.
- Matthew Bogyo
-
Perspective |
 Obstacles and opportunities in a forward vision for cancer nanomedicine
Obstacles and opportunities in a forward vision for cancer nanomedicine
This Perspective discusses biological barriers that have limited clinical translation of cancer nanomedicines and elaborates on new directions for the field that capitalize on a deeper understanding of the nano–bio interface.
- Irene de Lázaro
- & David J. Mooney
-
News & Views |
 A nanoparticle’s pathway into tumours
A nanoparticle’s pathway into tumours
New evidence now suggests that the dominant mechanism of extravasation of nanoparticles into solid tumours may be through an active process of endothelial transcytosis.
- Irene de Lázaro
- & David J. Mooney
-
Article |
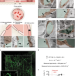 The entry of nanoparticles into solid tumours
The entry of nanoparticles into solid tumours
The dominant mechanism of nanoparticle entry into solid tumours has now been shown to be an active trans-endothelial pathway rather than the currently established passive transport via inter-endothelial gaps.
- Shrey Sindhwani
- , Abdullah Muhammad Syed
- & Warren C. W. Chan
-
News & Views |
 Materials modulate immunity and gut microbiome
Materials modulate immunity and gut microbiome
In a murine model of acute colitis, hyaluronic acid–bilirubin-based nanomaterials have been shown to modulate immune response and the gut microbiome, as well as restore the epithelial barrier.
- Ankur Singh
-
Article |
 Furin-mediated intracellular self-assembly of olsalazine nanoparticles for enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and tumour therapy
Furin-mediated intracellular self-assembly of olsalazine nanoparticles for enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and tumour therapy
An anticancer agent, olsalazine, conjugated to a cell-penetrating peptide has been synthesized and shows the ability to self-assemble intracellularly by the tumour-associated enzyme furin, with the potential for tumour therapy and chemical exchange saturation transfer magnetic resonance imaging in vivo.
- Yue Yuan
- , Jia Zhang
- & Jeff W. M. Bulte
-
Article |
 Hyaluronic acid–bilirubin nanomedicine for targeted modulation of dysregulated intestinal barrier, microbiome and immune responses in colitis
Hyaluronic acid–bilirubin nanomedicine for targeted modulation of dysregulated intestinal barrier, microbiome and immune responses in colitis
Imbalance of the gut microbiome has been implicated in numerous human diseases. Nanoparticles have now been designed to target colitis by modulating the gut microbiome, local innate immune response and restoration of the intestinal barrier function.
- Yonghyun Lee
- , Kohei Sugihara
- & James J. Moon
-
News & Views |
 Biomaterials driving repair after stroke
Biomaterials driving repair after stroke
An injectable biomaterial with angiogenic and immune-modulatory properties was developed and shown to support brain tissue repair and functional recovery in a mouse model of stroke.
- Anup Tuladhar
- & Molly S. Shoichet
-
Article |
 Designer vaccine nanodiscs for personalized cancer immunotherapy
Designer vaccine nanodiscs for personalized cancer immunotherapy
High-density lipoprotein nanodiscs loaded with immunostimulatory biomolecules can target draining lymph nodes for cancer vaccination.
- Rui Kuai
- , Lukasz J. Ochyl
- & James J. Moon
-
Article |
 Mechanism of hard-nanomaterial clearance by the liver
Mechanism of hard-nanomaterial clearance by the liver
The blood clearance mechanism, by the liver, of administered hard nanomaterials is reported in relation to blood flow dynamics, organ microarchitecture and cellular phenotype.
- Kim M. Tsoi
- , Sonya A. MacParland
- & Warren C. W. Chan
-
Article |
 Biomimetic proteolipid vesicles for targeting inflamed tissues
Biomimetic proteolipid vesicles for targeting inflamed tissues
Lipid nanoparticles incorporating proteins from the leukocyte plasma membrane retain the properties of liposomal formulations and enable delivery of drugs to inflamed tissues.
- R. Molinaro
- , C. Corbo
- & E. Tasciotti
-
Article |
 Directed migration of cancer cells guided by the graded texture of the underlying matrix
Directed migration of cancer cells guided by the graded texture of the underlying matrix
Cell migration can be directed by the gradient of nanoscale features in the underlying extracellular matrix, with the migration direction depending on the material properties of both the cell and the matrix.
- JinSeok Park
- , Deok-Ho Kim
- & Andre Levchenko
-
Letter |
 Photoexcited quantum dots for killing multidrug-resistant bacteria
Photoexcited quantum dots for killing multidrug-resistant bacteria
Light-activated quantum dots can selectively kill multidrug-resistant bacteria by altering the cellular redox environment.
- Colleen M. Courtney
- , Samuel M. Goodman
- & Prashant Nagpal
-
Review Article |
 Supramolecular biomaterials
Supramolecular biomaterials
This Review discusses the properties and applications of supramolecular biomaterials for drug delivery, tissue engineering, regenerative medicine and immunology.
- Matthew J. Webber
- , Eric A. Appel
- & Robert Langer
-
Article |
 Self-assembled RNA-triple-helix hydrogel scaffold for microRNA modulation in the tumour microenvironment
Self-assembled RNA-triple-helix hydrogel scaffold for microRNA modulation in the tumour microenvironment
Tissue-adhesive scaffolds made by the conjugation of RNA triple helices to dendrimers lead to ∼90% shrinkage of tumours two weeks after implantation in a triple-negative breast cancer mouse model.
- João Conde
- , Nuria Oliva
- & Natalie Artzi
-
Article |
 Phage-mediated counting by the naked eye of miRNA molecules at attomolar concentrations in a Petri dish
Phage-mediated counting by the naked eye of miRNA molecules at attomolar concentrations in a Petri dish
An ultrasensitive method that uses a genetically engineered bacteriophage to bind miRNA in a one-to-one manner allows the counting, by the naked eye, of miRNA molecules at attomolar concentrations on Petri dishes.
- Xin Zhou
- , Peng Cao
- & Chuanbin Mao
-
Article |
 Biodegradable silicon nanoneedles delivering nucleic acids intracellularly induce localized in vivo neovascularization
Biodegradable silicon nanoneedles delivering nucleic acids intracellularly induce localized in vivo neovascularization
Efficient in vivo cytosolic delivery of nucleic acids through cell-membrane puncturing by an array of biodegradable silicon nanoneedles induces sustained local neovascularization in muscle.
- C. Chiappini
- , E. De Rosa
- & E. Tasciotti
-
-
Editorial |
 Believing in seeing
Believing in seeing
Materials-based imaging agents are attractive candidates for a diverse range of imaging modalities and combined imaging–therapy applications, but economic implications and practical concerns remain obstacles to their clinical translation.
-
News & Views |
 Lighting up tumours
Lighting up tumours
Detection of a wide range of tumours remains a challenge in cancer diagnostics. By exploiting changes in the tumour microenvironment, a pH-responsive polymeric nanomaterial enables ultrasensitive tumour-specific imaging in many types of cancer.
- Daishun Ling
- , Michael J. Hackett
- & Taeghwan Hyeon
-
Commentary |
 A targeted approach to cancer imaging and therapy
A targeted approach to cancer imaging and therapy
Nanoparticle-based imaging plays a crucial role in cancer diagnosis and treatment. Here, we discuss the modalities used for molecular imaging of the tumour microenvironment and image-guided interventions including drug delivery, surgery and ablation therapy.
- Chun Li
-
Article |
 A nanoparticle-based strategy for the imaging of a broad range of tumours by nonlinear amplification of microenvironment signals
A nanoparticle-based strategy for the imaging of a broad range of tumours by nonlinear amplification of microenvironment signals
The imaging of tumours is challenging because of the wide range of different cancers. Now, the rapid detection of tumours, independent of type, is achieved using a nonlinear amplification strategy that employs ultrasensitive pH-responsive fluorescent nanoparticles that illuminate within tumour neovasculature or in response to the tumour’s acidic extracellular environment.
- Yiguang Wang
- , Kejin Zhou
- & Jinming Gao
-
-
-
-
Commentary |
 Strategies for advancing cancer nanomedicine
Strategies for advancing cancer nanomedicine
Cancer nanomedicines approved so far minimize toxicity, but their efficacy is often limited by physiological barriers posed by the tumour microenvironment. Here, we discuss how these barriers can be overcome through innovative nanomedicine design and through creative manipulation of the tumour microenvironment.
- Vikash P. Chauhan
- & Rakesh K. Jain
-
Commentary |
 Translating materials design to the clinic
Translating materials design to the clinic
Many materials-based therapeutic systems have reached the clinic or are in clinical trials. Here we describe materials design principles and the construction of delivery vehicles, as well as their adaptation and evaluation for human use.
- Jeffrey A. Hubbell
- & Robert Langer
-
-
News & Views |
 Death by magnetism
Death by magnetism
A magnetic on/off switch for cell-death signalling in cancer cells is developed using antibodies conjugated to magnetic nanoparticles. The control of cell death in in vivo systems is demonstrated by a tell-tale morphological change within the zebrafish.
- Jon Dobson
-
News & Views |
 Swarming towards the target
Swarming towards the target
A system comprising 'signalling' and 'receiving' modules — where the receiving module circulating in the bloodstream is directed to the tumour by a cascade triggered by the signalling module — improves the targeting effect of a nanomedicine.
- Yucai Wang
- , Paige Brown
- & Younan Xia
-
Article |
 Nanoparticles that communicate in vivo to amplify tumour targeting
Nanoparticles that communicate in vivo to amplify tumour targeting
A two-component nanoparticle system that communicates and enhances in vivo drug delivery and diagnostics has been devised. The system comprises ‘signalling’ nanoparticles that target tumours and then broadcast the tumour’s location to ’receiving’ nanoparticles in circulation, which carry therapeutic or diagnostic cargos, hence amplifying tumour targeting.
- Geoffrey von Maltzahn
- , Ji-Ho Park
- & Sangeeta N. Bhatia

 Accelerating ionizable lipid discovery for mRNA delivery using machine learning and combinatorial chemistry
Accelerating ionizable lipid discovery for mRNA delivery using machine learning and combinatorial chemistry