Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Designer phospholipid capping ligands for soft metal halide nanocrystals
Designer phospholipid capping ligands for soft metal halide nanocrystals
Phospholipids enhance the structural and colloidal integrity of hybrid organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites and lead-free metal halide nanocrystals, which then exhibit enhanced robustness and optical properties.
- Viktoriia Morad
- , Andriy Stelmakh
- & Maksym V. Kovalenko
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule electron spin resonance by means of atomic force microscopy
Single-molecule electron spin resonance by means of atomic force microscopy
By using a pump–probe atomic force microscopy detection scheme, electron spin transitions between non-equilibrium triplet states of individual pentacene molecules, as well as the ability to manipulate electron spins over tens of microseconds, is demonstrated.
- Lisanne Sellies
- , Raffael Spachtholz
- & Jascha Repp
-
Article |
 On-surface synthesis of aromatic cyclo[10]carbon and cyclo[14]carbon
On-surface synthesis of aromatic cyclo[10]carbon and cyclo[14]carbon
We provide a modified strategy for the on-surface synthesis of cyclocarbons with 10 or 14 carbon atoms that provides a route for characterizing annular carbon allotropes.
- Luye Sun
- , Wei Zheng
- & Wei Xu
-
Article |
 Adsorbate motors for unidirectional translation and transport
Adsorbate motors for unidirectional translation and transport
An adsorbate motor that moves unidirectionally on a copper surface is achieved by inducing intramolecular hydrogen transfer in a single molecule.
- Grant J. Simpson
- , Mats Persson
- & Leonhard Grill
-
Article |
 Structure evolution at the gate-tunable suspended graphene–water interface
Structure evolution at the gate-tunable suspended graphene–water interface
Using centimetre-sized substrate-free monolayer graphene suspended on aqueous electrolyte surface, the structural evolution versus gate voltage at the graphene–water interface is shown, demonstrating minimal influence of extrinsic factors.
- Ying Xu
- , You-Bo Ma
- & Chuan-Shan Tian
-
Matters Arising |
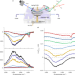 Chemistry governs water organization at a graphene electrode
Chemistry governs water organization at a graphene electrode
- Yongkang Wang
- , Takakazu Seki
- & Mischa Bonn
-
Article |
 Orbital-resolved visualization of single-molecule photocurrent channels
Orbital-resolved visualization of single-molecule photocurrent channels
Atomic-level imaging of photocurrents in a single molecule is achieved by combining a tunable laser with scanning tunnelling microscopy, revealing how photons turn into electric current via a photoexcited molecule.
- Miyabi Imai-Imada
- , Hiroshi Imada
- & Yousoo Kim
-
Article |
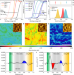 Stability-limiting heterointerfaces of perovskite photovoltaics
Stability-limiting heterointerfaces of perovskite photovoltaics
Surface treatments for the passivation of defects in perovskite solar cells have a detrimental side effect that limits the maximum stability improvement.
- Shaun Tan
- , Tianyi Huang
- & Yang Yang
-
Article |
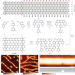 Spin splitting of dopant edge state in magnetic zigzag graphene nanoribbons
Spin splitting of dopant edge state in magnetic zigzag graphene nanoribbons
Decoupling spin-polarized edge states using substitutional N-atom dopants along the edges of a zigzag graphene nanoribbon (ZGNR) reveals giant spin splitting of a N-dopant edge state, and supports the predicted emergent magnetic order in ZGNRs.
- Raymond E. Blackwell
- , Fangzhou Zhao
- & Felix R. Fischer
-
Article |
 In situ Raman spectroscopy reveals the structure and dissociation of interfacial water
In situ Raman spectroscopy reveals the structure and dissociation of interfacial water
Interfacial water consists of hydrogen-bonded water and Na·H2O, its structure changes at hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) potentials, and when structurally ordered it aids interfacial electron transfer, resulting in higher HER rates.
- Yao-Hui Wang
- , Shisheng Zheng
- & Jian-Feng Li
-
Article |
 Observation of fractional edge excitations in nanographene spin chains
Observation of fractional edge excitations in nanographene spin chains
Using scanning tunnelling microscopy and spectroscopy, fractional edge excitations are observed in nanographene spin chains, enabling the potential to study strongly correlated phases in purely organic materials.
- Shantanu Mishra
- , Gonçalo Catarina
- & Roman Fasel
-
Article |
 Asymmetric response of interfacial water to applied electric fields
Asymmetric response of interfacial water to applied electric fields
Experimental measurements of vibrational sum-frequency generation spectra indicate that the dielectric response of water near an electrode may be strongly asymmetric, with different responses to positive and negative electrode charge.
- Angelo Montenegro
- , Chayan Dutta
- & Alexander V. Benderskii
-
Article |
 Direct assessment of the acidity of individual surface hydroxyls
Direct assessment of the acidity of individual surface hydroxyls
Non-contact atomic force microscopy measurements are used to probe the hydrogen bond strength of individual surface hydroxyl groups and determine their acidity with atomic precision.
- Margareta Wagner
- , Bernd Meyer
- & Ulrike Diebold
-
Article |
 Transporting and concentrating vibrational energy to promote isomerization
Transporting and concentrating vibrational energy to promote isomerization
Infrared absorption by a thick CO crystal produces many vibrational quanta that can be transported and concentrated at a salt interface to drive orientational isomerization of CO molecules with enhanced efficiency.
- Jascha A. Lau
- , Li Chen
- & Alec M. Wodtke
-
Article |
 Surface coordination layer passivates oxidation of copper
Surface coordination layer passivates oxidation of copper
High oxidation resistance, without degradation of thermal or electrical conductivity, is achieved in copper using surface modification by a solvothermal or electrochemical treatment with sodium formate and formation of a thin surface coordination layer.
- Jian Peng
- , Bili Chen
- & Nanfeng Zheng
-
Article |
 Sub-cycle atomic-scale forces coherently control a single-molecule switch
Sub-cycle atomic-scale forces coherently control a single-molecule switch
The near field of a terahertz wave confined to a scanning probe tip provides femtosecond atomic-scale forces that coherently modulate the switching probability of a molecule between two stable adsorption geometries.
- Dominik Peller
- , Lukas Z. Kastner
- & Jascha Repp
-
Letter |
 Selective triplet exciton formation in a single molecule
Selective triplet exciton formation in a single molecule
Recombination of excitons to produce molecular light emission is made more efficient by controlling electron spin within the molecule to produce spin-triplet excitons only, without the usual accompanying spin-singlet excitons.
- Kensuke Kimura
- , Kuniyuki Miwa
- & Yousoo Kim
-
Letter |
 Mapping orbital changes upon electron transfer with tunnelling microscopy on insulators
Mapping orbital changes upon electron transfer with tunnelling microscopy on insulators
Driving single-electron tunnelling in synchronization with the oscillations of the conductive tip of an atomic force microscope allows mapping of the electronic structure of individual molecules in different charge states.
- Laerte L. Patera
- , Fabian Queck
- & Jascha Repp
-
Letter |
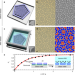 A Brownian quasi-crystal of pre-assembled colloidal Penrose tiles
A Brownian quasi-crystal of pre-assembled colloidal Penrose tiles
A lithographic patterning and release method is used to create a dense, fluctuating, Brownian system of mobile colloidal kite- and dart-shaped Penrose tiles over large areas that retains quasi-crystalline order.
- Po-Yuan Wang
- & Thomas G. Mason
-
Letter |
 A standing molecule as a single-electron field emitter
A standing molecule as a single-electron field emitter
Precision control over matter at the atomic scale enables a planar dye molecule to be lifted up and placed on its edge—a configuration that is surprisingly stable.
- Taner Esat
- , Niklas Friedrich
- & Ruslan Temirov
-
Letter |
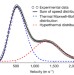 Velocity-resolved kinetics of site-specific carbon monoxide oxidation on platinum surfaces
Velocity-resolved kinetics of site-specific carbon monoxide oxidation on platinum surfaces
The catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide over platinum proceeds through two distinct channels: it is dominated at low temperatures by the more active step sites and at high temperatures by the more abundant terrace sites of the platinum surface.
- Jannis Neugebohren
- , Dmitriy Borodin
- & Theofanis N. Kitsopoulos
-
Letter |
 The effect of hydration number on the interfacial transport of sodium ions
The effect of hydration number on the interfacial transport of sodium ions
A sodium ion hydrated with three (rather than one, two, four or five) water molecules diffuses orders of magnitude more quickly than the other ion hydrates owing to the interfacial symmetry mismatch.
- Jinbo Peng
- , Duanyun Cao
- & Ying Jiang
-
Letter |
 Systems of mechanized and reactive droplets powered by multi-responsive surfactants
Systems of mechanized and reactive droplets powered by multi-responsive surfactants
Droplets covered with surfactants that respond to multiple stimuli can assemble into hierarchical assemblies or non-spherical, patchy structures, mimic systems of mechanical gears, and even harbour sequences of chemical reactions.
- Zhijie Yang
- , Jingjing Wei
- & Bartosz A. Grzybowski
-
Letter |
 Stable colloids in molten inorganic salts
Stable colloids in molten inorganic salts
A class of colloids is reported in which inorganic solute particles—such as metals and semiconductors—are dispersed in molten inorganic salts.
- Hao Zhang
- , Kinjal Dasbiswas
- & Dmitri V. Talapin
-
Letter |
 High-spatial-resolution mapping of catalytic reactions on single particles
High-spatial-resolution mapping of catalytic reactions on single particles
The chemical conversion of N-heterocyclic carbene molecules attached to catalytic particles is monitored at high spatial resolution using synchrotron-radiation-based infrared nanospectroscopy.
- Chung-Yeh Wu
- , William J. Wolf
- & Elad Gross
-
Letter |
 Tracking the ultrafast motion of a single molecule by femtosecond orbital imaging
Tracking the ultrafast motion of a single molecule by femtosecond orbital imaging
Watching a single molecule move calls for measurements that combine ultrafast temporal resolution with atomic spatial resolution; this is now shown to be possible by combining scanning tunnelling microscopy with lightwave electronics, through a technique that involves removing a single electron from the highest occupied orbital of a single pentacene molecule in a time window shorter than an oscillation cycle of light.
- Tyler L. Cocker
- , Dominik Peller
- & Rupert Huber
-
Letter |
 Surface patterning of nanoparticles with polymer patches
Surface patterning of nanoparticles with polymer patches
Surface patterning of nanoparticles with polymer patches is achieved in a poor solvent for the polymer by controlling the ratio between the sizes of polymer molecules and nanoparticles.
- Rachelle M. Choueiri
- , Elizabeth Galati
- & Eugenia Kumacheva
-
Letter |
 Continuous directional water transport on the peristome surface of Nepenthes alata
Continuous directional water transport on the peristome surface of Nepenthes alata
Insects are captured by the carnivorous plant Nepenthes alata when they ‘aquaplane’ on the wet rim, or ‘peristome’, of the plant’s pitcher organ; here it is shown that unidirectional water flow is crucial to the complete wetting of the peristome, and that the underlying mechanism involves multiscale structural features.
- Huawei Chen
- , Pengfei Zhang
- & Lei Jiang
-
Letter |
 On-surface synthesis of graphene nanoribbons with zigzag edge topology
On-surface synthesis of graphene nanoribbons with zigzag edge topology
Synthesis of atomically precise zigzag edges in graphene nanoribbons is demonstrated using a bottom-up strategy based on surface-assisted arrangement and reaction of precursor monomers; these nanoribbons have edge-localized states with large energy splittings.
- Pascal Ruffieux
- , Shiyong Wang
- & Roman Fasel
-
Letter |
 Electrostatic catalysis of a Diels–Alder reaction
Electrostatic catalysis of a Diels–Alder reaction
Theory suggests that many chemical reactions (not simply, as is often thought, redox reactions) might be catalysed by an applied electric field; experimental evidence for this is now provided from single-molecule studies of the formation of carbon–carbon bonds in a Diels–Alder reaction.
- Albert C. Aragonès
- , Naomi L. Haworth
- & Michelle L. Coote
-
Letter |
 Self-assembly of hydrogen-bonded two-dimensional quasicrystals
Self-assembly of hydrogen-bonded two-dimensional quasicrystals
Scanning tunnelling microscopy reveals that molecules of ferrocenecarboxylic acid can self-assemble into quasicrystal monolayers containing highly unusual cyclic hydrogen-bonded pentamers; this molecular framework could form the basis of a large range of supramolecular assemblies.
- Natalie A. Wasio
- , Rebecca C. Quardokus
- & S. Alex Kandel
-
Letter |
 Bonding and structure of a reconstructed (001) surface of SrTiO3 from TEM
Bonding and structure of a reconstructed (001) surface of SrTiO3 from TEM
A simple and accessible method of probing the nature of bonding on the very surface of a material is reported, using transmission electron microscopy: the technologically important compound strontium titanate is examined as an example.
- Guo-zhen Zhu
- , Guillaume Radtke
- & Gianluigi A. Botton
-
News & Views |
 Crystal cuts on the nanoscale
Crystal cuts on the nanoscale
A simple method has been developed to control the shape of nanoscale cuprous oxide crystals. Some shapes turn out to be much better than others as catalysts for a light-activated reaction.
- Peidong Yang
-
News & Views |
 Gold's enigmatic surface
Gold's enigmatic surface
Gold is not as inert as was believed — it can promote molecular synthesis. A study uses scanning tunnelling microscopy to catch gold in the act as it guides the formation of one-dimensional polymers from saturated hydrocarbons.
- Robert J. Madix
- & Cynthia M. Friend
-
News & Views |
 More than a bystander
More than a bystander
The tendency of hydrophobic surfaces to aggregate in water is often invoked to explain how biomolecules recognize and bind to each other. Water seems to have a much more active role in these processes than had been thought.
- Philip Ball
-
Letter |
 Hydrogen bonding at the water surface revealed by isotopic dilution spectroscopy
Hydrogen bonding at the water surface revealed by isotopic dilution spectroscopy
- Igor V. Stiopkin
- , Champika Weeraman
- & Alexander V. Benderskii
-
News & Views |
 Clear signals from surfaces
Clear signals from surfaces
Nuclear magnetic resonance is a versatile analytical technique, but acquiring well-resolved NMR spectra of chemical surfaces has been hard. The coming of age of a spectral enhancement method should change all that.
- Robert G. Griffin
-
Letter |
 Nanoscale scanning probe ferromagnetic resonance imaging using localized modes
Nanoscale scanning probe ferromagnetic resonance imaging using localized modes
Advances in nanomagnetics research have brought powerful applications in magnetic sensing technology, but so far no high-resolution magnetic-imaging tool is available to characterize complex, often buried, nanoscale structures. These authors have developed a scanning probe technique in which the intense, confined magnetic field of a micromagnetic probe tip is used to localize the ferromagnetic resonance mode immediately beneath the probe, and demonstrate that they can image magnetic features at a resolution of 200 nm.
- Inhee Lee
- , Yuri Obukhov
- & P. Chris Hammel
-
Letter |
 Lock and key colloids
Lock and key colloids
Many functional materials can be created by directing the assembly of colloidal particles into a desired structure. Control over particle assembly usually involves the use of molecules such as DNA that can recognize and bind each other. Here, a simple and effective alternative is described. Colloidal spheres serve as keys, and monodisperse colloidal particles with a spherical cavity as locks. These will spontaneously and reversibly bind to each other via the depletion interaction if their sizes match.
- S. Sacanna
- , W. T. M. Irvine
- & D. J. Pine
-
-
Letter |
 Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering is a powerful spectroscopy technique that can be used to study substances down to the level of single molecules. But the practical applications have been limited by the need for metal substrates with roughened surfaces or in the form of nanoparticles. Here a new approach — shell-insulated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy — is described, and its versatility demonstrated with numerous test substances.
- Jian Feng Li
- , Yi Fan Huang
- & Zhong Qun Tian
-
News & Views |
 When mica and water meet
When mica and water meet
A neat mode of operation of the atomic force microscope has been used to probe the interface between mica and water. The results help to settle a long-standing debate about the nature of this interface.
- Joost W. M. Frenken
- & Tjerk H. Oosterkamp
-
Research Highlights |
 Chemistry: Chase acid, solve maze
Chemistry: Chase acid, solve maze

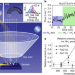 Operando probing of the surface chemistry during the Haber–Bosch process
Operando probing of the surface chemistry during the Haber–Bosch process Liquid marbles
Liquid marbles