Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A novel antibiotic class targeting the lipopolysaccharide transporter
A novel antibiotic class targeting the lipopolysaccharide transporter
A tethered macrocyclic peptide antibiotic class described here—which shows potent antibacterial activity against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii—blocks the transport of bacterial lipopolysaccharide from the inner membrane to its destination on the outer membrane through inhibition of the LptB2FGC complex.
- Claudia Zampaloni
- , Patrizio Mattei
- & Kenneth A. Bradley
-
Article |
 CD300ld on neutrophils is required for tumour-driven immune suppression
CD300ld on neutrophils is required for tumour-driven immune suppression
A CRISPR–Cas9 screen in a tumour mouse model identifies CD300ld as a tumour receptor on polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells and in vivo experiments indicate that it is a promising target for cancer immunotherapy.
- Chaoxiong Wang
- , Xichen Zheng
- & Min Luo
-
Review Article |
 From target discovery to clinical drug development with human genetics
From target discovery to clinical drug development with human genetics
This Review provides a perspective on the development of non-cancer therapies based on human genetics studies and suggests measures that can be taken to streamline the pipeline from initial genetic discovery to approved therapy.
- Katerina Trajanoska
- , Claude Bhérer
- & Vincent Mooser
-
Article |
 Conserved class B GPCR activation by a biased intracellular agonist
Conserved class B GPCR activation by a biased intracellular agonist
A study reports an orally available small-molecule agonist that binds between a G protein and its receptor, and characterizes this new binding mode.
- Li-Hua Zhao
- , Qian He
- & H. Eric Xu
-
Article |
 Tracking chromatin state changes using nanoscale photo-proximity labelling
Tracking chromatin state changes using nanoscale photo-proximity labelling
A proximity labelling-based approach for mapping nuclear protein–protein interactions is described that could advance epigenetic drug discovery.
- Ciaran P. Seath
- , Antony J. Burton
- & Tom W. Muir
-
Article |
 Inhibition of ASGR1 decreases lipid levels by promoting cholesterol excretion
Inhibition of ASGR1 decreases lipid levels by promoting cholesterol excretion
Inhibiting the asialoglycoprotein receptor ASGR1 increases cholesterol excretion to the bile and then faeces, providing a unique way to lower cholesterol, and therefore providing a safe and effective way to treat cardiovascular disease.
- Ju-Qiong Wang
- , Liang-Liang Li
- & Bao-Liang Song
-
Article |
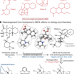 Synthesis and target annotation of the alkaloid GB18
Synthesis and target annotation of the alkaloid GB18
A synthetic route to GB18, an alkaloid from the bark of hallucinogenic Galbulimima sp., is developed, enabling its identification as an antagonist of κ- and μ-opioid receptors.
- Stone Woo
- & Ryan A. Shenvi
-
Article
| Open Access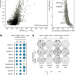 CCNE1 amplification is synthetic lethal with PKMYT1 kinase inhibition
CCNE1 amplification is synthetic lethal with PKMYT1 kinase inhibition
Genome-scale CRISPR–Cas9-based synthetic lethality screens identify PKMYT1 as a potential therapeutic target in tumours with CCNE1 amplification.
- David Gallo
- , Jordan T. F. Young
- & Daniel Durocher
-
Article |
 A pan-serotype dengue virus inhibitor targeting the NS3–NS4B interaction
A pan-serotype dengue virus inhibitor targeting the NS3–NS4B interaction
The small molecule JNJ-A07 interferes with the interaction between the NS3 and NS4B proteins of dengue virus and reduces the viral load in mice even when first administered at peak viraemia.
- Suzanne J. F. Kaptein
- , Olivia Goethals
- & Johan Neyts
-
Article |
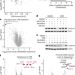 The CDK inhibitor CR8 acts as a molecular glue degrader that depletes cyclin K
The CDK inhibitor CR8 acts as a molecular glue degrader that depletes cyclin K
The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor CR8 acts as a molecular glue compound by inducing the formation of a complex between CDK12–cyclin K and DDB1, which results in the ubiquitination and degradation of cyclin K.
- Mikołaj Słabicki
- , Zuzanna Kozicka
- & Benjamin L. Ebert
-
Article |
 A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing
A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing
A human–SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map highlights cellular processes that are hijacked by the virus and that can be targeted by existing drugs, including inhibitors of mRNA translation and predicted regulators of the sigma receptors.
- David E. Gordon
- , Gwendolyn M. Jang
- & Nevan J. Krogan
-
Article |
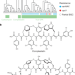 Evolution-guided discovery of antibiotics that inhibit peptidoglycan remodelling
Evolution-guided discovery of antibiotics that inhibit peptidoglycan remodelling
The glycopeptide antibiotic-related compounds complestatin and corbomycin function by binding to peptidoglycan and blocking the action of autolysins—peptidoglycan hydrolase enzymes that remodel the cell wall during growth.
- Elizabeth J. Culp
- , Nicholas Waglechner
- & Gerard D. Wright
-
Article |
 A new antibiotic selectively kills Gram-negative pathogens
A new antibiotic selectively kills Gram-negative pathogens
Bacterial symbionts of animals may contain antibiotics that are particularly suitable for development into therapeutics; one such compound, darobactin, is active against important Gram-negative pathogens both in vitro and in animal models of infection.
- Yu Imai
- , Kirsten J. Meyer
- & Kim Lewis
-
Article |
 Chimeric peptidomimetic antibiotics against Gram-negative bacteria
Chimeric peptidomimetic antibiotics against Gram-negative bacteria
A class of chimeric synthetic antibiotics that bind to lipopolysaccharide and BamA shows potent activity against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria, with the potential to address life-threatening infections.
- Anatol Luther
- , Matthias Urfer
- & Daniel Obrecht
-
Article |
 Large-scale chemical–genetics yields new M. tuberculosis inhibitor classes
Large-scale chemical–genetics yields new M. tuberculosis inhibitor classes
A high-throughput chemical–genetic screening approach for the discovery of targets and chemicals to treat Mycobacterium tuberculosis yields tenfold more hit compounds than conventional whole-cell screening methods.
- Eachan O. Johnson
- , Emily LaVerriere
- & Deborah T. Hung
-
Review Article |
 Challenges and recent progress in drug discovery for tropical diseases
Challenges and recent progress in drug discovery for tropical diseases
- Manu De Rycker
- , Beatriz Baragaña
- & Ian H. Gilbert
-
Letter |
 Accumulation of 8,9-unsaturated sterols drives oligodendrocyte formation and remyelination
Accumulation of 8,9-unsaturated sterols drives oligodendrocyte formation and remyelination
Many small molecules that stimulate oligodendrocyte formation act not through their canonical pathways but by inhibiting enzymes within the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway and thereby inducing the accumulation of 8,9-unsaturated sterols.
- Zita Hubler
- , Dharmaraja Allimuthu
- & Drew J. Adams
-
Letter |
 Structure of the insulin receptor–insulin complex by single-particle cryo-EM analysis
Structure of the insulin receptor–insulin complex by single-particle cryo-EM analysis
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of insulin in a complex with the insulin receptor define the S2 binding site on the receptor and suggest a mechanism for downstream propagation of insulin signalling.
- Giovanna Scapin
- , Venkata P. Dandey
- & Bridget Carragher
-
Article |
 Alcohol-abuse drug disulfiram targets cancer via p97 segregase adaptor NPL4
Alcohol-abuse drug disulfiram targets cancer via p97 segregase adaptor NPL4
Disulfiram is metabolized into copper–diethyldithiocarbamate, which binds to NPL4 and induces its aggregation in cells, leading to blockade of the p97–NPL4–UFD1 pathway and induction of a complex cellular phenotype that results in cell death.
- Zdenek Skrott
- , Martin Mistrik
- & Jiri Bartek
-
Letter |
 Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase prevents diabetic retinopathy
Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase prevents diabetic retinopathy
A product of the soluble epoxide hydrolase enzyme, 19,20-dihydroxydocosapentaenoic acid (19,20-DHDP), is implicated in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy; levels of 19,20-DHDP increase in the retinas of mice and humans with diabetes, and inhibition of its production can rescue vascular abnormalities in a mouse model of the disease.
- Jiong Hu
- , Sarah Dziumbla
- & Ingrid Fleming
-
Letter |
 IL-11 is a crucial determinant of cardiovascular fibrosis
IL-11 is a crucial determinant of cardiovascular fibrosis
Fibroblast-specific Il-11 expression causes heart and kidney fibrosis and organ failure, whereas IL-11 inhibition prevents fibroblast activation and organ fibrosis, indicating that IL-11 inhibition is a potential therapeutic strategy to treat fibrotic diseases.
- Sebastian Schafer
- , Sivakumar Viswanathan
- & Stuart A. Cook
-
Article |
 In vivo CRISPR screening identifies Ptpn2 as a cancer immunotherapy target
In vivo CRISPR screening identifies Ptpn2 as a cancer immunotherapy target
In vivo CRISPR screening reveals that loss of Ptpn2 increases the response of tumour cells to immunotherapy and increases IFNγ signalling, suggesting that PTPN2 inhibition may potentiate the effect of immunotherapies that invoke an IFNγ response.
- Robert T. Manguso
- , Hans W. Pope
- & W. Nicholas Haining
-
Letter |
 Selective depletion of uropathogenic E. coli from the gut by a FimH antagonist
Selective depletion of uropathogenic E. coli from the gut by a FimH antagonist
Both F17-like and type 1 pili promote intestinal colonization in mouse colonic crypts, and the high-affinity mannoside M4284 reduces intestinal colonization of uropathogenic Escherichia coli while simultaneously treating urinary tract infections without disrupting the composition of the gut microbiota.
- Caitlin N. Spaulding
- , Roger D. Klein
- & Scott J. Hultgren
-
Letter |
 Transcription control by the ENL YEATS domain in acute leukaemia
Transcription control by the ENL YEATS domain in acute leukaemia
ENL, identified in a genome-scale loss-of-function screen as a crucial requirement for proliferation of acute leukaemia, is required for leukaemic gene expression, and its YEATS chromatin-reader domain is essential for leukaemic growth.
- Michael A. Erb
- , Thomas G. Scott
- & James E. Bradner
-
Letter |
 Genomic deletion of malic enzyme 2 confers collateral lethality in pancreatic cancer
Genomic deletion of malic enzyme 2 confers collateral lethality in pancreatic cancer
Depletion of malic enzyme 3 in pancreatic cancer cells that have a deletion of the gene for malic enzyme 2 selectively kills the cells, suggesting that the enzyme might represent a therapeutic target for this subset of cancers.
- Prasenjit Dey
- , Joelle Baddour
- & Ronald A. DePinho
-
Article |
 Correcting mitochondrial fusion by manipulating mitofusin conformations
Correcting mitochondrial fusion by manipulating mitofusin conformations
Specific intramolecular interactions of mitofusin 2 amino acid sequences either constrain or permit mitochondrial fusion and the addition of short peptides matching these sequences stabilize the fusion-constrained or fusion-permissive form, thus inhibiting or promoting mitochondrial fusion.
- Antonietta Franco
- , Richard N. Kitsis
- & Gerald W. Dorn II
-
Letter |
 Proteasome inhibition for treatment of leishmaniasis, Chagas disease and sleeping sickness
Proteasome inhibition for treatment of leishmaniasis, Chagas disease and sleeping sickness
A selective inhibitor of the kinetoplastid proteasome (GNF6702) is identified that is highly efficacious in vivo, clearing the parasites that cause leishmaniasis, Chagas disease and sleeping sickness from mice, highlighting the possibility of developing a single class of drugs for these neglected diseases.
- Shilpi Khare
- , Advait S. Nagle
- & Frantisek Supek
-
Letter |
 CD47-blocking antibodies restore phagocytosis and prevent atherosclerosis
CD47-blocking antibodies restore phagocytosis and prevent atherosclerosis
Atherosclerotic lesions in mice and humans switch on a ‘don’t eat me’ signal—expression of CD47—that prevents effective removal of diseased tissue; anti-CD47 antibody therapy can normalize this defective efferocytosis, with beneficial results in several mouse models of atherosclerosis.
- Yoko Kojima
- , Jens-Peter Volkmer
- & Nicholas J. Leeper
-
Article |
 A novel cereblon modulator recruits GSPT1 to the CRL4CRBN ubiquitin ligase
A novel cereblon modulator recruits GSPT1 to the CRL4CRBN ubiquitin ligase
This paper reports the identification of a new cereblon-modulating agent, CC-885, which targets the translation termination factor GSPT1 and demonstrates anti-tumour activity in patient-derived tumour cells; the crystal structure of the cereblon–DDB1–GSPT1–CC-885 complex reveals a common motif for cereblon-substrate recruitment.
- Mary E. Matyskiela
- , Gang Lu
- & Philip P. Chamberlain
-
Letter |
 Mediator kinase inhibition further activates super-enhancer-associated genes in AML
Mediator kinase inhibition further activates super-enhancer-associated genes in AML
A small-molecule inhibitor of the Mediator-associated kinases CDK8 and CDK19 inhibits growth of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) cells and induces upregulation of super-enhancer-associated genes with tumour suppressor and lineage-controlling functions; Mediator kinase inhibition therefore represents a promising therapeutic approach for AML.
- Henry E. Pelish
- , Brian B. Liau
- & Matthew D. Shair
-
Article |
 A novel multiple-stage antimalarial agent that inhibits protein synthesis
A novel multiple-stage antimalarial agent that inhibits protein synthesis
The description of a compound (DDD107498) with antimalarial activity against multiple life-cycle stages of Plasmodium falciparum and good pharmacokinetic and safety properties, with potential for single-dose treatment, chemoprotection and prevention of transmission.
- Beatriz Baragaña
- , Irene Hallyburton
- & Ian H. Gilbert
-
Article |
 A new antibiotic kills pathogens without detectable resistance
A new antibiotic kills pathogens without detectable resistance
From a new species of β-proteobacteria, an antibiotic called teixobactin that does not generate resistance has been characterized; the antibiotic has two different lipid targets in different bacterial cell wall synthesis components, which may explain why resistance was not observed.
- Losee L. Ling
- , Tanja Schneider
- & Kim Lewis
-
Letter |
 Targeting transcription regulation in cancer with a covalent CDK7 inhibitor
Targeting transcription regulation in cancer with a covalent CDK7 inhibitor
Here, a covalent inhibitor targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) demonstrates in vitro and in vivo efficacy against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by downregulating oncogenic transcriptional programs.
- Nicholas Kwiatkowski
- , Tinghu Zhang
- & Nathanael S. Gray
-
Outlook |
 Nanotechnology: Deliver on a promise
Nanotechnology: Deliver on a promise
Effective treatment of cancer requires getting the drugs precisely to the target. Enter the nanoparticle.
- Jessica Wright
-
Letter |
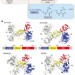 Ribosomal oxygenases are structurally conserved from prokaryotes to humans
Ribosomal oxygenases are structurally conserved from prokaryotes to humans
Crystal structures of human and prokaryotic ribosomal oxygenases reported here, with and without their ribosomal protein substrates, support their assignments as hydroxylases, and provide insights into the evolution of the JmjC-domain-containing hydroxylases and demethylases.
- Rasheduzzaman Chowdhury
- , Rok Sekirnik
- & Christopher J. Schofield
-
Letter |
 Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase knockdown protects against diet-induced obesity
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase knockdown protects against diet-induced obesity
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT) expression is increased in white adipose tissue and liver of obese and diabetic mice, Nnmt knockdown protects against diet-induced obesity by altering the availability of adipose S-adenosylmethionine and NAD+, rendering Nnmt a novel target for treating obesity and type 2 diabetes.
- Daniel Kraus
- , Qin Yang
- & Barbara B. Kahn
-
Article |
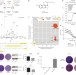 Stereospecific targeting of MTH1 by (S)-crizotinib as an anticancer strategy
Stereospecific targeting of MTH1 by (S)-crizotinib as an anticancer strategy
A chemoproteomic screen is used here to identify MTH1 as the target of SCH51344, an experimental RAS-dependent cancer drug; a further search for inhibitors revealed (S)-crizotinib as a potent MTH1 antagonist, which suppresses tumour growth in animal models of colon cancer, and could be part of a new class of anticancer drugs.
- Kilian V. M. Huber
- , Eidarus Salah
- & Giulio Superti-Furga
-
Article |
 FMRP targets distinct mRNA sequence elements to regulate protein expression
FMRP targets distinct mRNA sequence elements to regulate protein expression
RNA-recognition elements are identified for the fragile-X-syndrome-associated RNA-binding protein FMRP, in addition to its target messenger RNAs; although many of FMRP gene targets discovered are involved in brain function and autism spectrum disorder, a proportion are also dysregulated in mouse ovaries, suggesting cross-regulation of signalling pathways in different tissues.
- Manuel Ascano
- , Neelanjan Mukherjee
- & Thomas Tuschl
-
Letter |
 COUP-TFII inhibits TGF-β-induced growth barrier to promote prostate tumorigenesis
COUP-TFII inhibits TGF-β-induced growth barrier to promote prostate tumorigenesis
A cell-autonomous role for the COUP-TFII transcription factor in prostate cancer cells is identified, in which COUP-TFII inhibits TGF-β signalling by binding to SMAD4; COUP-TFII promotes prostate tumorigenesis and metastasis in a mouse model, and is associated with more aggressive disease in human prostate cancers.
- Jun Qin
- , San-Pin Wu
- & Sophia Y. Tsai
-
Letter |
 The TEL patch of telomere protein TPP1 mediates telomerase recruitment and processivity
The TEL patch of telomere protein TPP1 mediates telomerase recruitment and processivity
Using separation-of-function mutations of TPP1 that inhibit telomerase binding while maintaining telomere capping, a region on the surface of TPP1, the TEL patch, is identified and found to be required for both binding telomerase and enhancing its processivity.
- Jayakrishnan Nandakumar
- , Caitlin F. Bell
- & Thomas R. Cech
-
Letter |
 Black mamba venom peptides target acid-sensing ion channels to abolish pain
Black mamba venom peptides target acid-sensing ion channels to abolish pain
A new class of peptides, mambalgins, is isolated from the African snake the black mamba, which can abolish pain through inhibition of particular subtypes of acid-sensing ion channels expressed either in central or peripheral neurons.
- Sylvie Diochot
- , Anne Baron
- & Eric Lingueglia
-
Letter
| Open Access Recurrent R-spondin fusions in colon cancer
Recurrent R-spondin fusions in colon cancer
Exomes, transcriptomes and copy-number alterations in a sample of more than 70 primary human colonic tumours were analysed in an attempt to characterize the genomic landscape; in addition to finding alterations in genes associated with commonly mutated signalling pathways, recurrent gene fusions involving R-spondin family members were also found to occur in approximately 10% of colonic tumours, revealing a potential new therapeutic target.
- Somasekar Seshagiri
- , Eric W. Stawiski
- & Frederic J. de Sauvage
-
Research Highlights |
New target for melanoma fight
-
Article |
 Large-scale prediction and testing of drug activity on side-effect targets
Large-scale prediction and testing of drug activity on side-effect targets
A large-scale computational effort is used to predict the activity of 656 drugs against 73 protein targets that have been associated with adverse drug reactions; the abdominal pain side effect of the synthetic oestrogen chlorotrianisene is shown to be mediated through its inhibition of cyclooxygenase-1.
- Eugen Lounkine
- , Michael J. Keiser
- & Laszlo Urban
-
Research Highlights |
Blocking tumour sugar metabolism
-
News & Views |
The path to retinoblastoma
Genomic analyses of tumours of the childhood cancer retinoblastoma reveal a low mutation rate, challenging the view that genomic instability is crucial for its progression. The work also identifies a new therapeutic target. See Article p.329
- Julien Sage
- & Michael L. Cleary
-
Research Highlights |
Gene signature links to drug target
-
Letter |
 Small molecule inhibitors reveal Niemann–Pick C1 is essential for Ebola virus infection
Small molecule inhibitors reveal Niemann–Pick C1 is essential for Ebola virus infection
- Marceline Côté
- , John Misasi
- & James Cunningham
-
Letter |
 RNAi screen identifies Brd4 as a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukaemia
RNAi screen identifies Brd4 as a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukaemia
- Johannes Zuber
- , Junwei Shi
- & Christopher R. Vakoc

 Metabolic rewiring promotes anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids
Metabolic rewiring promotes anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids