Analysis
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access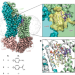 A new antibiotic traps lipopolysaccharide in its intermembrane transporter
A new antibiotic traps lipopolysaccharide in its intermembrane transporter
A mechanism of lipid transport inhibition has been identified for a class of peptide antibiotics effective against resistant Acinetobacter strains, which may have applications in the inhibition of other Gram-negative pathogens.
- Karanbir S. Pahil
- , Morgan S. A. Gilman
- & Daniel Kahne
-
Article |
 Mechanisms and inhibition of Porcupine-mediated Wnt acylation
Mechanisms and inhibition of Porcupine-mediated Wnt acylation
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of human Porcupine in complex with palmitoleoyl-coenzyme A, the inhibitor LGK974 and its peptide substrate suggest a mechanism for Wnt acylation.
- Yang Liu
- , Xiaofeng Qi
- & Xiaochun Li
-
Article
| Open Access A TMPRSS2 inhibitor acts as a pan-SARS-CoV-2 prophylactic and therapeutic
A TMPRSS2 inhibitor acts as a pan-SARS-CoV-2 prophylactic and therapeutic
A small-molecule inhibitor of TMPRSS2 is effective against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in human lung cells and in donor-derived colonoids, and also shows prophylactic and therapeutic benefits in a mouse model of COVID-19.
- Tirosh Shapira
- , I. Abrrey Monreal
- & François Jean
-
Article |
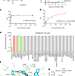 Small-molecule inhibition of METTL3 as a strategy against myeloid leukaemia
Small-molecule inhibition of METTL3 as a strategy against myeloid leukaemia
Treatment with a specific inhibitor of the N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase METTL3 leads to reduced growth of cancer cells, indicating the potential of approaches targeting RNA-modifying enzymes for anticancer therapy.
- Eliza Yankova
- , Wesley Blackaby
- & Tony Kouzarides
-
Article |
 Clinical targeting of HIV capsid protein with a long-acting small molecule
Clinical targeting of HIV capsid protein with a long-acting small molecule
The small molecule GS-6207, which disrupts the function of the HIV capsid protein, shows potential as a long-acting therapeutic agent for the treatment and prevention of HIV infection.
- John O. Link
- , Martin S. Rhee
- & Tomas Cihlar
-
Article |
 Suppression of proteolipid protein rescues Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease
Suppression of proteolipid protein rescues Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease
In a mouse model of the leukodystrophy Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease, myelination, motor performance, respiratory function and lifespan are improved by suppressing proteolipid protein expression, suggesting PLP1 as a therapeutic target for human patients with this disease and, more broadly, antisense oligonucleotides as a pharmaceutical modality for treatment of myelin disorders.
- Matthew S. Elitt
- , Lilianne Barbar
- & Paul J. Tesar
-
Analysis
| Open Access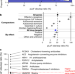 Evaluating drug targets through human loss-of-function genetic variation
Evaluating drug targets through human loss-of-function genetic variation
Analysis of predicted loss-of-function variants from 125,748 human exomes and 15,708 whole genomes in the Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD) provides a roadmap for human ‘knockout’ studies and a guide for future research into disease biology and drug-target selection.
- Eric Vallabh Minikel
- , Konrad J. Karczewski
- & Daniel G. MacArthur
-
Article |
 Structure of nevanimibe-bound tetrameric human ACAT1
Structure of nevanimibe-bound tetrameric human ACAT1
The structure of human ACAT1 in complex with the inhibitor nevanimibe is resolved by cryo-electron microscopy.
- Tao Long
- , Yingyuan Sun
- & Xiaochun Li
-
Article |
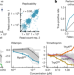 Large-scale chemical–genetics yields new M. tuberculosis inhibitor classes
Large-scale chemical–genetics yields new M. tuberculosis inhibitor classes
A high-throughput chemical–genetic screening approach for the discovery of targets and chemicals to treat Mycobacterium tuberculosis yields tenfold more hit compounds than conventional whole-cell screening methods.
- Eachan O. Johnson
- , Emily LaVerriere
- & Deborah T. Hung
-
Letter |
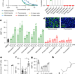 Accumulation of 8,9-unsaturated sterols drives oligodendrocyte formation and remyelination
Accumulation of 8,9-unsaturated sterols drives oligodendrocyte formation and remyelination
Many small molecules that stimulate oligodendrocyte formation act not through their canonical pathways but by inhibiting enzymes within the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway and thereby inducing the accumulation of 8,9-unsaturated sterols.
- Zita Hubler
- , Dharmaraja Allimuthu
- & Drew J. Adams
-
Letter |
 Resistance-gene-directed discovery of a natural-product herbicide with a new mode of action
Resistance-gene-directed discovery of a natural-product herbicide with a new mode of action
Fungal genome mining targeted to self-resistance genes close to biosynthetic gene clusters identifies a pathway that produces aspterric acid, which proves to be a potent inhibitor of plant growth.
- Yan Yan
- , Qikun Liu
- & Yi Tang
-
Article |
 Genomic atlas of the human plasma proteome
Genomic atlas of the human plasma proteome
A genetic atlas of the human plasma proteome, comprising 1,927 genetic associations with 1,478 proteins, identifies causes of disease and potential drug targets.
- Benjamin B. Sun
- , Joseph C. Maranville
- & Adam S. Butterworth
-
Article |
 Structural basis for dual-mode inhibition of the ABC transporter MsbA
Structural basis for dual-mode inhibition of the ABC transporter MsbA
Crystal structures of the ABC transporter MsbA in complex with two selective small-molecule antagonists reveal an unprecedented allosteric mechanism of inhibition.
- Hoangdung Ho
- , Anh Miu
- & Christopher M. Koth
-
Letter |
 Discovery of a selective catalytic p300/CBP inhibitor that targets lineage-specific tumours
Discovery of a selective catalytic p300/CBP inhibitor that targets lineage-specific tumours
A potent and selective catalytic inhibitor of p300/CBP histone acetyltransferases suppresses tumour proliferation across multiple cell lineages, illustrating the therapeutic potential of drug-like small molecules that target histone acetyltransferases.
- Loren M. Lasko
- , Clarissa G. Jakob
- & Kenneth D. Bromberg
-
Letter |
 On-target efficacy of a HIF-2α antagonist in preclinical kidney cancer models
On-target efficacy of a HIF-2α antagonist in preclinical kidney cancer models
The small-molecule HIF-2α antagonist PT2399 causes tumour regression in animal models of clear cell renal cell carcinoma, but cell lines of this tumour type show unexpectedly variable responses to PT2399.
- Hyejin Cho
- , Xinlin Du
- & William G. Kaelin
-
Letter |
 Proteasome inhibition for treatment of leishmaniasis, Chagas disease and sleeping sickness
Proteasome inhibition for treatment of leishmaniasis, Chagas disease and sleeping sickness
A selective inhibitor of the kinetoplastid proteasome (GNF6702) is identified that is highly efficacious in vivo, clearing the parasites that cause leishmaniasis, Chagas disease and sleeping sickness from mice, highlighting the possibility of developing a single class of drugs for these neglected diseases.
- Shilpi Khare
- , Advait S. Nagle
- & Frantisek Supek
-
Letter |
 Inhibiting fungal multidrug resistance by disrupting an activator–Mediator interaction
Inhibiting fungal multidrug resistance by disrupting an activator–Mediator interaction
A small molecule, inhibitor of a protein–protein interaction between the transcription factor Pdr1 and the Med15 subunit of Mediator in the fungal pathogen Candida glabrata, is identified and characterized here; the compound iKIX1 inhibits Pdr1-mediated gene activation and resensitizes drug-resistant C. glabrata to azole antifungals in vitro and in animal models of disseminated and urinary tract infection.
- Joy L. Nishikawa
- , Andras Boeszoermenyi
- & Haribabu Arthanari
-
Letter |
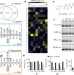 Structure- and function-based design of Plasmodium-selective proteasome inhibitors
Structure- and function-based design of Plasmodium-selective proteasome inhibitors
Structural and functional characterizations show that the specificity of the Plasmodium falciparum proteasome is sufficiently unique from that of the human proteasome to allow selective targeting with inhibitors.
- Hao Li
- , Anthony J. O’Donoghue
- & Matthew Bogyo
-
Article |
 Selective small-molecule inhibition of an RNA structural element
Selective small-molecule inhibition of an RNA structural element
A novel drug, ribocil, is shown to mimic the binding of a natural ligand to a bacterial riboflavin riboswitch (a non-coding stretch of messenger RNA whose structure is affected by a ligand—usually one related to the function of the protein encoded by the messenger RNA) to cause inhibition of bacterial growth; the ability to target an RNA structural element with a synthetic small molecule may expand our view of the target space susceptible to therapeutic intervention.
- John A. Howe
- , Hao Wang
- & Terry Roemer
-
Article |
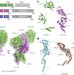 Structural integration in hypoxia-inducible factors
Structural integration in hypoxia-inducible factors
This study describes the long-awaited crystal structures for hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) heterodimers, including complexes bound to small molecules and DNA; the HIF–ARNT architecture is distinct from the bHLH-PAS-containing CLOCK–BMAL1 heterodimer, and HIF mutations linked to cancer can be mapped to important structural regions, with the structures providing future reference for small-molecule drug discovery efforts.
- Dalei Wu
- , Nalini Potluri
- & Fraydoon Rastinejad
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Inhibition of demethylases by GSK-J1/J4
Inhibition of demethylases by GSK-J1/J4
- Bo Heinemann
- , Jesper Morten Nielsen
- & Kristian Helin
-
Brief Communications Arising |
Kruidenier et al. reply
- Laurens Kruidenier
- , Chun-wa Chung
- & David M. Wilson
-
Outlook |
 Nanotechnology: Deliver on a promise
Nanotechnology: Deliver on a promise
Effective treatment of cancer requires getting the drugs precisely to the target. Enter the nanoparticle.
- Jessica Wright
-
Article |
 Cell death by pyroptosis drives CD4 T-cell depletion in HIV-1 infection
Cell death by pyroptosis drives CD4 T-cell depletion in HIV-1 infection
Quiescent CD4 T cells in lymphoid tissues are shown to die after HIV-1 infection by caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis, a highly inflammatory form of programmed cell death; caspase 1 inhibitors, which are safe for human use, can rescue the cell death in vitro raising the possibility of new therapeutics targeting the host instead of the virus.
- Gilad Doitsh
- , Nicole L. K. Galloway
- & Warner C. Greene
-
Article |
 Targeting Plasmodium PI(4)K to eliminate malaria
Targeting Plasmodium PI(4)K to eliminate malaria
The lipid kinase phosphatidylinositol-4-OH kinase (PI(4)K) is identified as a target of the imidazopyrazines, a new antimalarial compound class that can inhibit several Plasmodium species at each stage of the parasite life cycle; the imidazopyrazines exert their inhibitory action by interacting with the ATP-binding pocket of PI(4)K.
- Case W. McNamara
- , Marcus C. S. Lee
- & Elizabeth A. Winzeler
-
Letter |
 Structure of the proton-gated urea channel from the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori
Structure of the proton-gated urea channel from the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori
The crystal structure of the inner-membrane urea channel HpUreI from Helicobacter pylori, the causative organism of peptic ulcers, reveals how the channel selectively transports urea across the membrane and buffers the pathogen’s periplasmic pH against the acidic gastric environment.
- David Strugatsky
- , Reginald McNulty
- & Hartmut Luecke

 Refining the impact of genetic evidence on clinical success
Refining the impact of genetic evidence on clinical success