Abstract
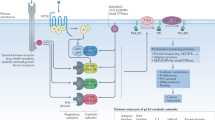
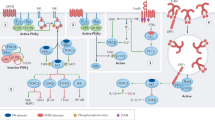
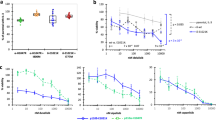
The γ isoform of Class I PI3Ks (PI3Kγ) is primarily found in leukocytes and is essential for the function of myeloid cells, as it regulates the migration, differentiation, and activation of myeloid-lineage immune cells. Thus, PI3Kγ has been identified as a promising drug target for the treatment of inflammation, autoimmune disease, and immuno-oncology. Due to the high incidence of serious adverse events (AEs) associated with PI3K inhibitors, in the development of PI3Kγ inhibitors, isoform selectivity was deemed crucial. In this review, an overview of the development of PI3Kγ selective inhibitors in the past years is provided. The isoform selectivity of related drugs was achieved by different strategies, including inducing a specificity pocket by a propeller-shape structure, targeting steric differences in the solvent channel, and modulating the conformation of the Asp-Phe-Gly DFG motif, which have been demonstrated feasible by several successful cases. The insights in this manuscript may provide a potential direction for rational drug design and accelerate the discovery of PI3Kγ selective inhibitors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thorpe LM, Yuzugullu H, Zhao JJ. PI3K in cancer: divergent roles of isoforms, modes of activation and therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15:7–24.
Ma X, Hu Y. Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR cascade: the medicinal potential, updatedresearch highlights and challenges ahead. Curr Med Chem. 2013;20:2991–3010.
Jr PJ, Janku, F. Molecular targets for cancer therapy in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;142:164–75.
Yap TA, Bjerke L, Clarke PA, Workman P. Drugging PI3K in cancer: refining targets and therapeutic strategies. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2015;23:98–107.
Janku F. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway inhibitors in solid tumors: from laboratory to patients. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017;59:93–101.
Stark AK, Sriskantharajah S, Hessel EM, Okkenhaug K. PI3K inhibitors in inflammation, autoimmunity and cancer. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2015;23:82–91.
Krish P, Pagel JM. Exploring a future for PI3K inhibitors in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2019;14:292–301.
Hashemzadeh K, Jokar MH, Sedighi S, Moradzadeh M. Therapeutic potency of PI3K pharmacological inhibitors of gastrointestinal cancer. Middle East J Dig Dis. 2018;11:5–16.
Elmenier FM, Lasheen DS, Abouzid KAM. Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K) inhibitors as new weapon to combat cancer. Eur J Med Chem. 2019;183:111718.
Wullenkord R, Friedrichs B, Erdmann T, Lenz G. Therapeutic potential of pi3k signaling in distinct entities of b-cell lymphoma. Expert Rev Hematol. 2019;12:1053–62.
Markhan A. Alpelisib: first global approval. Drugs. 2019;79:1249–53.
Flinn IW, Kahl BS, Leonard JP, Furman RR, Brown JR, Byrd JC, et al. Idelalisib, an inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol3-kinase p110δ, for relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2014;123:3406–13.
Fowler NH, Samaniego F, Jurczak W, Ghosh N, Derenzini E, Reeves JA, et al. Umbralisib, a dual PI3Kδ/CK1ε inhibitor in patients with relapsed or refractory indolent lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:1609–18.
Wee S, Wiederschain D, Maira S, Loo A, Miller C, deBeaumont, et al. PTEN-deficient cancers depend on PIK3CB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:13057–62.
Lynch JT, Polanska UM, Delpuech O, Hancox U, Trinidad AG, Michopoulos F, et al. Inhibiting PI3Kβ with AZD8186 regulates key metabolic pathways in PTEN-null tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:7584–95.
Wymann MP, Pirola L. Structure and function of phosphoinositide 3-kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 1998;1436:127–50.
Wymann MP, Björklöf K, Calvez R, Finan P, Thomast M, Trifilieff A, et al. Phosphoinositide 3‐kinase gamma: a key modulator in inflammation and allergy. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31:275–80.
Lanahan SM, Wymann MP, Lucas CL. The role of PI3Kγ in the immune system: new insights and translational implications. Nat Rev Immunol. 2022;22:687–700.
Takeda AJ, Maher TJ, Zhang Y, Lanahan SM, Bucklin ML, Compton SR, et al. Human PI3Kgamma deficiency and its microbiota-dependent mouse model reveal immunodeficiency and tissue immunopathology. Nat Commun. 2019;10:4364.
Rommel C, Camps M, Ji H. PI3Kδ and PI3Kγ: partners in crime in inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis and beyond? Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:191–201.
Kaneda MM, Messer KS, Ralainirina N, Li HY, Leem CJ, Gorjestani S, et al. PI3Kγ is a molecular switch that controls immune suppression. Nature. 2016;539:437–42.
Li H, Park D, Abdul-Muneer PM, Xu B, Wang H, Xing B, et al. PI3Kγ inhibition alleviates symptoms and increases axon number in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice. Neuroscience. 2013;253:89–99.
Perino A, Ghigo A, Ferrero E, Morello F, Santulli G, Baille GS, et al. Integrating cardiac PIP(3) and cAMP signaling through a PKA anchoring function of p110gamma. Mol Cell. 2011;42:84–95.
Collier PN, Messersmith D, Le Tiran A, Bandarage UK, Boucher C. Come Jon, et al. Discovery of highly isoform selective thiazolopiperidine inhibitors of phosphoinositide 3-kinase γ. J Med Chem. 2015;58:5684–8.
Fruman DA, ChiuH, Hopkins BD, Bagrodia S, Cantley LC, Abraham RT. The PI3K pathway in human disease. Cell. 2017;170:605–35.
Rodon J, Dienstmann R, Serra V, Tabernero J. Development of PI3K inhibitors: lessons learned from early clinical trials. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013;10:143–53.
Zhu J, Li K, Yu L, et al. Targeting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase gamma (PI3Kγ): Discovery and development of its selective inhibitors. Med Res Rev. 2021;41:1599–621.
Knight ZA, Gonzalez B, Feldman ME, Zunder ER, Goldenberg DD, Williams O, et al. A pharmacological map of the PI3-K family defines a role for p110alpha in insulin signaling. Cell. 2006;125:733–47.
Rodrigues DA, Sagrillo FS, Fraga CAM. Duvelisib: a 2018 novel FDA-approved small molecule inhibiting phosphoinositide 3-kinases. Pharmaceuticals. 2019;12:69.
Shin N, Li Y, Mei S, Wang KH, Hall L, Katiyar K, et al. INCB040093 is a novel PI3Kδ inhibitor for the treatment of B cell lymphoid malignancies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018;364:120–30.
Garces AE, Stocks MJ. Class 1 PI3K clinical candidates and recent inhibitor design strategies: a medicinal chemistry perspective. J Med Chem. 2019;62:4815–50.
Rhizen Pharmaceuticals SA. Receives FDA fast track designation for tenalisib (RP6530), a highly selective dual PI3K delta/gamma inhibitor for the treatment of patients with relapsed and/or refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). https://globenewswire.com/news-release/2018/04/13/1471290/0/en/Rhizen-Pharmaceuticals-S-A-receives-FDA-Fast-Track-Designationfor-Tenalisib-RP6530-a-highly-selective-dual-PI3K-delta-gammainhibitor-for-the-treatment-of-patients-with-relapsed-a.html.
King-Unerwood J, Ito K, Murray PJ, Hardy G, Brookfiled FA, Brown CJ, et al. inventors. Respivert Limited, applicant. Quinazolin-4 (3h) -one derivatives used as pi3 kinase inhibitors. WO2012052753. 2011.
Onions ST, Copmans AH, Broeckx RLM, Smith AJ, Taddei DMA, inventors. Respivert Limited, applicant. 2-((4-amino-3-(3-fluoro-5-hydroxyphenyl)-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-1-yl)methyl)-3-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one derivatives and their use as phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors. WO2014140597. 2014.
Evans CA, Liu T, Lescarbeau A, Nair SJ, Grenier L, Pradeilles JA, et al. Discovery of a selective phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K)-γ inhibitor (IPI-549) as an immuno-oncology clinical candidate. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2016;7:862–7.
Drew SL, Thomas‐Tran R, Beatty JW, Fournier J, Lawson KV, Miles DH, et al. Discovery of potent and selective PI3Kγ inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2020;63:11235–57.
Tolcher A, Hong D, Sullivan R, Mier J, Shapiro G, Pearlberg J, et al. IPI-549-01: a phase I/Ib first in human study of IPI-549, a PI3K-gamma inhibitor, as monotherapy and in combination with an anti-PD-1 antibody in subjects with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Immunol Res. 2016;4:B070.
Hong DS, Postow M, Chmielowski B, Sullivan R, Patnaik A, Cohen EEW. et al. Eganelisib, a first-in-class PI3Kγ inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors: results of the phase 1/1b. MARIO-1 trial. Clin Cancer Res. 2023;29:2210–9.
Collier PN, Martinez-Botella G, Cornebise M, Cottrell KM, Doran JD, Griffith JP, et al. Structural basis for isoform selectivity in a class of benzothiazole inhibitors of phosphoinositide 3-kinase γ. J Med Chem. 2015;58:517–21.
Come JH, Collier PN, Henderson JA, Pierce AC, Davis RJ, Tiran AL, et al. Design and synthesis of a novel series of orally bioavailable, CNS-penetrant, isoform selective phosphoinositide 3-kinase γ (PI3Kγ) inhibitors with potential for the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS). J Med Chem. 2018;61:5245–56.
Collier PN, Messersmith D, Tiran AL, Bandarage UK, Boucher C, Come J, et al. Discovery of highly isoform selective thiazolopiperidine inhibitors of phosphoinositide 3-kinase γ. J Med Chem. 2015;58:5684–8.
Bandarage UK, Aronov AM, Cao J, Come JH, Cottrell KM, Davis RJ, et al. Discovery of a novel series of potent and selective alkynylthiazole-derived PI3Kγ inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2021;12:129–35.
Pemberton N, Mogemark M, Arlbrandt S, Bold P, Cox RJ, Gardelli C, et al. Discovery of highly isoform selective orally bioavailable phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-γ inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2018;61:5435–41.
Gangadhara G, Dahl G, Bohnacker T, Rae R, Gunnarsson J, Blaho S, et al. A class of highly selective inhibitors bind to an active state of PI3Kγ. Nat Chem Biol. 2019;15:348–57.
Miles DH, Yan X, Thomas-Tran R, Fournier J, Sharif EU, Drew SL, et al. Discovery of potent and selective 7-azaindole isoindolinone-based PI3Kγ inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020;11:2244–52.
Mata G, Miles DH, Drew SL, Fournier J, Lawson KV, Mailyan AK, et al. Design, synthesis, and structure−activity relationship optimization of pyrazolopyrimidine amide inhibitors of phosphoinositide 3-kinase γ (PI3Kγ). J Med Chem. 2022;65:1418–44.
Hao X, inventor. Hangzhou Zhengxiang Pharmaceutical CO., LTD, applicant. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors. WO2020210379A1. 2020.
Chen ZH, Liu GB, Yan X, Chen SZ, Du PJ, Yin HJ, inventors. The National Institutes of Pharmaceutical R&D CO., LTD, applicant. WO2022017371A1. 2021.
Esposito A, Viale G, Curigliano G. Safety, tolerability, and management of toxic effects of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor treatment in patients with cancer: a review. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5:1347–54.
Fruman DA, Rommel C. PI3K and cancer: lessons, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13:140–56.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82003780).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, Dy., Zhang, Mm., Li, J. et al. Development of PI3Kγ selective inhibitors: the strategies and application. Acta Pharmacol Sin 45, 238–247 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-023-01166-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-023-01166-8