Article |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Stereoselective amino acid synthesis by photobiocatalytic oxidative coupling
Stereoselective amino acid synthesis by photobiocatalytic oxidative coupling
We report on the oxidative cross-coupling of organoboron reagents and amino acids via pyridoxal biocatalysis to produce non-canonical amino acids, uncovering stereoselective, intermolecular free-radical transformations.
- Tian-Ci Wang
- , Binh Khanh Mai
- & Yang Yang
-
Article |
 A light-driven enzymatic enantioselective radical acylation
A light-driven enzymatic enantioselective radical acylation
Enzyme-bound ketyl radicals derived from thiamine diphosphate are selectively generated through single-electron oxidation by a photoexcited organic dye and shown to lead to enantioselective radical acylation reactions.
- Yuanyuan Xu
- , Hongwei Chen
- & Xiaoqiang Huang
-
Article |
 Complete integration of carbene-transfer chemistry into biosynthesis
Complete integration of carbene-transfer chemistry into biosynthesis
The α-diazoester azaserine can be produced by Streptomyces albus engineered with a biosynthetic gene cluster and act as the carbene precursor for coupling with intracellularly produced styrene to generate unnatural amino acids containing a cyclopropyl group.
- Jing Huang
- , Andrew Quest
- & Jay D. Keasling
-
Article |
 NMR-guided directed evolution
NMR-guided directed evolution
NMR spectroscopy has been used to guide the directed evolution of myoglobin to a Kemp eliminase with high catalytic efficiency, outlining an approach that is likely to be generally applicable to other enzyme activities.
- Sagar Bhattacharya
- , Eleonora G. Margheritis
- & Ivan V. Korendovych
-
Article |
 A designed photoenzyme for enantioselective [2+2] cycloadditions
A designed photoenzyme for enantioselective [2+2] cycloadditions
A genetically encoded triplet photosensitizer is used to develop an efficient photoenzyme that can promote enantioselective intramolecular and bimolecular [2+2] cycloadditions by means of triplet energy transfer.
- Jonathan S. Trimble
- , Rebecca Crawshaw
- & Anthony P. Green
-
Article |
 Enantioselective [2+2]-cycloadditions with triplet photoenzymes
Enantioselective [2+2]-cycloadditions with triplet photoenzymes
Triplet photoenzymes developed through genetic encoding and directed evolution result in excited-state photocatalysts that provide a valuable approach to enantioselective photochemical synthesis.
- Ningning Sun
- , Jianjian Huang
- & Yuzhou Wu
-
Article |
 An asymmetric sp3–sp3 cross-electrophile coupling using ‘ene’-reductases
An asymmetric sp3–sp3 cross-electrophile coupling using ‘ene’-reductases
A highly chemoselective and enantioselective cross-electrophile coupling using ‘ene’-reductases is reported, and photoexcited enzymes demonstrate the ability to carry out reactions between electrophiles that are not known for small-molecule catalysis.
- Haigen Fu
- , Jingzhe Cao
- & Todd K. Hyster
-
Review Article |
 The road to fully programmable protein catalysis
The road to fully programmable protein catalysis
Recent progress in computational enzyme design, active site engineering and directed evolution are reviewed, highlighting methodological innovations needed to deliver improved designer biocatalysts.
- Sarah L. Lovelock
- , Rebecca Crawshaw
- & Anthony P. Green
-
Article |
 Multifunctional biocatalyst for conjugate reduction and reductive amination
Multifunctional biocatalyst for conjugate reduction and reductive amination
A biocatalytic enzyme originating from bacteria, EneIRED, facilitates amine-activated conjugate alkene reduction followed by reductive amination, efficiently preparing chiral amine diastereomers, which are commonly used in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
- Thomas W. Thorpe
- , James R. Marshall
- & Nicholas J. Turner
-
Article |
 Biocatalytic oxidative cross-coupling reactions for biaryl bond formation
Biocatalytic oxidative cross-coupling reactions for biaryl bond formation
A study presents a biocatalytic method for the formation of sterically hindered biaryl bonds, providing a tunable approach for assembling molecules with catalyst-controlled reactivity, site selectivity and atroposelectivity.
- Lara E. Zetzsche
- , Jessica A. Yazarians
- & Alison R. H. Narayan
-
Article
| Open Access Crystallographic snapshots of a B12-dependent radical SAM methyltransferase
Crystallographic snapshots of a B12-dependent radical SAM methyltransferase
Structural and spectroscopic studies show how a B12-dependent radical SAM enzyme catalyses unique and challenging alkylation chemistry, including protein post-translational modification required for methane biosynthesis.
- Cameron D. Fyfe
- , Noelia Bernardo-García
- & Olivier Berteau
-
Article |
 Time-resolved structural analysis of an RNA-cleaving DNA catalyst
Time-resolved structural analysis of an RNA-cleaving DNA catalyst
Using high-resolution NMR characterization, the kinetics and dynamics of the catalytic function of a DNAzyme are shown.
- Jan Borggräfe
- , Julian Victor
- & Manuel Etzkorn
-
Article |
 Discovery, characterization and engineering of ligases for amide synthesis
Discovery, characterization and engineering of ligases for amide synthesis
A family of enzymes—coronafacic acid ligases, involved in the synthesis of bacterial phytotoxins—are found to catalyse amide bond formation with a wide range of substrates.
- Michael Winn
- , Michael Rowlinson
- & Jason Micklefield
-
Article |
 Discovery and engineering of colchicine alkaloid biosynthesis
Discovery and engineering of colchicine alkaloid biosynthesis
Discovery of a near-complete colchicine biosynthetic pathway enables the engineered production of the tropolone-containing alkaloid N-formyldemecolcine from amino acid precursors in Nicotiana benthamiana.
- Ryan S. Nett
- , Warren Lau
- & Elizabeth S. Sattely
-
Article |
 Photoenzymatic enantioselective intermolecular radical hydroalkylation
Photoenzymatic enantioselective intermolecular radical hydroalkylation
A transformation in which an ‘ene’ reductase catalyses the visible-light-induced intermolecular radical hydroalkylation of alkenes gives carbonyl compounds with a remote stereocentre in high yield and enantioselectivity.
- Xiaoqiang Huang
- , Binju Wang
- & Huimin Zhao
-
Article |
 An engineered PET depolymerase to break down and recycle plastic bottles
An engineered PET depolymerase to break down and recycle plastic bottles
Computer-aided engineering produces improvements to an enzyme that breaks down poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) into its constituent monomers, which are used to synthesize PET of near-petrochemical grade that can be further processed into bottles.
- V. Tournier
- , C. M. Topham
- & A. Marty
-
Letter |
 Design and evolution of an enzyme with a non-canonical organocatalytic mechanism
Design and evolution of an enzyme with a non-canonical organocatalytic mechanism
A hydrolytic enzyme with a non-canonical organocatalytic mechanism was generated by introducing Nδ-methylhistidine into a designed active site using engineered translation components, allowing optimization of enzyme performance using laboratory evolution.
- Ashleigh J. Burke
- , Sarah L. Lovelock
- & Anthony P. Green
-
Letter |
 Enzymatic assembly of carbon–carbon bonds via iron-catalysed sp3 C–H functionalization
Enzymatic assembly of carbon–carbon bonds via iron-catalysed sp3 C–H functionalization
Evolved iron-containing enzymes based on cytochrome P450 achieve selective intermolecular alkylation of sp3 C–H bonds through a carbene C–H insertion strategy.
- Ruijie K. Zhang
- , Kai Chen
- & Frances H. Arnold
-
Letter |
 Cooperative asymmetric reactions combining photocatalysis and enzymatic catalysis
Cooperative asymmetric reactions combining photocatalysis and enzymatic catalysis
A cooperative chemoenzymatic reaction combines photocatalytic alkene isomerization with enzymatic reduction to generate enantioenriched products in a stereoconvergent manner.
- Zachary C. Litman
- , Yajie Wang
- & John F. Hartwig
-
Letter |
 Genetically programmed chiral organoborane synthesis
Genetically programmed chiral organoborane synthesis
A genetically encoded platform can produce chiral organoboranes in bacteria with high turnover, enantioselectivity and chemoselectivity, and can be tuned and configured through DNA manipulation.
- S. B. Jennifer Kan
- , Xiongyi Huang
- & Frances H. Arnold
-
Letter |
 Accessing non-natural reactivity by irradiating nicotinamide-dependent enzymes with light
Accessing non-natural reactivity by irradiating nicotinamide-dependent enzymes with light
hotoexcitation of a catalytic enzyme enzyme’s co-factor is shown to change the reactivity of the enzyme, enabling it to carry out a non-natural enantioselective dehalogenation of lactone molecules.
- Megan A. Emmanuel
- , Norman R. Greenberg
- & Todd K. Hyster
-
Letter |
 Directed evolution of artificial metalloenzymes for in vivo metathesis
Directed evolution of artificial metalloenzymes for in vivo metathesis
An artificial metalloenzyme is compartmentalized and evolved in vivo for olefin metathesis—an archetypal organometallic reaction without equivalent in nature; the evolved metathase reveals broad substrate scope and compares favourably with commercial catalysts.
- Markus Jeschek
- , Raphael Reuter
- & Thomas R. Ward
-
Letter |
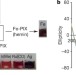 Abiological catalysis by artificial haem proteins containing noble metals in place of iron
Abiological catalysis by artificial haem proteins containing noble metals in place of iron
Replacing the iron atom in Fe-porphyrin IX proteins with a noble-metal atom enables the creation of enzymes that catalyse reactions not catalysed by native Fe-enzymes or other metalloenzymes; this approach could be used to generate other artificial enzymes that could catalyse a wide range of abiological transformations.
- Hanna M. Key
- , Paweł Dydio
- & John F. Hartwig
-
Article |
 Basomedial amygdala mediates top-down control of anxiety and fear
Basomedial amygdala mediates top-down control of anxiety and fear
Activation of the ventral medial prefrontal cortex–basomedial amygdala pathway is shown to suppress anxiety and fear-related freezing in mice, thus identifying the basomedial amygdala (and not intercalated cells, as posited by earlier models) as a novel target of top-down control.
- Avishek Adhikari
- , Talia N. Lerner
- & Karl Deisseroth
-
Letter |
 RETRACTED ARTICLE: Endoperoxide formation by an α-ketoglutarate-dependent mononuclear non-haem iron enzyme
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Endoperoxide formation by an α-ketoglutarate-dependent mononuclear non-haem iron enzyme
The X-ray crystal structures of FtmOx1, the first known α-ketoglutarate-dependent mononuclear non-haem iron enzyme that can catalyse an endoperoxide formation reaction, are presented, along with further biochemical analyses which reveal the catalytic versatility of mononuclear non-haem iron enzymes, and help to unravel the mechanisms of endoperoxide biosyntheses.
- Wupeng Yan
- , Heng Song
- & Yan Jessie Zhang
-
Article |
 Structural insights into the bacterial carbon–phosphorus lyase machinery
Structural insights into the bacterial carbon–phosphorus lyase machinery
The crystal structure of the 240-kilodalton C–P lyase core complex from the bacterium E. coli offers insights into the relatively unknown mechanisms of the enzymatic machinery that allows some microbes to extract phosphate from phosphonate compounds.
- Paulina Seweryn
- , Lan Bich Van
- & Ditlev E. Brodersen
-
Letter |
 Mechanism of farnesylated CAAX protein processing by the intramembrane protease Rce1
Mechanism of farnesylated CAAX protein processing by the intramembrane protease Rce1
The crystal structure of an archaeal Rce1 protein has been determined; this protein represents a novel type of intramembrane protease, with a distinct architecture and catalytic site.
- Ioannis Manolaridis
- , Kiran Kulkarni
- & David Barford
-
Review Article |
 Engineering the third wave of biocatalysis
Engineering the third wave of biocatalysis
Over the past ten years, protein engineering has established biocatalysis as a practical and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional forms of catalysis both in the laboratory and in industry.
- U. T. Bornscheuer
- , G. W. Huisman
- & K. Robins
-
Feature |
 Chemistry: Enzyme expertise
Chemistry: Enzyme expertise
Biocatalysis specialists are in high demand in industry.
- Katharine Sanderson
-
Article |
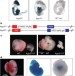 A dicer-independent miRNA biogenesis pathway that requires Ago catalysis
A dicer-independent miRNA biogenesis pathway that requires Ago catalysis
MicroRNAs, which regulate gene expression, are transcribed as longer sequences that are processed to produce the mature form. Two nuclease enzymes, Drosha and Dicer, are known to act sequentially to trim the microRNA to size. Here, however, a subset of microRNAs that includes miR-451, important for erythropoiesis, is found to be processed independently of Dicer. Rather, the Argonaute protein — part of the complex that aligns microRNA and messenger RNA — carries out the secondary cleavage.
- Sihem Cheloufi
- , Camila O. Dos Santos
- & Gregory J. Hannon

 Boron catalysis in a designer enzyme
Boron catalysis in a designer enzyme