Perspective |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Boron catalysis in a designer enzyme
Boron catalysis in a designer enzyme
A completely genetically encoded boronic-acid-containing designer enzyme was created and characterized using X-ray crystallography, high-resolution mass spectrometry and 11B NMR spectroscopy, allowing chemistry that is unknown in nature and currently not possible with small-molecule catalysts.
- Lars Longwitz
- , Reuben B. Leveson-Gower
- & Gerard Roelfes
-
Article |
 Regioselective hydroformylation of propene catalysed by rhodium-zeolite
Regioselective hydroformylation of propene catalysed by rhodium-zeolite
Rhodium catalysts confined in zeolite pores exhibit high regioselectivity in the hydroformylation process of propene to high-value n-butanal, surpassing the performance of all heterogeneous and most homogeneous catalysts developed so far.
- Xiangjie Zhang
- , Tao Yan
- & Zhi Cao
-
Research Briefing |
 Scalable, high-quality 2D telluride nanosheets for energy and catalysis applications
Scalable, high-quality 2D telluride nanosheets for energy and catalysis applications
An innovative solid-state lithiation strategy allows the exfoliation of layered transition-metal tellurides into nanosheets in an unprecedentedly short time, without sacrificing their quality. The observation of physical phenomena typically seen in highly crystalline TMT nanosheets opens the way to their use in applications such as batteries and micro-supercapacitors.
-
Article |
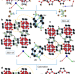 Interchain-expanded extra-large-pore zeolites
Interchain-expanded extra-large-pore zeolites
We report a strategy that yields thermally and hydrothermally stable silicates by expansion of a one-dimensional silicate chain with an intercalated silylating agent that separates and connects the chains.
- Zihao Rei Gao
- , Huajian Yu
- & Miguel A. Camblor
-
Article |
 Long-term continuous ammonia electrosynthesis
Long-term continuous ammonia electrosynthesis
Use of a chain-ether-based solvent instead of tetrahydrofuran for lithium-mediated nitrogen reduction enables long-term continuous ammonia electrosynthesis with high efficiency and improved gas-phase ammonia distribution.
- Shaofeng Li
- , Yuanyuan Zhou
- & Ib Chorkendorff
-
Article |
 Site-specific reactivity of stepped Pt surfaces driven by stress release
Site-specific reactivity of stepped Pt surfaces driven by stress release
Stress release at stepped platinum surfaces is shown to influence the strain experienced by atoms near the steps, resulting in effects on the catalytic activity of the whole surface.
- Guangdong Liu
- , Arthur J. Shih
- & Zhenhua Zeng
-
Research Briefing |
 Reducing carbon dioxide efficiently to reuse and recycle it
Reducing carbon dioxide efficiently to reuse and recycle it
Electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide holds promise for converting CO2 into valuable products but is hampered by stability issues and wasted carbon. A proton-exchange membrane that uses lead as a catalyst demonstrates the feasibility of durable and efficient CO2 reduction.
-
Article |
 Alkene dialkylation by triple radical sorting
Alkene dialkylation by triple radical sorting
We use bimolecular homolytic substitution catalysis to sort an electrophilic radical and a nucleophilic radical across an unactivated alkene, accelerating access to pharmaceutically relevant C(sp3)-rich molecules and defining a mechanistic approach for alkene dialkylation.
- Johnny Z. Wang
- , William L. Lyon
- & David W. C. MacMillan
-
Article |
 Establishing reaction networks in the 16-electron sulfur reduction reaction
Establishing reaction networks in the 16-electron sulfur reduction reaction
We investigate the mechanism underlying the sulfur reduction reaction that plays a central role in high-capacity lithium sulfur batteries, highlighting the electrocatalytic approach as a promising strategy for tackling the fundamental challenges associated with these batteries.
- Rongli Liu
- , Ziyang Wei
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Article |
 Durable CO2 conversion in the proton-exchange membrane system
Durable CO2 conversion in the proton-exchange membrane system
We develop a proton-exchange membrane system that reduces CO2 to formic acid at a catalyst that is derived from waste lead–acid batteries and in which a lattice carbon activation mechanism contributes.
- Wensheng Fang
- , Wei Guo
- & Bao Yu Xia
-
Research Briefing |
 Directly observing catalytic chemistry in the Haber–Bosch process
Directly observing catalytic chemistry in the Haber–Bosch process
The Haber–Bosch process for making ammonia has been world-changing, but is highly energy-intensive owing to the high temperatures and pressures involved. A detailed understanding of the catalytic steps that occur in the basic reactions, and what limits them, opens the way to developing greener versions of the process.
-
Article
| Open Access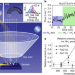 Operando probing of the surface chemistry during the Haber–Bosch process
Operando probing of the surface chemistry during the Haber–Bosch process
Using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, the surface composition of iron and ruthenium catalysts during ammonia synthesis at pressures up to 1 bar and temperatures as high as 723 K can be revealed.
- Christopher M. Goodwin
- , Patrick Lömker
- & Anders Nilsson
-
Research Briefing |
 Atomic electron tomography reveals chemical order in medium- and high-entropy alloys
Atomic electron tomography reveals chemical order in medium- and high-entropy alloys
Medium- and high-entropy alloys are hugely promising materials in metallurgy and catalysis, but their atomic-scale structure — and how that relates to their properties — is not well understood. A powerful method is beginning to reveal their secrets, with hopes for engineering better materials in the future.
-
Article |
 A light-driven enzymatic enantioselective radical acylation
A light-driven enzymatic enantioselective radical acylation
Enzyme-bound ketyl radicals derived from thiamine diphosphate are selectively generated through single-electron oxidation by a photoexcited organic dye and shown to lead to enantioselective radical acylation reactions.
- Yuanyuan Xu
- , Hongwei Chen
- & Xiaoqiang Huang
-
Article |
 Arenium-ion-catalysed halodealkylation of fully alkylated silanes
Arenium-ion-catalysed halodealkylation of fully alkylated silanes
A new method is described that uses arenium-ion-catalysed halodealkylation of silanes with four alkyl groups, typically considered synthetic dead ends, to convert Me4Si and related quaternary silanes into orthogonally substituted (functionalized) silanes.
- Tao He
- , Hendrik F. T. Klare
- & Martin Oestreich
-
Article |
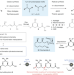 Complex molecule synthesis by electrocatalytic decarboxylative cross-coupling
Complex molecule synthesis by electrocatalytic decarboxylative cross-coupling
We report a radical-based Ni/Ag-electrocatalytic cross-coupling of substituted carboxylic acids, enabling an approach to accessing complex molecular architectures, which relies on a silver additive that forms an active Ag nanoparticle-coated electrode surface along with carefully chosen ligands.
- Benxiang Zhang
- , Jiayan He
- & Phil S. Baran
-
Article |
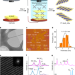 Phase-dependent growth of Pt on MoS2 for highly efficient H2 evolution
Phase-dependent growth of Pt on MoS2 for highly efficient H2 evolution
We report the production of MoS2 nanosheets with high phase purity, showing that the 2H-phase templates facilitate epitaxial growth of Pt nanoparticles, whereas the 1T′ phase supports single-atomically dispersed Pt atoms.
- Zhenyu Shi
- , Xiao Zhang
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A catalytically active oscillator made from small organic molecules
A catalytically active oscillator made from small organic molecules
We report a small-organic-molecule oscillator that catalyses an independent chemical reaction in situ without impairing its oscillating properties, allowing the construction of complex systems enhancing applications in automated synthesis and systems and polymerization chemistry.
- Matthijs ter Harmsel
- , Oliver R. Maguire
- & Syuzanna R. Harutyunyan
-
Article |
 Hydrogen-bond-acceptor ligands enable distal C(sp3)–H arylation of free alcohols
Hydrogen-bond-acceptor ligands enable distal C(sp3)–H arylation of free alcohols
Ligands enable alcohol-directed arylation of δ-C(sp3)–H bonds by stabilizing hydroxyl coordination to palladium through charge balance and hydrogen bonding.
- Daniel A. Strassfeld
- , Chia-Yu Chen
- & Jin-Quan Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Light-enabled deracemization of cyclopropanes by Al-salen photocatalysis
Light-enabled deracemization of cyclopropanes by Al-salen photocatalysis
Irradiation of chiral Al-salen complexes with violet light demonstrates efficient deracemization of cyclopropanes, enabling reactivity and enantioselectivity to be regulated simultaneously, negating the requirement for tailored catalyst–substrate recognition motifs.
- Carina Onneken
- , Tobias Morack
- & Ryan Gilmour
-
Article |
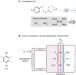 Quinone-mediated hydrogen anode for non-aqueous reductive electrosynthesis
Quinone-mediated hydrogen anode for non-aqueous reductive electrosynthesis
A quinone-mediated hydrogen anode design shows that hydrogen can be used as the electron source in non-aqueous reductive electrosynthesis, for a more sustainable way to make molecules at larger scale.
- Jack Twilton
- , Mathew R. Johnson
- & Shannon S. Stahl
-
Article
| Open Access Photocatalytic phosphine-mediated water activation for radical hydrogenation
Photocatalytic phosphine-mediated water activation for radical hydrogenation
Using a photocatalytic phosphine-mediated radical process under mild conditions enables direct hydrogen atom transfer to closed-shell π systems for activation of water.
- Jingjing Zhang
- , Christian Mück-Lichtenfeld
- & Armido Studer
-
Article |
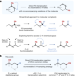 Functional-group translocation of cyano groups by reversible C–H sampling
Functional-group translocation of cyano groups by reversible C–H sampling
Using light-based, reversible C−H sampling catalysis, a cyano functional group can be swapped with a C−H bond in a molecule, providing access to valuable structures that are difficult to obtain by other methods.
- Ken Chen
- , Qingrui Zeng
- & Yan Xu
-
Article |
 General cross-coupling reactions with adaptive dynamic homogeneous catalysis
General cross-coupling reactions with adaptive dynamic homogeneous catalysis
A self-adjustive catalytic system with nickel under visible-light-driven redox reaction conditions provides a general method for carbon–(hetero)atom cross-coupling reactions and is demonstrated for nine different bond-forming reactions.
- Indrajit Ghosh
- , Nikita Shlapakov
- & Burkhard König
-
Research Briefing |
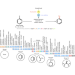 Nickel catalyses a host of chemical reactions in a general method
Nickel catalyses a host of chemical reactions in a general method
A minimal but general method has been developed for catalysing many different cross-coupling reactions — those in which two chemical fragments are joined. It requires only the two substrate substances, a nickel salt as a catalyst precursor, a catalyst for light-driven redox reactions and, in some cases, a nitrogen-containing base.
-
Article |
 Transannular C–H functionalization of cycloalkane carboxylic acids
Transannular C–H functionalization of cycloalkane carboxylic acids
Quinuclidine-pyridone and sulfonamide-pyridone ligands enable transannular γ-methylene C–H arylation of cycloalkane carboxylic acids with a range of ring sizes, bringing us closer to molecular editing of saturated carbocycles.
- Guowei Kang
- , Daniel A. Strassfeld
- & Jin-Quan Yu
-
Outlook |
 How to lower carbon levels using light
How to lower carbon levels using light
Photocatalysis using light-emitting diodes could reduce the amount of carbon dioxide emitted by industrial chemical processes.
- Neil Savage
-
News & Views |
 Organic catalyst opens way to energy-efficient chlorine production
Organic catalyst opens way to energy-efficient chlorine production
The industrial process for making chlorine uses a vast amount of energy globally. An organic catalyst has been developed that could form the basis of a more energy-efficient process, replacing expensive inorganic catalysts.
- Thomas Turek
-
Article |
 CO2-mediated organocatalytic chlorine evolution under industrial conditions
CO2-mediated organocatalytic chlorine evolution under industrial conditions
A study shows that an organocatalyst with an amide functional group, and carbon dioxide, can efficiently and selectively produce chlorine, potentially offering a low-cost and less energy intensive alternative to the chlor-alkali process.
- Jiarui Yang
- , Wen-Hao Li
- & Yadong Li
-
Article |
 Promoting active site renewal in heterogeneous olefin metathesis catalysts
Promoting active site renewal in heterogeneous olefin metathesis catalysts
The authors identify a dynamic site renewal and decay cycle, mediated by proton transfers involving proximal Brønsted acidic OH groups, which operates concurrently with the Chauvin cycle and could address roadblocks associated with industrial metathesis processes.
- Terry Z. H. Gani
- , Zachariah J. Berkson
- & Yuriy Román-Leshkov
-
Article |
 Constrained C2 adsorbate orientation enables CO-to-acetate electroreduction
Constrained C2 adsorbate orientation enables CO-to-acetate electroreduction
A study using a copper-in-silver dilute alloy catalyst in a high-pressure gas flow reactor reports highly selective electrosynthesis of acetate from carbon monoxide.
- Jian Jin
- , Joshua Wicks
- & Yuanjie Pang
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic disconnection of C–O bonds in epoxy resins and composites
Catalytic disconnection of C–O bonds in epoxy resins and composites
The authors report a transition-metal-catalysed protocol for recovery of polymer building block bisphenol A and intact fibres from epoxy composites, demonstrating that chemical recycling approaches for thermoset epoxy resins and composites are achievable.
- Alexander Ahrens
- , Andreas Bonde
- & Troels Skrydstrup
-
Research Briefing |
 Enzyme-inspired catalyst helps to convert methane into methanol
Enzyme-inspired catalyst helps to convert methane into methanol
A catalyst with a hydrophobic cavity that contains an active iron centre has been developed to convert methane into methanol. It has a ‘catch-and-release’ mechanism whereby a hydrophobic methane molecule enters the cavity for oxidation and the resulting hydrophilic methanol molecule is released into the surrounding aqueous solution.
-
Article |
 Selective methane oxidation by molecular iron catalysts in aqueous medium
Selective methane oxidation by molecular iron catalysts in aqueous medium
Methane can be oxidized to methanol using N-heterocyclic carbene-ligated FeII complexes, in which the hydrophobic cavity captures the methane substrate from an aqueous solution and releases the hydrophilic methanol product back into the solution.
- Hiroto Fujisaki
- , Tomoya Ishizuka
- & Takahiko Kojima
-
Article |
 Copper-catalysed enantioconvergent alkylation of oxygen nucleophiles
Copper-catalysed enantioconvergent alkylation of oxygen nucleophiles
The enantioconvergent alkylation of oxygen nucleophiles is achieved using α-haloamides and a readily available copper catalyst, and the reaction proceeds under mild conditions in the presence of a wide variety of functional groups.
- Caiyou Chen
- & Gregory C. Fu
-
Article |
 Enantioconvergent Cu-catalysed N-alkylation of aliphatic amines
Enantioconvergent Cu-catalysed N-alkylation of aliphatic amines
The chemoselective and enantioconvergent N-alkylation of aliphatic amines, including ammonia, is achieved using chiral tridentate anionic ligands and a copper catalyst; the method shows excellent enantioselectivity and functional-group tolerance.
- Ji-Jun Chen
- , Jia-Heng Fang
- & Xin-Yuan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic asymmetric synthesis of cannabinoids and menthol from neral
Catalytic asymmetric synthesis of cannabinoids and menthol from neral
An unsymmetric, strong and confined chiral acid, a highly fluorinated imino-imidodiphosphate, catalyses the selective conversion of neral to (1R,6S)-trans-isopiperitenol, enabling sustainable routes to menthol and cannabinoids.
- Joyce A. A. Grimm
- , Hui Zhou
- & Benjamin List
-
Article |
 Enantioselective transition-metal catalysis via an anion-binding approach
Enantioselective transition-metal catalysis via an anion-binding approach
Chiral hydrogen-bond donors bind anions of organometallic catalysts to achieve enantiocontrol and reaction-rate enhancement through ion pairing together with other non-covalent interactions.
- John M. Ovian
- , Petra Vojáčková
- & Eric N. Jacobsen
-
Research Briefing |
 Designer silicon nanowires produce hydrogen from water and light
Designer silicon nanowires produce hydrogen from water and light
Silicon nanowires that can convert light into electricity were engineered to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. When integrated with co-catalysts and suspended in water, these light-activated nanoreactors produced hydrogen gas under visible and infrared light.
-
Article |
 Water splitting with silicon p–i–n superlattices suspended in solution
Water splitting with silicon p–i–n superlattices suspended in solution
The simplicity of particle suspension reactors and the precise synthetic control afforded by silicon nanowire growth are used to develop a system that can produce hydrogen fuel by splitting water with sunlight.
- Taylor S. Teitsworth
- , David J. Hill
- & James F. Cahoon
-
News & Views |
 Light-activated catalysts point the way to sustainable chemistry
Light-activated catalysts point the way to sustainable chemistry
A light-activated ‘plasmonic’ catalyst, made from abundant elements, produces as much hydrogen from ammonia as do the most-used heat-activated catalysts based on a rarer element, suggesting a strategy for sustainable chemical production.
- Emiliano Cortés
-
Research Highlight |
 Copper-studded catalyst turns pollutant into potent fuel
Copper-studded catalyst turns pollutant into potent fuel
Nanoparticles bristling with copper atoms convert carbon dioxide into an alcohol that can be used in fuel cells.
-
News & Views |
 Machine learning classifies catalytic-reaction mechanisms
Machine learning classifies catalytic-reaction mechanisms
The study of how chemical reactions work is key to the design of new reactions, but relies on hard work and expert knowledge. A machine-learning tool has been developed that could change the way this challenge is approached.
- Danilo M. Lustosa
- & Anat Milo
-
Article |
 Organic reaction mechanism classification using machine learning
Organic reaction mechanism classification using machine learning
Mechanistic elucidation through currently available kinetic analysis is limited by mathematical approximations and human interpretation, here a deep neural network model has been trained to analyse ordinary kinetic data and automatically elucidate the corresponding mechanism class.
- Jordi Burés
- & Igor Larrosa
-
Article |
 Solar-to-hydrogen efficiency of more than 9% in photocatalytic water splitting
Solar-to-hydrogen efficiency of more than 9% in photocatalytic water splitting
Photocatalytic water splitting with a high solar-to-hydrogen efficiency of more than nine per cent is achieved using pure water, concentrated solar light and an indium gallium nitride photocatalyst.
- Peng Zhou
- , Ishtiaque Ahmed Navid
- & Zetian Mi
-
Article |
 Electrophotocatalytic oxygenation of multiple adjacent C–H bonds
Electrophotocatalytic oxygenation of multiple adjacent C–H bonds
Installation of multiple C–O bonds by concurrent oxygenation of contiguous C–H bonds in a selective fashion is highly desirable, and this is achieved by repeated operation of a potent oxidative catalyst via electrophotocatalysis.
- Tao Shen
- , Yi-Lun Li
- & Tristan H. Lambert
-
Research Briefing |
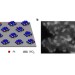 Nanoglues isolate metal atoms for better catalysis
Nanoglues isolate metal atoms for better catalysis
Single atoms of platinum-group metals are excellent catalysts, but they tend to aggregate and lose their activity during chemical reactions. We used nanoislands of cerium oxide, peppered through the interior surfaces of high-surface-area porous oxide supports, to confine and stabilize single atoms of these expensive metals, turning them into efficient and long-lasting catalysts.
-
Article |
 Functional CeOx nanoglues for robust atomically dispersed catalysts
Functional CeOx nanoglues for robust atomically dispersed catalysts
Nanometre-sized ‘nanoglue’ islands of CeOx on high-surface-area SiO2 are shown to suppress sintering and confine on average one Pt atom per island, leading to stable single-atom catalysts under oxidizing and reducing environments.
- Xu Li
- , Xavier Isidro Pereira-Hernández
- & Jingyue Liu
-
News |
 Heat and bacteria recycle mixed plastics into useful chemicals
Heat and bacteria recycle mixed plastics into useful chemicals
Two-step process converts mixtures of plastic into small molecules, but could be challenging to implement at scale.
- Katharine Sanderson

 The refinery of the future
The refinery of the future