Perspective |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Regioselective hydroformylation of propene catalysed by rhodium-zeolite
Regioselective hydroformylation of propene catalysed by rhodium-zeolite
Rhodium catalysts confined in zeolite pores exhibit high regioselectivity in the hydroformylation process of propene to high-value n-butanal, surpassing the performance of all heterogeneous and most homogeneous catalysts developed so far.
- Xiangjie Zhang
- , Tao Yan
- & Zhi Cao
-
Article |
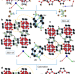 Interchain-expanded extra-large-pore zeolites
Interchain-expanded extra-large-pore zeolites
We report a strategy that yields thermally and hydrothermally stable silicates by expansion of a one-dimensional silicate chain with an intercalated silylating agent that separates and connects the chains.
- Zihao Rei Gao
- , Huajian Yu
- & Miguel A. Camblor
-
Article |
 Site-specific reactivity of stepped Pt surfaces driven by stress release
Site-specific reactivity of stepped Pt surfaces driven by stress release
Stress release at stepped platinum surfaces is shown to influence the strain experienced by atoms near the steps, resulting in effects on the catalytic activity of the whole surface.
- Guangdong Liu
- , Arthur J. Shih
- & Zhenhua Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access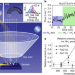 Operando probing of the surface chemistry during the Haber–Bosch process
Operando probing of the surface chemistry during the Haber–Bosch process
Using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, the surface composition of iron and ruthenium catalysts during ammonia synthesis at pressures up to 1 bar and temperatures as high as 723 K can be revealed.
- Christopher M. Goodwin
- , Patrick Lömker
- & Anders Nilsson
-
Article |
 Promoting active site renewal in heterogeneous olefin metathesis catalysts
Promoting active site renewal in heterogeneous olefin metathesis catalysts
The authors identify a dynamic site renewal and decay cycle, mediated by proton transfers involving proximal Brønsted acidic OH groups, which operates concurrently with the Chauvin cycle and could address roadblocks associated with industrial metathesis processes.
- Terry Z. H. Gani
- , Zachariah J. Berkson
- & Yuriy Román-Leshkov
-
Article |
 Functional CeOx nanoglues for robust atomically dispersed catalysts
Functional CeOx nanoglues for robust atomically dispersed catalysts
Nanometre-sized ‘nanoglue’ islands of CeOx on high-surface-area SiO2 are shown to suppress sintering and confine on average one Pt atom per island, leading to stable single-atom catalysts under oxidizing and reducing environments.
- Xu Li
- , Xavier Isidro Pereira-Hernández
- & Jingyue Liu
-
Article |
 Bifunctional hydroformylation on heterogeneous Rh-WOx pair site catalysts
Bifunctional hydroformylation on heterogeneous Rh-WOx pair site catalysts
Catalysts consisting of oxide-supported pair sites can enable bifunctional reaction mechanisms with high activity and selectivity for reactions and so overcome the limitations in industry imposed by the use of homogeneous catalysts.
- Insoo Ro
- , Ji Qi
- & Phillip Christopher
-
Article |
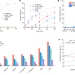 Au–Pd separation enhances bimetallic catalysis of alcohol oxidation
Au–Pd separation enhances bimetallic catalysis of alcohol oxidation
‘Cooperative redox enhancement (CORE) effects, which arise through the coupling of oxidative dehydrogenation and oxygen reduction reactions, can lead to increased rates of reaction over spatially separated bimetallic heterogeneous catalysts.
- Xiaoyang Huang
- , Ouardia Akdim
- & Graham J. Hutchings
-
Article
| Open Access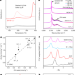 In situ formation of ZnOx species for efficient propane dehydrogenation
In situ formation of ZnOx species for efficient propane dehydrogenation
Propene is obtained through propane dehydrogenation using catalysts that are toxic, expensive or demanding to regenerate with ecologically harmful compounds, but the ZnO-based alternative reported here is cheap, clean and scalable.
- Dan Zhao
- , Xinxin Tian
- & Evgenii V. Kondratenko
-
Article |
 A stable low-temperature H2-production catalyst by crowding Pt on α-MoC
A stable low-temperature H2-production catalyst by crowding Pt on α-MoC
A stable, low-temperature water–gas shift catalyst is achieved by crowding platinum atoms and clusters on α-molybdenum carbide; the crowding protects the support from oxidation that would cause catalyst deactivation.
- Xiao Zhang
- , Mengtao Zhang
- & Ding Ma
-
Article |
 Key role of chemistry versus bias in electrocatalytic oxygen evolution
Key role of chemistry versus bias in electrocatalytic oxygen evolution
Spectroscopic studies and theoretical calculations of the electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction establish that reaction rates depend on the amount of charge stored in the electrocatalyst, and not on the applied potential.
- Hong Nhan Nong
- , Lorenz J. Falling
- & Travis E. Jones
-
Article |
 Rare-earth–platinum alloy nanoparticles in mesoporous zeolite for catalysis
Rare-earth–platinum alloy nanoparticles in mesoporous zeolite for catalysis
Alloy nanoparticles of platinum and rare-earth elements are formed using zeolites with pore-wall defects, producing stable, highly active and selective catalysts for the propane dehydrogenation reaction.
- Ryong Ryoo
- , Jaeheon Kim
- & Jae Won Shin
-
Article |
 Vacancy-enabled N2 activation for ammonia synthesis on an Ni-loaded catalyst
Vacancy-enabled N2 activation for ammonia synthesis on an Ni-loaded catalyst
Ammonia is synthesized using a dual-site approach, whereby nitrogen vacancies on LaN activate N2, which then reacts with hydrogen atoms produced over the Ni metal to give ammonia.
- Tian-Nan Ye
- , Sang-Won Park
- & Hideo Hosono
-
Letter |
 Atomically dispersed iron hydroxide anchored on Pt for preferential oxidation of CO in H2
Atomically dispersed iron hydroxide anchored on Pt for preferential oxidation of CO in H2
Atomically dispersed iron hydroxide deposited on silica-supported platinum nanoparticles enables complete and selective carbon monoxide removal through preferential oxidation in hydrogen in the temperature range from 198 to 380 kelvin.
- Lina Cao
- , Wei Liu
- & Junling Lu
-
Letter |
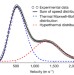 Velocity-resolved kinetics of site-specific carbon monoxide oxidation on platinum surfaces
Velocity-resolved kinetics of site-specific carbon monoxide oxidation on platinum surfaces
The catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide over platinum proceeds through two distinct channels: it is dominated at low temperatures by the more active step sites and at high temperatures by the more abundant terrace sites of the platinum surface.
- Jannis Neugebohren
- , Dmitriy Borodin
- & Theofanis N. Kitsopoulos
-
Letter |
 Low-temperature hydrogen production from water and methanol using Pt/α-MoC catalysts
Low-temperature hydrogen production from water and methanol using Pt/α-MoC catalysts
As an alternative vehicle fuel, hydrogen can be generated in situ from methanol and water—a process that is shown here to occur under mild conditions using a catalyst that comprises platinum atomically dispersed on an α-molybdenum carbide substrate.
- Lili Lin
- , Wu Zhou
- & Ding Ma
-
Letter |
 High-spatial-resolution mapping of catalytic reactions on single particles
High-spatial-resolution mapping of catalytic reactions on single particles
The chemical conversion of N-heterocyclic carbene molecules attached to catalytic particles is monitored at high spatial resolution using synchrotron-radiation-based infrared nanospectroscopy.
- Chung-Yeh Wu
- , William J. Wolf
- & Elad Gross
-
Letter |
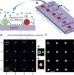 Catalyst support effects on hydrogen spillover
Catalyst support effects on hydrogen spillover
The mechanism of hydrogen spillover is described using a precisely nanofabricated model system, explaining why it is slower on an aluminum oxide catalyst support than on a titanium oxide catalyst support.
- Waiz Karim
- , Clelia Spreafico
- & Jeroen A. van Bokhoven
-
Letter |
 Metal–organic frameworks as selectivity regulators for hydrogenation reactions
Metal–organic frameworks as selectivity regulators for hydrogenation reactions
The flavouring, perfume and pharmaceutical industries rely on the selective hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes to generate unsaturated alcohols; here, a new type of highly selective catalyst is described in which platinum nanoparticles are sandwiched between a core and a shell of a metal−organic framework.
- Meiting Zhao
- , Kuo Yuan
- & Zhiyong Tang
-
Letter |
 Cobalt carbide nanoprisms for direct production of lower olefins from syngas
Cobalt carbide nanoprisms for direct production of lower olefins from syngas
Lower olefins are hydrocarbons that are widely used in the chemical industry, and can be generated from syngas by the ‘Fischer–Tropsch to olefins’ process; here, a new catalyst is described that can generate lower olefins from syngas with high selectivity, with little formation of undesirable methane.
- Liangshu Zhong
- , Fei Yu
- & Hui Wang
-
Letter |
 The active site of low-temperature methane hydroxylation in iron-containing zeolites
The active site of low-temperature methane hydroxylation in iron-containing zeolites
Iron-containing zeolites have an exceptional ability to convert methane into methanol, but their active site have been hard to study; now, magnetic circular dichroism has been used to explore the reactive species, providing a technique that should be generally applicable, and revealing the value of constraining active sites within a lattice to improve catalyst functionality.
- Benjamin E. R. Snyder
- , Pieter Vanelderen
- & Edward I. Solomon
-
Letter |
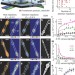 Sub-particle reaction and photocurrent mapping to optimize catalyst-modified photoanodes
Sub-particle reaction and photocurrent mapping to optimize catalyst-modified photoanodes
Using single-molecule fluorescence imaging of photoelectrocatalysis, the charge-carrier activities on single TiO2 nanorods and the corresponding water-oxidation photocurrent are mapped at high spatiotemporal resolution, revealing the best catalytic sites and the most effective sites for depositing an oxygen evolution catalyst.
- Justin B. Sambur
- , Tai-Yen Chen
- & Peng Chen
-
Letter |
 Nanoscale intimacy in bifunctional catalysts for selective conversion of hydrocarbons
Nanoscale intimacy in bifunctional catalysts for selective conversion of hydrocarbons
The conversion of hydrocarbons to produce high-quality diesel fuel can be catalysed by bifunctional materials that contain a metal site and an acid site; it has been assumed that these sites should be as close as possible in order to enhance catalysis, but it is now shown that having them too close together can be detrimental to selectivity.
- Jovana Zecevic
- , Gina Vanbutsele
- & Johan A. Martens
-
Letter |
 Thermal maps of gases in heterogeneous reactions
Thermal maps of gases in heterogeneous reactions
A technique of NMR thermometry that relies on the inverse relationship between NMR linewidths and temperature can be used to map non-invasively the gas temperatures inside catalytic reactors, offering unprecedented capabilities for testing the approximations used in reactor modelling.
- Nanette N. Jarenwattananon
- , Stefan Glöggler
- & Louis-S. Bouchard

 The refinery of the future
The refinery of the future