Featured
-
-
Article |
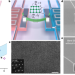 Suppressed thermal transport in silicon nanoribbons by inhomogeneous strain
Suppressed thermal transport in silicon nanoribbons by inhomogeneous strain
We report on a method for inducing uncontaminated and precise inhomogeneous strain in nanoscale silicon ribbons and its use for determining physical effects in these strained materials, in particular, an increase in the range and control of thermal conductivity.
- Lin Yang
- , Shengying Yue
- & Peng Gao
-
Article |
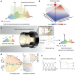 Dispersion-assisted high-dimensional photodetector
Dispersion-assisted high-dimensional photodetector
By combining spatial and frequency dispersive thin-film interfaces with deep residual learning, a miniature photodetector allowing the acquisition of high-dimensional information on light in a single-shot fashion is described.
- Yandong Fan
- , Weian Huang
- & Wei Li
-
News & Views |
 Vibration isolation could boost performance of near-infrared organic LEDs
Vibration isolation could boost performance of near-infrared organic LEDs
The development of high-performance organic LEDs and other devices that emit near-infrared light has been hindered by seemingly fundamental features of the light-emitting molecules. A potential solution has been identified.
- Margherita Maiuri
-
Article |
 Observation of Nagaoka polarons in a Fermi–Hubbard quantum simulator
Observation of Nagaoka polarons in a Fermi–Hubbard quantum simulator
Emergence of Nagaoka polarons and kinetic magnetism is observed in a Hubbard system realized with strongly interacting fermions trapped in a triangular optical lattice.
- Martin Lebrat
- , Muqing Xu
- & Markus Greiner
-
Article |
 Chemical short-range disorder in lithium oxide cathodes
Chemical short-range disorder in lithium oxide cathodes
The introduction of chemical short-range disorder substantially affects the crystal structure of layered lithium oxide cathodes, leading to improved charge transfer and structural stability.
- Qidi Wang
- , Zhenpeng Yao
- & Chenglong Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Decoupling excitons from high-frequency vibrations in organic molecules
Decoupling excitons from high-frequency vibrations in organic molecules
A molecular design strategy for reducing the vibration-induced non-radiative losses in emissive organic semiconductors is realized by decoupling excitons from high-frequency vibrations.
- Pratyush Ghosh
- , Antonios M. Alvertis
- & Akshay Rao
-
Article
| Open Access Measurement of the superfluid fraction of a supersolid by Josephson effect
Measurement of the superfluid fraction of a supersolid by Josephson effect
A new method based on the Josephson effect is described, allowing to measure the superfluid fraction of a supersolid, which captures the effect of spatially periodic modulation leading to reduction in the stiffness of superfluids.
- G. Biagioni
- , N. Antolini
- & G. Modugno
-
Research Briefing |
 A quantum solid made of electrons: observing the elusive Wigner crystal
A quantum solid made of electrons: observing the elusive Wigner crystal
In ordinary materials, electrons move too quickly for their negative electric charges to affect their interactions. But at low temperatures and densities, they can be made to crystallize into an exotic type of electron solid — a phenomenon predicted by Eugene Wigner 90 years ago and only now directly observed.
-
Article
| Open Access Probing single electrons across 300-mm spin qubit wafers
Probing single electrons across 300-mm spin qubit wafers
Using a cryogenic 300-mm wafer prober, a new approach for the testing of hundreds of industry-manufactured spin qubit devices at 1.6 K provides high-volume data on performance, allowing optimization of the complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS)-compatible fabrication process.
- Samuel Neyens
- , Otto K. Zietz
- & James S. Clarke
-
Article |
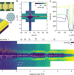 One-dimensional proximity superconductivity in the quantum Hall regime
One-dimensional proximity superconductivity in the quantum Hall regime
We show that domain walls in minimally twisted bilayer graphene support exceptionally robust proximity superconductivity in the quantum Hall regime.
- Julien Barrier
- , Minsoo Kim
- & A. K. Geim
-
Nature Careers Podcast |
 How a young physicist’s job move helped Argentina join the ATLAS collaboration
How a young physicist’s job move helped Argentina join the ATLAS collaboration
A stint at CERN exposed María Teresa Dova to longstanding collaborators and mentors, culminating in a successful bid to join a landmark project.
- Julie Gould
-
Article
| Open Access Light-wave-controlled Haldane model in monolayer hexagonal boron nitride
Light-wave-controlled Haldane model in monolayer hexagonal boron nitride
We introduce strong tailored light-wave-driven time-reversal symmetry breaking in monolayer hexagonal boron nitride, realizing a sub-laser-cycle controllable analogue of the topological model of Haldane and inducing non-resonant valley polarization.
- Sambit Mitra
- , Álvaro Jiménez-Galán
- & Shubhadeep Biswas
-
News & Views |
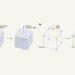 Light makes atoms behave like electromagnetic coils
Light makes atoms behave like electromagnetic coils
Microscopic magnetic fields form in non-magnetic materials when light makes the atoms rotate. A similar macroscopic effect has long been known, but proof of its atomic equivalent could give rise to ultrafast data processing.
- Carl P. Romao
- & Dominik M. Juraschek
-
Article |
 Phononic switching of magnetization by the ultrafast Barnett effect
Phononic switching of magnetization by the ultrafast Barnett effect
Ultrafast light-induced driving of phonons at resonance in a substrate facilitates the permanent reversal of the magnetic state of a material mounted on it.
- C. S. Davies
- , F. G. N. Fennema
- & A. Kirilyuk
-
Article |
 Direct observation of a magnetic-field-induced Wigner crystal
Direct observation of a magnetic-field-induced Wigner crystal
A magnetic-field-induced Wigner crystal in Bernal-stacked bilayer graphene was directly imaged using high-resolution scanning tunnelling microscopy and its structural properties as a function of electron density, magnetic field and temperature were examined.
- Yen-Chen Tsui
- , Minhao He
- & Ali Yazdani
-
Article |
 A hybrid topological quantum state in an elemental solid
A hybrid topological quantum state in an elemental solid
A hybrid topological phase of matter is discovered in the simple elemental-solid arsenic and explored using tunnelling microscopy, photoemission spectroscopy and a theoretical analysis.
- Md Shafayat Hossain
- , Frank Schindler
- & M. Zahid Hasan
-
Article
| Open Access Terahertz electric-field-driven dynamical multiferroicity in SrTiO3
Terahertz electric-field-driven dynamical multiferroicity in SrTiO3
We demonstrate the emergence of magnetism induced by a terahertz electric field in SrTiO3.
- M. Basini
- , M. Pancaldi
- & S. Bonetti
-
Article |
 Giant energy storage and power density negative capacitance superlattices
Giant energy storage and power density negative capacitance superlattices
Using a three-pronged approach — spanning field-driven negative capacitance stabilization to increase intrinsic energy storage, antiferroelectric superlattice engineering to increase total energy storage, and conformal three-dimensional deposition to increase areal energy storage density — very high electrostatic energy storage density and power density are reported in HfO2–ZrO2-based thin film microcapacitors integrated into silicon.
- Suraj S. Cheema
- , Nirmaan Shanker
- & Sayeef Salahuddin
-
News & Views |
 Electrons flip a switch on optical communications
Electrons flip a switch on optical communications
Clever manipulation of electrons has enabled scientists to change a key property of light emitted by a device using electrically controlled magnetization. The method could lead to stable and energy-efficient information transfer.
- Satoshi Hiura
-
Article |
 Evidence for chiral graviton modes in fractional quantum Hall liquids
Evidence for chiral graviton modes in fractional quantum Hall liquids
Through inelastic light scattering chiral spin-2 long-wavelength magnetorotons are observed, revealing chiral graviton modes in fractional quantum Hall states and aiding in understanding the quantum metric impacts in topological correlated systems.
- Jiehui Liang
- , Ziyu Liu
- & Aron Pinczuk
-
Article |
 Optomechanical realization of the bosonic Kitaev chain
Optomechanical realization of the bosonic Kitaev chain
We report the experimental realization of a bosonic Kitaev chain in a nano-optomechanical network.
- Jesse J. Slim
- , Clara C. Wanjura
- & Ewold Verhagen
-
Article
| Open Access High-fidelity spin qubit operation and algorithmic initialization above 1 K
High-fidelity spin qubit operation and algorithmic initialization above 1 K
Initialization and operation of spin qubits in silicon above 1 K reach fidelities sufficient for fault-tolerant operations at these temperatures.
- Jonathan Y. Huang
- , Rocky Y. Su
- & Chih Hwan Yang
-
Article |
 Controlling the helicity of light by electrical magnetization switching
Controlling the helicity of light by electrical magnetization switching
The helicity of light from a light-emitting diode can be electrically controlled by spin–orbit torque effects, enabling a seamless integration of magnetization dynamics with photonics.
- Pambiang Abel Dainone
- , Nicholas Figueiredo Prestes
- & Yuan Lu
-
Article |
 Evidence of the fractional quantum spin Hall effect in moiré MoTe2
Evidence of the fractional quantum spin Hall effect in moiré MoTe2
Transport evidence of a fractional quantum spin Hall insulator is reported in 2.1°-twisted bilayer MoTe2, which supports spin-Sz conservation and flat spin-contrasting Chern bands.
- Kaifei Kang
- , Bowen Shen
- & Kin Fai Mak
-
News & Views |
 Magnetic whirlpools offer improved data storage
Magnetic whirlpools offer improved data storage
Complex magnetic structures called skyrmions have been generated on a nanometre scale and controlled electrically — a promising step for fast, energy-efficient computer hardware systems that can store large amounts of data.
- Qiming Shao
-
News & Views |
 Complex motions emerge from robot interactions
Complex motions emerge from robot interactions
An array of robots has been set up so that pushes between them produce movements that do not conform to the usual laws of motion. Fascinating behaviour emerges from these interactions: wave phenomena known as solitons.
- Sebastian D. Huber
- & Kukka-Emilia Huhtinen
-
Article |
 Dual quantum spin Hall insulator by density-tuned correlations in TaIrTe4
Dual quantum spin Hall insulator by density-tuned correlations in TaIrTe4
A study reports a dual quantum spin Hall insulator in monolayer TaIrTe4, arising from the interplay of its single-particle topology and density-tuned electron correlations.
- Jian Tang
- , Thomas Siyuan Ding
- & Qiong Ma
-
Article |
 All-electrical skyrmionic magnetic tunnel junction
All-electrical skyrmionic magnetic tunnel junction
Wafer-scale realization of a nanoscale magnetic tunnel junction hosting a single, ambient skyrmion enables its large readout, efficient switching, and compatibility with lateral manipulation, and thereby provides the backbone for all-electrical skyrmionic device architectures.
- Shaohai Chen
- , James Lourembam
- & Anjan Soumyanarayanan
-
Article
| Open Access Rotating curved spacetime signatures from a giant quantum vortex
Rotating curved spacetime signatures from a giant quantum vortex
By stabilizing a stationary giant quantum vortex in superfluid 4He and introducing a minimally invasive way to characterize the vortex flow, intricate wave–vortex interactions are shown to simulate black hole ringdown physics.
- Patrik Švančara
- , Pietro Smaniotto
- & Silke Weinfurtner
-
Article |
 Non-reciprocal topological solitons in active metamaterials
Non-reciprocal topological solitons in active metamaterials
A local driving mechanism for solitons that accelerates both solitons and antisolitons in the same direction, called non-reciprocal driving, is introduced, showing a subtle interplay between non-reciprocity and topological solitons and providing waveguiding and wave-processing possibilities for other fields.
- Jonas Veenstra
- , Oleksandr Gamayun
- & Corentin Coulais
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous electrons in a metallic kagome ferromagnet
Anomalous electrons in a metallic kagome ferromagnet
Laser-based micro-focused angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy reveals both fractionalized and marginal quasiparticles in C3-symmetric electron pockets near the Brillouin zone centre of the ferromagnetic kagome metal Fe3Sn2.
- Sandy Adhitia Ekahana
- , Y. Soh
- & G. Aeppli
-
News & Views |
 Quantum sensor settles debate about superconductivity in hydrides
Quantum sensor settles debate about superconductivity in hydrides
By adapting a device designed to create extremely high pressures into one that can sense magnetic fields, researchers have obtained evidence that a hydrogen-rich material is a superconductor, eliminating long-standing doubts.
- Kin On Ho
- & Sen Yang
-
Article |
 Imaging the Meissner effect in hydride superconductors using quantum sensors
Imaging the Meissner effect in hydride superconductors using quantum sensors
In order to explore superconductivity in hydride materials, local magnetometry inside a diamond anvil cell is performed with sub-micron spatial resolution at megabar pressures using nitrogen-vacancy colour centres.
- P. Bhattacharyya
- , W. Chen
- & N. Y. Yao
-
Article |
 Fractional quantum anomalous Hall effect in multilayer graphene
Fractional quantum anomalous Hall effect in multilayer graphene
Integer and fractional quantum anomalous Hall effects in a rhombohedral pentalayer graphene–hBN moiré superlattice are observed, providing an ideal platform for exploring charge fractionalization and (non-Abelian) anyonic braiding at zero magnetic field.
- Zhengguang Lu
- , Tonghang Han
- & Long Ju
-
Article |
 Observation of plaid-like spin splitting in a noncoplanar antiferromagnet
Observation of plaid-like spin splitting in a noncoplanar antiferromagnet
Examining the in-plane spin components of the noncoplanar antiferromagnet manganese ditelluride provides spectroscopic and computational evidence of materials with a new type of plaid-like spin splitting in the antiferromagnetic ground state.
- Yu-Peng Zhu
- , Xiaobing Chen
- & Chang Liu
-
News & Views |
 New type of magnetism splits from convention
New type of magnetism splits from convention
Magnetic materials with zero net magnetization fall into two classes: conventional antiferromagnets and altermagnets. Physicists have identified a property in altermagnets that widens the divide between the two groups.
- Carmine Autieri
-
News & Views |
 Layered ferroelectric materials make waves — and vortices
Layered ferroelectric materials make waves — and vortices
By combining materials-synthesis techniques, researchers have come up with a way of building layered structures that display intriguing wave-like patterns of electric polarization, and could be useful for next-generation electronics.
- Berit H. Goodge
-
Research Briefing |
 Topological matter created on a quantum chip produces quasiparticles with computing power
Topological matter created on a quantum chip produces quasiparticles with computing power
Non-Abelian anyons are emergent quasiparticles found in exotic quantum states of matter, which could have applications in fault-tolerant topological quantum computing. But performing the manipulations necessary to make these quasiparticles has proved a challenge — now overcome through a happy confluence of theoretical and experimental innovation.
-
Article
| Open Access A 2D ferroelectric vortex pattern in twisted BaTiO3 freestanding layers
A 2D ferroelectric vortex pattern in twisted BaTiO3 freestanding layers
The stacking of freestanding ferroelectric perovskite layers with controlled twist angles results in a peculiar pattern of polarization vortices and antivortices that emerges from the flexoelectric coupling of polarization to strain gradients.
- G. Sánchez-Santolino
- , V. Rouco
- & J. Santamaria
-
Article
| Open Access Altermagnetic lifting of Kramers spin degeneracy
Altermagnetic lifting of Kramers spin degeneracy
Using photoemission spectroscopy and ab initio calculations, evidence is given of two distinct unconventional mechanisms of lifted Kramers spin degeneracy generated by the altermagnetic phase of centrosymmetric MnTe with vanishing net magnetization.
- J. Krempaský
- , L. Šmejkal
- & T. Jungwirth
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of superconducting Fermi arcs
Evidence of superconducting Fermi arcs
We provide evidence for superconducting topological Fermi arcs in PbBi2—a Weyl semimetal previously studied mostly for its bulk properties—from which Marjorama fermions could be derived for research in quantum computers.
- Andrii Kuibarov
- , Oleksandr Suvorov
- & Sergey Borisenko
-
Article
| Open Access Signatures of a surface spin–orbital chiral metal
Signatures of a surface spin–orbital chiral metal
A spin–orbital- and angular-momentum-sensitive methodology used to study Sr2RuO4 reveals subtle spectroscopic signatures that are consistent with the formation of spin–orbital chiral currents at the surface of the material.
- Federico Mazzola
- , Wojciech Brzezicki
- & Antonio Vecchione
-
Article |
 Observation and quantification of the pseudogap in unitary Fermi gases
Observation and quantification of the pseudogap in unitary Fermi gases
This study describes experiments with ultracold lithium Fermi gases in which many-body pairing leads to the emergence of a pseudogap, and it confirms theoretical predictions relevant to cuprate superconductivity.
- Xi Li
- , Shuai Wang
- & Jian-Wei Pan
-
Article |
 Observing dynamical phases of BCS superconductors in a cavity QED simulator
Observing dynamical phases of BCS superconductors in a cavity QED simulator
The dynamical phases of out-of-equilibrium Bardeen–Cooper–Schrieffer superconductors have been simulated using cold atoms levitated inside an optical cavity.
- Dylan J. Young
- , Anjun Chu
- & James K. Thompson
-
Article |
 Tuning commensurability in twisted van der Waals bilayers
Tuning commensurability in twisted van der Waals bilayers
Using valley-resolved scanning tunnelling spectroscopy, twisted WSe2 bilayers are studied, including incommensurate dodecagon quasicrystals at 30° and commensurate moiré crystals at 21.8° and 38.2°.
- Yanxing Li
- , Fan Zhang
- & Chih-Kang Shih
-
Article |
 Two-dimensional heavy fermions in the van der Waals metal CeSiI
Two-dimensional heavy fermions in the van der Waals metal CeSiI
We present comprehensive thermodynamic and spectroscopic evidence for an antiferromagnetically ordered heavy-fermion ground state in the van der Waals metal CeSiI.
- Victoria A. Posey
- , Simon Turkel
- & Xavier Roy
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of interband Berry phase in laser-driven crystals
Observation of interband Berry phase in laser-driven crystals
The Berry phase is resolved in light-driven crystals, via attosecond interferometry, in which the electronic wavefunction accumulates a geometric phase as it interacts with the laser field, mapping its coherence into the emission of high-order harmonics.
- Ayelet J. Uzan-Narovlansky
- , Lior Faeyrman
- & Nirit Dudovich
-
Article |
 Giant magnetocaloric effect in spin supersolid candidate Na2BaCo(PO4)2
Giant magnetocaloric effect in spin supersolid candidate Na2BaCo(PO4)2
Evidence for a quantum magnetic analogue of a supersolid appears in a recently synthesized antiferromagnet showing a strong magnetocaloric effect of the spin supersolid phase with potential for applications in sub-kelvin refrigeration.
- Junsen Xiang
- , Chuandi Zhang
- & Gang Su
-
News & Views |
 Tailoring graphene for electronics beyond silicon
Tailoring graphene for electronics beyond silicon
The integration of non-silicon semiconductors into systems on chips is needed for advanced power and sensing technologies. A semiconducting graphene ‘buffer’ layer grown on silicon carbide is a step on this path.
- Francesca Iacopi
- & Andrea C. Ferrari
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Bose–Einstein condensates
- Electronic properties and materials
- Ferroelectrics and multiferroics
- Ferromagnetism
- Magnetic properties and materials
- Molecular electronics
- Phase transitions and critical phenomena
- Quantum fluids and solids
- Quantum Hall
- Semiconductors
- Spintronics
- Structure of solids and liquids
- Superconducting properties and materials
- Surfaces, interfaces and thin films
- Topological matter

 Superconducting diode effect and interference patterns in kagome CsV3Sb5
Superconducting diode effect and interference patterns in kagome CsV3Sb5