Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Selective control of parasitic nematodes using bioactivated nematicides
Selective control of parasitic nematodes using bioactivated nematicides
A metabolically bioactivated selective imidazothiazole nematicide shows comparable effectiveness at controlling plant root infection by Meloidogyne incognita to commercial nematicides, which are traditionally nonselective and toxic.
- Andrew R. Burns
- , Rachel J. Baker
- & Peter J. Roy
-
Review Article |
 Computational approaches streamlining drug discovery
Computational approaches streamlining drug discovery
Recent advances in computational approaches and challenges in their application to streamlining drug discovery are discussed.
- Anastasiia V. Sadybekov
- & Vsevolod Katritch
-
Article |
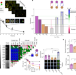 Antibiotic combinations reduce Staphylococcus aureus clearance
Antibiotic combinations reduce Staphylococcus aureus clearance
Different pairs of antibiotics show qualitatively different bacterial clearance interactions—some pairs show reciprocal suppression whereby the drug mixture efficacy is weaker than the individual drugs alone, and the clearance efficacy decreases as more drugs are added.
- Viktória Lázár
- , Olga Snitser
- & Roy Kishony
-
Article
| Open Access A TMPRSS2 inhibitor acts as a pan-SARS-CoV-2 prophylactic and therapeutic
A TMPRSS2 inhibitor acts as a pan-SARS-CoV-2 prophylactic and therapeutic
A small-molecule inhibitor of TMPRSS2 is effective against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in human lung cells and in donor-derived colonoids, and also shows prophylactic and therapeutic benefits in a mouse model of COVID-19.
- Tirosh Shapira
- , I. Abrrey Monreal
- & François Jean
-
Article
| Open Access Effective drug combinations in breast, colon and pancreatic cancer cells
Effective drug combinations in breast, colon and pancreatic cancer cells
A survey of potency and efficacy of 2,025 clinically relevant two-drug combinations against 125 molecularly characterized breast, colorectal and pancreatic cancer cell lines identifies rare synergistic effects of anticancer drugs, informing rational combination treatments for specific cancer subtypes.
- Patricia Jaaks
- , Elizabeth A. Coker
- & Mathew J. Garnett
-
Article |
 Pyrimidine inhibitors synergize with nucleoside analogues to block SARS-CoV-2
Pyrimidine inhibitors synergize with nucleoside analogues to block SARS-CoV-2
A combination of pyrimidine biosynthesis inhibitors and antiviral nucleoside analogues can boost the antiviral effect of nucleoside analogues against SARS-CoV-2.
- David C. Schultz
- , Robert M. Johnson
- & Sara Cherry
-
Article |
 Synthon-based ligand discovery in virtual libraries of over 11 billion compounds
Synthon-based ligand discovery in virtual libraries of over 11 billion compounds
V-SYNTHES, a scalable and computationally cost-effective synthon-based approach to compound screening, identified compounds with a high affinity for CB2 and CB1 in a hierarchical structure-based screen of more than 11 billion compounds.
- Arman A. Sadybekov
- , Anastasiia V. Sadybekov
- & Vsevolod Katritch
-
Article |
 Identification of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors using lung and colonic organoids
Identification of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors using lung and colonic organoids
The use of lung and colonic organoid systems to assess the susceptibility of lung and gut cells to SARS-CoV-2 and to screen FDA-approved drugs that have antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 is demonstrated.
- Yuling Han
- , Xiaohua Duan
- & Shuibing Chen
-
Article |
 Single-particle cryo-EM at atomic resolution
Single-particle cryo-EM at atomic resolution
Advances in electron cryo-microscopy hardware allow proteins to be studied at atomic resolution.
- Takanori Nakane
- , Abhay Kotecha
- & Sjors H. W. Scheres
-
Article |
 Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drugs through large-scale compound repurposing
Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drugs through large-scale compound repurposing
A screen of the ReFRAME library of approximately 12,000 known drugs for antiviral activity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) identified several candidate compounds with suitable activities and pharmacological profiles, which could potentially expedite the deployment of therapies for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
- Laura Riva
- , Shuofeng Yuan
- & Sumit K. Chanda
-
Article |
 An open-source drug discovery platform enables ultra-large virtual screens
An open-source drug discovery platform enables ultra-large virtual screens
VirtualFlow, an open-source drug discovery platform, enables the efficient preparation and virtual screening of ultra-large ligand libraries to identify molecules that bind with high affinity to target proteins.
- Christoph Gorgulla
- , Andras Boeszoermenyi
- & Haribabu Arthanari
-
Article |
 Allele-selective lowering of mutant HTT protein by HTT–LC3 linker compounds
Allele-selective lowering of mutant HTT protein by HTT–LC3 linker compounds
Compounds that interact with mutant huntingtin and an autophagosomal protein are able to reduce cellular levels of mutant huntingtin by targeting it for autophagic degradation, demonstrating an approach that may have potential for treating proteopathies.
- Zhaoyang Li
- , Cen Wang
- & Boxun Lu
-
Letter |
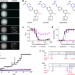 A new class of synthetic retinoid antibiotics effective against bacterial persisters
A new class of synthetic retinoid antibiotics effective against bacterial persisters
Synthetic retinoid compounds can kill both growing and persister MRSA cells by disrupting the membrane lipid bilayer, and are effective in a mouse model of chronic MRSA infection.
- Wooseong Kim
- , Wenpeng Zhu
- & Eleftherios Mylonakis
-
Article |
 Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria
Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria
A screen of more than 1,000 drugs shows that about a quarter of the non-antibiotic drugs inhibit the growth of at least one commensal bacterial strain in vitro.
- Lisa Maier
- , Mihaela Pruteanu
- & Athanasios Typas
-
Letter |
 Proteasome inhibition for treatment of leishmaniasis, Chagas disease and sleeping sickness
Proteasome inhibition for treatment of leishmaniasis, Chagas disease and sleeping sickness
A selective inhibitor of the kinetoplastid proteasome (GNF6702) is identified that is highly efficacious in vivo, clearing the parasites that cause leishmaniasis, Chagas disease and sleeping sickness from mice, highlighting the possibility of developing a single class of drugs for these neglected diseases.
- Shilpi Khare
- , Advait S. Nagle
- & Frantisek Supek
-
Letter |
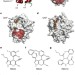 Discovery and characterization of small molecules that target the GTPase Ral
Discovery and characterization of small molecules that target the GTPase Ral
Using a structure-based approach, small molecule inhibitors that selectively target the GTPase Ral are identified and characterized; these first-generation inhibitors will be valuable tools for elucidating the Ral signalling pathway and constitute a step towards developing Ral-specific agents for cancer therapy.
- Chao Yan
- , Degang Liu
- & Dan Theodorescu
-
Article |
 Unexpected link between an antibiotic, pannexin channels and apoptosis
Unexpected link between an antibiotic, pannexin channels and apoptosis
The pannexin 1 channel on the plasma membrane of apoptotic cells mediates the release of find-me molecular signals to attract phagocytic cells for clearance of the apoptotic cells; here the quinolone antibiotic trovafloxacin is identified as a direct inhibitor of pannexin 1, which results in dysregulated fragmentation of apoptotic cells and may partly explain quinolone toxicity.
- Ivan K. H. Poon
- , Yu-Hsin Chiu
- & Kodi S. Ravichandran
-
Letter |
 Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis contributes to biology and drug discovery
Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis contributes to biology and drug discovery
A genome-wide association study meta-analysis of more than 100,000 subjects of European and Asian ancestries reveals 42 new risk loci for rheumatoid arthritis, with follow-up studies identifying 98 biological candidate genes that are either already being targeted by drugs or could be in the future.
- Yukinori Okada
- , Di Wu
- & Robert M. Plenge
-
News & Views |
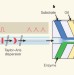 Analog-to-digital drug screening
Analog-to-digital drug screening
Current methods for screening libraries of compounds for biological activity are rather cumbersome, slow and imprecise. A method that breaks up a continuous flow of a compound's solution into droplets offers radical improvements.
- Robert C. R. Wootton
- & Andrew J. deMello
-
News |
 Cells snag top modelling job
Cells snag top modelling job
Heart disorder joins growing list of conditions getting the 'disease in a dish' treatment.
- Ewen Callaway
-
News |
 Breast cancer protein is finally purified
Breast cancer protein is finally purified
Isolation of BRCA2 could help understanding of cancer risk and aid drug screening.
- Alla Katsnelson
-

 Phase separation of FSP1 promotes ferroptosis
Phase separation of FSP1 promotes ferroptosis Testing time for stem cells
Testing time for stem cells