Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Long-range order enabled stability in quantum dot light-emitting diodes
Long-range order enabled stability in quantum dot light-emitting diodes
Improving the long-range order of the quantum dots in perovskite LEDs can markedly enhance their operational stability.
- Ya-Kun Wang
- , Haoyue Wan
- & Liang-Sheng Liao
-
Article |
 Corner- and edge-mode enhancement of near-field radiative heat transfer
Corner- and edge-mode enhancement of near-field radiative heat transfer
Near-field radiative heat transfer between two coplanar silicon carbide membranes in close proximity is enhanced by the electromagnetic corner and edge modes.
- Lei Tang
- , Lívia M. Corrêa
- & Chris Dames
-
Article |
 Phase-change memory via a phase-changeable self-confined nano-filament
Phase-change memory via a phase-changeable self-confined nano-filament
We present a device that can reduce the phase-change memory reset current while maintaining a high on/off ratio, fast speed and small variations, representing advances for neuromorphic computing systems.
- See-On Park
- , Seokman Hong
- & Shinhyun Choi
-
Article |
 Optomechanical realization of the bosonic Kitaev chain
Optomechanical realization of the bosonic Kitaev chain
We report the experimental realization of a bosonic Kitaev chain in a nano-optomechanical network.
- Jesse J. Slim
- , Clara C. Wanjura
- & Ewold Verhagen
-
Article
| Open Access High-fidelity spin qubit operation and algorithmic initialization above 1 K
High-fidelity spin qubit operation and algorithmic initialization above 1 K
Initialization and operation of spin qubits in silicon above 1 K reach fidelities sufficient for fault-tolerant operations at these temperatures.
- Jonathan Y. Huang
- , Rocky Y. Su
- & Chih Hwan Yang
-
Article |
 Graphene nanoribbons grown in hBN stacks for high-performance electronics
Graphene nanoribbons grown in hBN stacks for high-performance electronics
A strategy for the transfer-free direct growth of ultralong, high-quality graphene nanoribbons, which have desirable electronic properties, between layers of a boron nitride insulator is reported.
- Bosai Lyu
- , Jiajun Chen
- & Zhiwen Shi
-
Article |
 Dual quantum spin Hall insulator by density-tuned correlations in TaIrTe4
Dual quantum spin Hall insulator by density-tuned correlations in TaIrTe4
A study reports a dual quantum spin Hall insulator in monolayer TaIrTe4, arising from the interplay of its single-particle topology and density-tuned electron correlations.
- Jian Tang
- , Thomas Siyuan Ding
- & Qiong Ma
-
Article |
 All-electrical skyrmionic magnetic tunnel junction
All-electrical skyrmionic magnetic tunnel junction
Wafer-scale realization of a nanoscale magnetic tunnel junction hosting a single, ambient skyrmion enables its large readout, efficient switching, and compatibility with lateral manipulation, and thereby provides the backbone for all-electrical skyrmionic device architectures.
- Shaohai Chen
- , James Lourembam
- & Anjan Soumyanarayanan
-
Article |
 High-speed and large-scale intrinsically stretchable integrated circuits
High-speed and large-scale intrinsically stretchable integrated circuits
High-density, intrinsically stretchable transistors with high driving ability and integrated circuits with high operation speed and large-scale integration were enabled by a combination of innovations in materials, fabrication process design, device engineering and circuit design.
- Donglai Zhong
- , Can Wu
- & Zhenan Bao
-
Article
| Open Access Light-driven nanoscale vectorial currents
Light-driven nanoscale vectorial currents
Vectorial optoelectronic metasurfaces are described, showing that light pulses can be used to drive and direct local charge flows around symmetry-broken plasmonic nanostructures, leading to tunable responses in terahertz emission.
- Jacob Pettine
- , Prashant Padmanabhan
- & Hou-Tong Chen
-
Article |
 Kerr-induced synchronization of a cavity soliton to an optical reference
Kerr-induced synchronization of a cavity soliton to an optical reference
The passive and electronics-free Kerr-induced synchronization of optical-frequency combs could be used in their control and stabilization and to simplify optical clock systems.
- Grégory Moille
- , Jordan Stone
- & Kartik Srinivasan
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembled photonic cavities with atomic-scale confinement
Self-assembled photonic cavities with atomic-scale confinement
Silicon photonic nanocavities based on surface forces and conventional lithography and etching are developed, demonstrating pioneering technology that integrates atomic dimensions with the scalability of planar semiconductors.
- Ali Nawaz Babar
- , Thor August Schimmell Weis
- & Søren Stobbe
-
Article |
 A superconducting nanowire single-photon camera with 400,000 pixels
A superconducting nanowire single-photon camera with 400,000 pixels
The development of a 400,000-pixel superconducting nanowire single-photon detector array is described, improving the current state of the art by a factor of 400 and showing scalability well beyond the present demonstration.
- B. G. Oripov
- , D. S. Rampini
- & A. N. McCaughan
-
Article |
 Adsorbate motors for unidirectional translation and transport
Adsorbate motors for unidirectional translation and transport
An adsorbate motor that moves unidirectionally on a copper surface is achieved by inducing intramolecular hydrogen transfer in a single molecule.
- Grant J. Simpson
- , Mats Persson
- & Leonhard Grill
-
Article
| Open Access An analog-AI chip for energy-efficient speech recognition and transcription
An analog-AI chip for energy-efficient speech recognition and transcription
A low-power chip that runs AI models using analog rather than digital computation shows comparable accuracy on speech-recognition tasks but is more than 14 times as energy efficient.
- S. Ambrogio
- , P. Narayanan
- & G. W. Burr
-
Perspective |
 The future transistors
The future transistors
The challenges and opportunities for the design of field-effect transistors are discussed and a vision of future transistors and potential innovation opportunities is provided.
- Wei Cao
- , Huiming Bu
- & Kaustav Banerjee
-
Article |
 Harnessing a paper-folding mechanism for reconfigurable DNA origami
Harnessing a paper-folding mechanism for reconfigurable DNA origami
A method is presented to harness the paper-folding mechanism of reconfigurable macroscale systems to create reconfigurable DNA origami structures, in anticipation that it will advance the development of complex molecular systems.
- Myoungseok Kim
- , Chanseok Lee
- & Do-Nyun Kim
-
Article |
 Observation of the orbital Hall effect in a light metal Ti
Observation of the orbital Hall effect in a light metal Ti
The orbital Hall effect is observed in the light metal titanium, confirming the orbital Hall effect and indicating that orbital angular momentum is an important degree of freedom in solids.
- Young-Gwan Choi
- , Daegeun Jo
- & Hyun-Woo Lee
-
Article |
 Many-body cavity quantum electrodynamics with driven inhomogeneous emitters
Many-body cavity quantum electrodynamics with driven inhomogeneous emitters
Under strong excitation, inhomogeneously broadened solid-state emitters coupled with high cooperativity to a cavity demonstrate collectively induced transparency and dissipative many-body dynamics, resulting from cavity–ion coupling.
- Mi Lei
- , Rikuto Fukumori
- & Andrei Faraon
-
Article |
 Ballistic two-dimensional InSe transistors
Ballistic two-dimensional InSe transistors
A two-dimensional field-effect transistor made of indium selenide is shown to outperform state-of-the-art silicon-based transistors, operating at lower supply voltage and achieving record high transconductance and ballistic ratio.
- Jianfeng Jiang
- , Lin Xu
- & Lian-Mao Peng
-
Article |
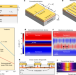 Electronic metadevices for terahertz applications
Electronic metadevices for terahertz applications
Through microscopic manipulation of radiofrequency fields, a new class of compact terahertz devices is proposed, setting the stage for next-generation ultrafast semiconductor electronics.
- Mohammad Samizadeh Nikoo
- & Elison Matioli
-
Article |
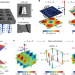 Observation of intrinsic chiral bound states in the continuum
Observation of intrinsic chiral bound states in the continuum
Chiral metasurfaces have been produced, with experimental observation of intrinsic chiral bound states in the continuum, which may lead to applications in chiral light sources and detectors, chiral sensing, valleytronics and asymmetric photocatalysis.
- Yang Chen
- , Huachun Deng
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access An electric molecular motor
An electric molecular motor
An electrically driven motor on the molecular scale based on [3]catenane is described, in which two cyclobis(paraquat-p-phenylene) rings operate by means of redox reactions, demonstrating highly unidirectional movement around a circular loop.
- Long Zhang
- , Yunyan Qiu
- & J. Fraser Stoddart
-
Article |
 Approaching the quantum limit in two-dimensional semiconductor contacts
Approaching the quantum limit in two-dimensional semiconductor contacts
The electrical contact of two-dimensional transistors is pushed close to the quantum limit by hybridization of the energy bands with antimony; the contacts have low contact resistance and excellent stability.
- Weisheng Li
- , Xiaoshu Gong
- & Xinran Wang
-
Article |
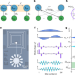 Topological lattices realized in superconducting circuit optomechanics
Topological lattices realized in superconducting circuit optomechanics
Optomechanical lattices in one and two dimensions with exceptionally low disorder are realized, showing how the optomechanical interaction can be exploited for direct measurements of the Hamiltonian, beyond the tight-binding approximation.
- Amir Youssefi
- , Shingo Kono
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article |
 Spin cross-correlation experiments in an electron entangler
Spin cross-correlation experiments in an electron entangler
Spin correlation experiments are demonstrated in an electron entangler device based on the ‘splitting’ of Cooper pairs from a superconductor, which can potentially be used to investigate many fundamental phases and processes related to the electron spin.
- Arunav Bordoloi
- , Valentina Zannier
- & Andreas Baumgartner
-
Article |
 Integrated femtosecond pulse generator on thin-film lithium niobate
Integrated femtosecond pulse generator on thin-film lithium niobate
A femtosecond pulse generator is realized using an electro-optic time-lens system integrated on a lithium niobate photonic chip, capable of tunable repetition rates and wavelengths.
- Mengjie Yu
- , David Barton III
- & Marko Lončar
-
Article |
 A tape-reading molecular ratchet
A tape-reading molecular ratchet
A molecular ratchet, in which a crown ether is pumped from solution onto an encoded molecular strand by a pulse of chemical fuel, opens the way for the reading of information along molecular tapes.
- Yansong Ren
- , Romain Jamagne
- & David A. Leigh
-
Article
| Open Access Universal control of a six-qubit quantum processor in silicon
Universal control of a six-qubit quantum processor in silicon
The universal control of six qubits in a 28Si/SiGe quantum dot array is demonstrated, achieving Rabi oscillations for each qubit with visibilities of 93.5–98.0%, implying high readout and initialization fidelities.
- Stephan G. J. Philips
- , Mateusz T. Mądzik
- & Lieven M. K. Vandersypen
-
Article |
 Femtosecond laser writing of lithium niobate ferroelectric nanodomains
Femtosecond laser writing of lithium niobate ferroelectric nanodomains
We propose and experimentally demonstrate a non-reciprocal near-infrared femtosecond laser-writing technique for reconfigurable three-dimensional nanoscale ferroelectric domain engineering in LiNbO3 crystals.
- Xiaoyi Xu
- , Tianxin Wang
- & Yong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access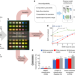 A compute-in-memory chip based on resistive random-access memory
A compute-in-memory chip based on resistive random-access memory
A compute-in-memory neural-network inference accelerator based on resistive random-access memory simultaneously improves energy efficiency, flexibility and accuracy compared with existing hardware by co-optimizing across all hierarchies of the design.
- Weier Wan
- , Rajkumar Kubendran
- & Gert Cauwenberghs
-
Article |
 P-type electrical contacts for 2D transition-metal dichalcogenides
P-type electrical contacts for 2D transition-metal dichalcogenides
Clean van der Waals contacts of high-work-function metals have been demonstrated on few- and single-layered MoS2 and WSe2, leading to p-type characteristics on single-layer MoS2 and purely p-type characteristics on WSe2.
- Yan Wang
- , Jong Chan Kim
- & Manish Chhowalla
-
Perspective |
 Two-dimensional materials prospects for non-volatile spintronic memories
Two-dimensional materials prospects for non-volatile spintronic memories
Developments, challenges and opportunities in using two-dimensional materials for the next generation of non-volatile spin-based memory technologies are reviewed, and possible disruptive improvements are discussed.
- Hyunsoo Yang
- , Sergio O. Valenzuela
- & Stephan Roche
-
Article |
 Non-Hermitian chiral phononics through optomechanically induced squeezing
Non-Hermitian chiral phononics through optomechanically induced squeezing
Time-reversal symmetry breaking is combined with non-Hermitian dynamics in an optomechanical system with squeezing interactions to produce chirality in the system, and a non-Hermitian Aharonov–Bohm effect is observed.
- Javier del Pino
- , Jesse J. Slim
- & Ewold Verhagen
-
Article |
 Light-field control of real and virtual charge carriers
Light-field control of real and virtual charge carriers
Light-field control of real and virtual charge carriers in a gold–graphene–gold heterostructure is demonstrated, and used to create a logic gate for application in lightwave electronics.
- Tobias Boolakee
- , Christian Heide
- & Peter Hommelhoff
-
Article |
 Single electrons on solid neon as a solid-state qubit platform
Single electrons on solid neon as a solid-state qubit platform
A solid-state single-electron qubit platform is demonstrated based on trapping and manipulating isolated single electrons on an ultraclean solid neon surface in vacuum, which performs near the state of the art for a charge qubit.
- Xianjing Zhou
- , Gerwin Koolstra
- & Dafei Jin
-
Article |
 Quantum state preparation and tomography of entangled mechanical resonators
Quantum state preparation and tomography of entangled mechanical resonators
Piezoelectric coupling of a single superconducting qubit to two phononic crystal nanoresonators results in an integrated device that is able to control and read out the quantum state of the two mechanical resonators.
- E. Alex Wollack
- , Agnetta Y. Cleland
- & Amir H. Safavi-Naeini
-
Article |
 Perovskite–organic tandem solar cells with indium oxide interconnect
Perovskite–organic tandem solar cells with indium oxide interconnect
A thin low-loss indium oxide interconnect layer grown by atomic layer deposition enables perovskite–organic hybrid tandem solar cells with a high open-circuit voltage and a high power conversion efficiency.
- K. O. Brinkmann
- , T. Becker
- & T. Riedl
-
Article |
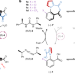 Autonomous fuelled directional rotation about a covalent single bond
Autonomous fuelled directional rotation about a covalent single bond
The molecular chemical ‘fuelling’ of the catalysis-driven motor 1-phenylpyrrole 2,2′-dicarboxylic acid, which operates by a Brownian information ratchet mechanism, facilitates dynamics that are otherwise kinetically inaccessible.
- Stefan Borsley
- , Elisabeth Kreidt
- & Benjamin M. W. Roberts
-
Article |
 Ultrathin ferroic HfO2–ZrO2 superlattice gate stack for advanced transistors
Ultrathin ferroic HfO2–ZrO2 superlattice gate stack for advanced transistors
In the standard Si transistor gate stack, replacing conventional dielectric HfO2 with an ultrathin ferroelectric–antiferroelectric HfO2–ZrO2 heterostructure exhibiting the negative capacitance effect demonstrates ultrahigh capacitance without degradation in leakage and mobility, promising for ferroelectric integration into advanced logic technology.
- Suraj S. Cheema
- , Nirmaan Shanker
- & Sayeef Salahuddin
-
Article |
 Vertical MoS2 transistors with sub-1-nm gate lengths
Vertical MoS2 transistors with sub-1-nm gate lengths
Ultra-scaled transistors based on two-dimensional MoS2 with physical gate lengths of 0.34 nm are reported, which show relatively good electrical characteristics and can be switched off.
- Fan Wu
- , He Tian
- & Tian-Ling Ren
-
Article |
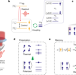 Nuclear spin-wave quantum register for a solid-state qubit
Nuclear spin-wave quantum register for a solid-state qubit
Via spin-exchange interactions with 51V5+ ions, an optically addressed 171Yb3+ qubit in a nuclear-spin-rich yttrium orthovanadate crystal is used to implement a reproducible nuclear-spin-based quantum memory, and entangled Yb–V Bell states are demonstrated.
- Andrei Ruskuc
- , Chun-Ju Wu
- & Andrei Faraon
-
Article |
 Fast universal quantum gate above the fault-tolerance threshold in silicon
Fast universal quantum gate above the fault-tolerance threshold in silicon
Single- and two-qubit gate fidelities above the fault-tolerance threshold for quantum computation are demonstrated in silicon quantum dots by fast electrical control using a micromagnet-induced gradient field and tunable coupling.
- Akito Noiri
- , Kenta Takeda
- & Seigo Tarucha
-
Article |
 Precision tomography of a three-qubit donor quantum processor in silicon
Precision tomography of a three-qubit donor quantum processor in silicon
Universal quantum logic operations with fidelity exceeding 99%, approaching the threshold of fault tolerance, are realized in a scalable silicon device comprising an electron and two phosphorus nuclei, and a fidelity of 92.5% is obtained for a three-qubit entangled state.
- Mateusz T. Mądzik
- , Serwan Asaad
- & Andrea Morello
-
Article |
 On-chip electro-optic frequency shifters and beam splitters
On-chip electro-optic frequency shifters and beam splitters
Engineering of the coupling between optical modes in a lithium niobate chip enables the realization of tunable, bi-directional and low-loss electro-optic frequency shifters controlled using only continuous and single-tone microwaves.
- Yaowen Hu
- , Mengjie Yu
- & Marko Lončar
-
Article |
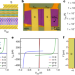 Approaching the intrinsic exciton physics limit in two-dimensional semiconductor diodes
Approaching the intrinsic exciton physics limit in two-dimensional semiconductor diodes
Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide diodes with defect-free van der Waals contacts allows minimization of the extrinsic interfacial disorder-dominated recombination and access to the intrinsic excitonic behaviour in two-dimensional semiconductor devices.
- Peng Chen
- , Timothy L. Atallah
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Article |
 Electron phase-space control in photonic chip-based particle acceleration
Electron phase-space control in photonic chip-based particle acceleration
In a tiny chip-based particle accelerator, phase-space control of the emerging electron beam demonstrates guiding over a length of nearly 80 micrometres and an indispensable prerequisite to electron acceleration to high energies.
- R. Shiloh
- , J. Illmer
- & P. Hommelhoff
-
Article |
 Tunable self-assembled Casimir microcavities and polaritons
Tunable self-assembled Casimir microcavities and polaritons
Gold nanoflake pairs form by self-assembly in an aqueous ligand solution and offer stable and tunable microcavities by virtue of equilibrium between attractive Casimir forces and repulsive electrostatic forces.
- Battulga Munkhbat
- , Adriana Canales
- & Timur O. Shegai
-
Article |
 Actively variable-spectrum optoelectronics with black phosphorus
Actively variable-spectrum optoelectronics with black phosphorus
High-performance optoelectronic devices that operate in the infrared regime at room temperature exhibit wide-range, active and reversible tunability of the operating wavelengths with black phosphorus.
- Hyungjin Kim
- , Shiekh Zia Uddin
- & Ali Javey

 Full-colour 3D holographic augmented-reality displays with metasurface waveguides
Full-colour 3D holographic augmented-reality displays with metasurface waveguides