Featured
-
-
Perspective
| Open Access Rediscovery of mononuclear phagocyte system blockade for nanoparticle drug delivery
Rediscovery of mononuclear phagocyte system blockade for nanoparticle drug delivery
Temporal blockade of the mononuclear phagocyte system is an approach to enhance the therapeutic efficiency of nanocarrier drug-delivery systems but the broad applicability is hindered by the complexity of optimisation and management of potential side effects. Here, the authors review the development of this technique and show its efficiency using meta-analysis of the published data and discuss essential features for its successful translation to clinic.
- Ivan V. Zelepukin
- , Konstantin G. Shevchenko
- & Sergey M. Deyev
-
Article
| Open Access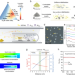 General synthesis of ionic-electronic coupled two-dimensional materials
General synthesis of ionic-electronic coupled two-dimensional materials
2D AMX2 compounds (where A is a monovalent metal ion, M is a trivalent metal, and X is a chalcogen) are a family of materials with coupled ionic-electronic properties. Here, the authors report a chemical vapor deposition strategy to fabricate 20 types of 2D AMX2 flakes, exhibiting superionic conductivity or room temperature ferroelectricity.
- Xiang Xu
- , Yunxin Chen
- & Tianyou Zhai
-
Article
| Open Access Electrostatic-induced ion-confined partitioning in graphene nanolaminate membrane for breaking anion–cation co-transport to enhance desalination
Electrostatic-induced ion-confined partitioning in graphene nanolaminate membrane for breaking anion–cation co-transport to enhance desalination
Two-dimensional graphene-based membranes have gained much interest, but they suffer from poor rejection for monovalent salts. Here, the authors develop an electrostatic-induced ion partitioning strategy to suppress anion-cation transmembrane co-transport, improving the desalination performance.
- Haiguang Zhang
- , Jiajian Xing
- & Xie Quan
-
Article
| Open Access Firing feature-driven neural circuits with scalable memristive neurons for robotic obstacle avoidance
Firing feature-driven neural circuits with scalable memristive neurons for robotic obstacle avoidance
The authors proposed a strategy for sensorimotor control using memristive H-H neurons, integrating bio-inspired neural circuits and computational capabilities of neurons’ firing features with a robot for avoidance control.
- Yue Yang
- , Fangduo Zhu
- & Ming Liu
-
Article
| Open Access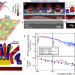 Bounds to electron spin qubit variability for scalable CMOS architectures
Bounds to electron spin qubit variability for scalable CMOS architectures
Understanding the microscopic variability of CMOS spin qubits is crucial for developing scalable quantum processors. Here the authors report a combined experimental and numerical study of the effect of interface roughness on variability of quantum dot spin qubits formed at the Si/SiO2 interface.
- Jesús D. Cifuentes
- , Tuomo Tanttu
- & Andre Saraiva
-
Article
| Open Access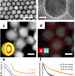 Bright and durable scintillation from colloidal quantum shells
Bright and durable scintillation from colloidal quantum shells
Traditional scintillators face challenges in achieving fast response and avoiding afterglow. Guzelturk et al. report colloidal quantum shell heterostructures with bright multiexciton emission, enabling efficient, fast, and robust scintillation for high-resolution and high-speed X-ray imaging.
- Burak Guzelturk
- , Benjamin T. Diroll
- & Mikhail Zamkov
-
Article
| Open Access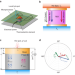 Thermoelectric active cooling for transient hot spots in microprocessors
Thermoelectric active cooling for transient hot spots in microprocessors
The authors model the transient temperature response of micro-thermoelectric devices with AC current applied, which is locally integrated under a transient hot spot. They develop a strategy for actively canceling the transient temperature variations.
- Yihan Liu
- , Hao-Yuan Cheng
- & Feng Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Centimeter-scale nanomechanical resonators with low dissipation
Centimeter-scale nanomechanical resonators with low dissipation
Exploring new mechanics regime, researchers created centimeter-long, nanometer-thin resonators, achieving unmatched room temperature mechanical isolation via cutting edge nanoengineering and machine learning design; rivaling cryogenic counterparts.
- Andrea Cupertino
- , Dongil Shin
- & Richard A. Norte
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for multiferroicity in single-layer CuCrSe2
Evidence for multiferroicity in single-layer CuCrSe2
The authors observe multiferroicity in a single-layer non van der Waals material, CuCrSe2. The coexistence of room-temperature ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism up to 120 K is corroborated by a set of comprehensive experimental techniques.
- Zhenyu Sun
- , Yueqi Su
- & Baojie Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Electric pulse-tuned piezotronic effect for interface engineering
Electric pulse-tuned piezotronic effect for interface engineering
Interface engineering by local polarization is becoming increasingly important for tunable electronics. Here, authors demonstrate an electric pulse-tuned piezotronic effect in Ag/HfO2/n-ZnO junction, enabling reversible and accurate regulation of barrier height and piezotronic modification range.
- Qiuhong Yu
- , Rui Ge
- & Yong Qin
-
Article
| Open Access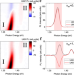 Tunable exciton valley-pseudospin orders in moiré superlattices
Tunable exciton valley-pseudospin orders in moiré superlattices
Control of correlated excitonic states is a key goal of modern optoelectronic physics. Here, the authors demonstrate filling- and field-tunable exciton valley-pseudospin orders in a moiré heterostructure.
- Richen Xiong
- , Samuel L. Brantly
- & Chenhao Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamically stable radiation pressure propulsion of flexible lightsails for interstellar exploration
Dynamically stable radiation pressure propulsion of flexible lightsails for interstellar exploration
Ultrathin laser-driven lightsails represent a unique vision for interstellar space exploration. Here, the authors show how spinning flexible membranes can be both shape- and trajectory-stable with multiphysics structural and nanophotonic engineering.
- Ramon Gao
- , Michael D. Kelzenberg
- & Harry A. Atwater
-
Article
| Open Access Remote epitaxy of single-crystal rhombohedral WS2 bilayers
Remote epitaxy of single-crystal rhombohedral WS2 bilayers
Rhombohedral-stacked (R-stacked) transition metal dichalcogenide bilayers exhibit remarkable properties, but their large-area epitaxial growth remains challenging. Here, the authors report the remote epitaxy of centimetre-scale single-crystal R-stacked WS2 bilayer films on sapphire substrates.
- Chao Chang
- , Xiaowen Zhang
- & Xiaozhi Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic microfluidic single-cell screening identifies pheno-tuning compounds to potentiate tuberculosis therapy
Dynamic microfluidic single-cell screening identifies pheno-tuning compounds to potentiate tuberculosis therapy
Tuberculosis is a major global health threat. Here, the authors develop a single-cell drug discovery approach and identify a compound that tunes bacterial phenotypic variation. This enhances the activity of anti-tubercular drugs against the pathogen.
- Maxime Mistretta
- , Mena Cimino
- & Giulia Manina
-
Article
| Open Access Spontaneously established reverse electric field to enhance the performance of triboelectric nanogenerators via improving Coulombic efficiency
Spontaneously established reverse electric field to enhance the performance of triboelectric nanogenerators via improving Coulombic efficiency
Performance of triboelectric nanogenerators is limited by electrostatic breakdown. Here, the spontaneously established reverse electric field is introduced to restrict the side-discharge problem caused by electrostatic breakdown, leading to a high Coulombic efficiency and enhanced output power.
- Yikui Gao
- , Lixia He
- & Jie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access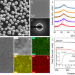 Dual-phase nano-glass-hydrides overcome the strength-ductility trade-off and magnetocaloric bottlenecks of rare earth based amorphous alloys
Dual-phase nano-glass-hydrides overcome the strength-ductility trade-off and magnetocaloric bottlenecks of rare earth based amorphous alloys
Metals often suffer from reduced strength and ductility after hydrogenation. Here, the authors show hydrogenation can lead to enhancement in strength and ductility accompanied by a large change in magnetic entropy, overcoming the bottlenecks of using amorphous alloys for magnetic refrigerants.
- Liliang Shao
- , Qiang Luo
- & Weihua Wang
-
Article
| Open Access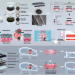 E-cardiac patch to sense and repair infarcted myocardium
E-cardiac patch to sense and repair infarcted myocardium
Infarted myocardium hampers the synchronous electroactivity of the cardiac tissue. Here, the authors showcase a battery-free conductive cardiac patch made of reduced graphene and its therapeutic efficacy for cardiac repair.
- Renjie Qiu
- , Xingying Zhang
- & Leyu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental demonstration of an on-chip p-bit core based on stochastic magnetic tunnel junctions and 2D MoS2 transistors
Experimental demonstration of an on-chip p-bit core based on stochastic magnetic tunnel junctions and 2D MoS2 transistors
Probabilistic bits (p-bits) are the base units of probabilistic computing, a computing scheme offering a more efficient approach than conventional binary logic in various applications. Here, the authors report the realization of a p-bit core device by combining stochastic magnetic tunnel junctions and 2D MoS2 transistors on the same chip.
- John Daniel
- , Zheng Sun
- & Joerg Appenzeller
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular fingerprinting of biological nanoparticles with a label-free optofluidic platform
Molecular fingerprinting of biological nanoparticles with a label-free optofluidic platform
Biosensing tools to detect multiple analytes in a high-throughput manner are still hindered by many limitations. Here, the authors present a label-free optofluidic platform integrating digital holography and microfluidics for analyte detection, allowing for the fingerprinting of heterogenous biological samples.
- Alexia Stollmann
- , Jose Garcia-Guirado
- & Romain Quidant
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrastrong magnon-magnon coupling and chiral spin-texture control in a dipolar 3D multilayered artificial spin-vortex ice
Ultrastrong magnon-magnon coupling and chiral spin-texture control in a dipolar 3D multilayered artificial spin-vortex ice
Extending magnetic nanostructures into three dimensions offers a vast increase in potential functionalities, but this typically comes at the expense of ease of fabrication and measurement. Here, Dion et al. demonstrate an approach to creating three dimensional magnetic nanostructures while retaining easy fabrication and readout of established two dimensional approaches.
- Troy Dion
- , Kilian D. Stenning
- & Jack C. Gartside
-
Article
| Open Access Synergistic growth of nickel and platinum nanoparticles via exsolution and surface reaction
Synergistic growth of nickel and platinum nanoparticles via exsolution and surface reaction
Utilizing “Chemistry at a point”, Ni is exsolved from a perovskite lattice under deposited Pt nanoparticles. This yields even smaller Ni Pt alloy nanoparticles on a perovskite nanofiber structure, exhibiting high catalytic activity.
- Min Xu
- , Yukwon Jeon
- & John T. S. Irvine
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning instability in suspended monolayer 2D materials
Tuning instability in suspended monolayer 2D materials
Tuning the instabilities of 2D materials can control their wrinkling behavior for interesting physical properties, but still challenging. Here, the authors report a push-to-shear experimental approach to control the wrinkling patterns of monolayer 2D materials and measure their bending stiffness.
- Yuan Hou
- , Jingzhuo Zhou
- & Yang Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-narrowband and rainbow-free mid-infrared thermal emitters enabled by a flat band design in distorted photonic lattices
Ultra-narrowband and rainbow-free mid-infrared thermal emitters enabled by a flat band design in distorted photonic lattices
Narrowband thermal emitters realized with photonic nanostructures usually suffer from the rainbow effect. Here, the authors demonstrate rainbow-free thermal emissions with high temporal coherence through harnessing flatband high-Q resonances.
- Kaili Sun
- , Yangjian Cai
- & Zhanghua Han
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochemical-repaired porous graphene membranes for precise ion-ion separation
Electrochemical-repaired porous graphene membranes for precise ion-ion separation
The preparation of atom-thick lattices with Å-scale pores is desirable for achieving ion selectivity and high ion flux. Here authors present a cm-scale membrane made of atom-thick graphene film hosting zero-dimensional pores spanning only a few Å, repaired using an in situ electrochemical strategy, yielding high Li+/Mg2+ separation performance.
- Zongyao Zhou
- , Kangning Zhao
- & Kumar Varoon Agrawal
-
Article
| Open Access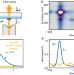 Cavity-enhanced photon indistinguishability at room temperature and telecom wavelengths
Cavity-enhanced photon indistinguishability at room temperature and telecom wavelengths
Carbon nanotube-based single photon emitters allow for room-temperature operation, but suffer from vanishing indistinguishability due to strong dephasing. Following a theoretical proposal, the authors tackle the problem experimentally by using a cavity to enhance the photon coherence time and the emission spectral density in the regime of incoherent good cavity-coupling.
- Lukas Husel
- , Julian Trapp
- & Alexander Högele
-
Article
| Open Access Firefly-inspired bipolar information indication system actuated by white light
Firefly-inspired bipolar information indication system actuated by white light
Inspired by fireflies, a bimodal information indication system using a photochemical afterglow material within a photonic crystal matrix is developed to display both static and changing information, such as sample type and degree of degradation.
- Hanwen Huang
- , Jiamiao Yin
- & Changchun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Halide Perovskite Inducing Anomalous Nonvolatile Polarization in Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based Flexible Nanocomposites
Halide Perovskite Inducing Anomalous Nonvolatile Polarization in Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based Flexible Nanocomposites
Wang et al. report large nonvolatile polarization in stretchable polymer ferroelectrics incorporating perovskite nanocrystals. The built-in electric field from poled ferroelectrics stabilises Frenkel defects via interfacial coupling, which can also enhance the polarization of nonferroelectrics.
- Yao Wang
- , Chen Huang
- & Jiangyu Li
-
Article
| Open Access Single-photon detection using large-scale high-temperature MgB2 sensors at 20 K
Single-photon detection using large-scale high-temperature MgB2 sensors at 20 K
Superconducting nanowire single-photon detectors require operation at T < 4 K, and successful attempts to extend their operation at 20 K and above using high-TC BSCCO flakes come at the cost of lower scalability to large areas. Here, the authors break this trade-off by using high-quality MgB2 films and exploiting a helium-ion beam-based irradiation process.
- Ilya Charaev
- , Emma K. Batson
- & Karl K. Berggren
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Technical challenges of studying the impact of plasma components on the efficacy of lipid nanoparticles for vaccine and therapeutic applications
Technical challenges of studying the impact of plasma components on the efficacy of lipid nanoparticles for vaccine and therapeutic applications
- Jens B. Simonsen
-
Article
| Open Access Bicontinuous RuO2 nanoreactors for acidic water oxidation
Bicontinuous RuO2 nanoreactors for acidic water oxidation
Developing stable water oxidation catalysts is of great importance for proton-exchange membrane water electrolyzers. Here the authors report a bicontinuous nanoreactor composed of multiscale defected RuO2 nanocrystals for robust acidic water oxidation reactivity.
- Ding Chen
- , Ruohan Yu
- & Shichun Mu
-
Article
| Open Access Implication of thermal signaling in neuronal differentiation revealed by manipulation and measurement of intracellular temperature
Implication of thermal signaling in neuronal differentiation revealed by manipulation and measurement of intracellular temperature
The role of subcellular thermogenesis during neuronal differentiation remains poorly understood. Here, the authors employ methods to monitor local intracellular temperature, and they investigate the effects of non-invasive temperature changes on cell differentiation using neuron-like cells.
- Shunsuke Chuma
- , Kazuyuki Kiyosue
- & Yoshie Harada
-
Article
| Open Access Correlating activities and defects in (photo)electrocatalysts using in-situ multi-modal microscopic imaging
Correlating activities and defects in (photo)electrocatalysts using in-situ multi-modal microscopic imaging
Physicochemical heterogeneity poses a significant constraint in photocatalyst advancement. Here the authors introduce a multimodal optical microscopy platform to assess activity and defects concurrently in photoelectrocatalysts, revealing that disorder can unexpectedly enhance local photoelectrocatalytic performance in certain instances.
- Camilo A. Mesa
- , Michael Sachs
- & Raj Pandya
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembly of nanocrystal checkerboard patterns via non-specific interactions
Self-assembly of nanocrystal checkerboard patterns via non-specific interactions
The self-assembly of nanocrystals into checkerboard lattice patterns is difficult to control. Here, the authors investigate the formation of such patterns from hydrophilic/hydrophobic bifunctionalized Ag nanocubes and use multiscale simulations to understand the effects of physical forces.
- Yufei Wang
- , Yilong Zhou
- & Andrea R. Tao
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of crystal facets in plasmonic catalysis
Effect of crystal facets in plasmonic catalysis
Crystal facets are known to be important in traditional heterogeneous catalysis, yet this effect has not been studied in plasmon-assisted catalysis. Here, the authors investigate the impact facets have on CO2 reduction using plasmonic Au NPs.
- Yicui Kang
- , Simão M. João
- & Emiliano Cortés
-
Review Article
| Open Access Critical learning from industrial catalysis for nanocatalytic medicine
Critical learning from industrial catalysis for nanocatalytic medicine
The knowledge gained from industrial catalysis benefits advancements of nanocatalytic medicines. Here the authors review the similarities, differences and connections in catalytic reactions between industrial and medical applications to support deep understanding and rational design of nanocatalytic medicines.
- Zhaokui Jin
- , Lingdong Jiang
- & Qianjun He
-
Article
| Open Access Capture of single Ag atoms through high-temperature-induced crystal plane reconstruction
Capture of single Ag atoms through high-temperature-induced crystal plane reconstruction
Terminal hydroxyl groups on γ-Al2O3 surfaces serve as anchoring sites for Ag. Based on the surface energy of different crystal planes of γ-Al2O3 at various temperatures, the authors propose a high-temperature-induced crystal plane transformation method to construct terminal hydroxyl anchoring sites.
- Jiaxin Li
- , Kai Li
- & Hong He
-
Article
| Open Access Universal Murray’s law for optimised fluid transport in synthetic structures
Universal Murray’s law for optimised fluid transport in synthetic structures
Improving mass transfer through hierarchically porous synthetic materials is a great challenge. Here the authors address this by expanding the original Murray’s law, a biomimetic principle defining the branching of veins in living structures.
- Binghan Zhou
- , Qian Cheng
- & Tawfique Hasan
-
Article
| Open Access A fast-charging/discharging and long-term stable artificial electrode enabled by space charge storage mechanism
A fast-charging/discharging and long-term stable artificial electrode enabled by space charge storage mechanism
Lithium-ion batteries with fast-charging properties are urgently needed for wide adoption of electric vehicles. Here, the authors show a fast charging/discharging and long-term stable electrode made from a mixed electronic/ionic conductor material enabled by a space charge mechanism.
- Linyi Zhao
- , Tiansheng Wang
- & Guihua Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic molecular switches driven by DNA-modifying enzymes
Synthetic molecular switches driven by DNA-modifying enzymes
Molecular switches are ubiquitous in the biochemistry regulatory network. Here, the authors construct synthetic molecular switches controlled by DNA-modifying enzymes such as DNA polymerase and nicking endonuclease to control and cascade assembly and disassembly.
- Hong Kang
- , Yuexuan Yang
- & Bryan Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-site integrated optical addressing of trapped ions
Multi-site integrated optical addressing of trapped ions
A promising strategy for scaling trapped-ion-based quantum technologies is to use fully integrated optical waveguides to deliver light to numerous ions at multiple sites. Here, the authors. optically address three ions using on-chip waveguides to deliver three distinct wavelengths per ion, and perform Rabi flopping on each ion simultaneously.
- Joonhyuk Kwon
- , William J. Setzer
- & Hayden J. McGuinness
-
Article
| Open Access Tunneling current-controlled spin states in few-layer van der Waals magnets
Tunneling current-controlled spin states in few-layer van der Waals magnets
Magnetic tunnel junctions consist of two magnetic layers, separated by a thin insulator. The simplicity belies the industrial importance: magnetic tunnel junctions have a very wide variety of applications in contemporary society. Here, Fu et al present a magnetic tunnel junction composed of single van der Waals magnetic insulator, CrI3, exhibiting remarkably low power consumption.
- ZhuangEn Fu
- , Piumi I. Samarawickrama
- & Jifa Tian
-
Article
| Open Access An artificial visual neuron with multiplexed rate and time-to-first-spike coding
An artificial visual neuron with multiplexed rate and time-to-first-spike coding
Multiplexed spiking data coding schemes could enable artificial visual neurons to emulate the human visual system in a more biologically plausible way. Here, Li et al. present an artificial neuron device capable of encoding visual analog signals into spike trains using multiplexed rate and temporal fusion coding. Reviewer recognition:
- Fanfan Li
- , Dingwei Li
- & Bowen Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Biocomposite thermoplastic polyurethanes containing evolved bacterial spores as living fillers to facilitate polymer disintegration
Biocomposite thermoplastic polyurethanes containing evolved bacterial spores as living fillers to facilitate polymer disintegration
Plastic pollution severely threatens the resilience of nature. Here, the authors utilize the spore-forming, polymer-degrading bacteria, Bacillus subtilis, as a living filler to develop biocomposite thermoplastic polyurethane with improved mechanical properties and biodegradation.
- Han Sol Kim
- , Myung Hyun Noh
- & Jonathan K. Pokorski
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated 2D multi-fin field-effect transistors
Integrated 2D multi-fin field-effect transistors
Here, the authors report the ledge-guided epitaxial growth of high-density 2D Bi2O2Se fin arrays and their application for the realization of 2D multi-channel fin field-effect transistors, showing improved on-state currents as the number of integrated channels is increased.
- Mengshi Yu
- , Congwei Tan
- & Hailin Peng
-
Article
| Open Access In situ enzymatic control of colloidal phoresis and catalysis through hydrolysis of ATP
In situ enzymatic control of colloidal phoresis and catalysis through hydrolysis of ATP
The design of synthetic systems that can sense chemical gradients and respond with directional motility and chemical activity is of interest. Here, the authors realize and control such behaviors in a synthetic system by tailoring multivalent interactions of adenosine nucleotides with catalytic microbeads.
- Ekta Shandilya
- , Bhargav Rallabandi
- & Subhabrata Maiti
-
Article
| Open Access All-natural 2D nanofluidics as highly-efficient osmotic energy generators
All-natural 2D nanofluidics as highly-efficient osmotic energy generators
Researchers report a sustainable nanofluidic osmotic energy harvester made from natural montmorillonite clay nanosheets and recycled cellulose. Scaled-up films of 700 cm2 show power output of 8 W m−2 with stability over 30 days
- Jiadong Tang
- , Yun Wang
- & Tieyong Zuo
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature low-threshold avalanche effect in stepwise van-der-Waals homojunction photodiodes
Room-temperature low-threshold avalanche effect in stepwise van-der-Waals homojunction photodiodes
The avalanche or carrier-multiplication effect has the potential to improve the performance of photodetectors and solar cells, but usually requires high threshold energies. Here, the authors report stepwise WSe2 homojunctions exhibiting threshold energies approaching the semiconductor bandgap at room temperature.
- Hailu Wang
- , Hui Xia
- & Wei Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing hidden spin polarization in centrosymmetric van der Waals materials on ultrafast timescales
Revealing hidden spin polarization in centrosymmetric van der Waals materials on ultrafast timescales
A major challenge for spin-based information technologies is the generation of spin polarization in otherwise nonmagnetic materials. Here, Arnoldi et al. demonstrate how ultrafast laser excitations can be used to generate spin polarization in a fullerene/tungsten diselenide heterostructure.
- B. Arnoldi
- , S. L. Zachritz
- & B. Stadtmüller
-
Article
| Open Access Staggered structural dynamic-mediated selective adsorption of H2O/D2O on flexible graphene oxide nanosheets
Staggered structural dynamic-mediated selective adsorption of H2O/D2O on flexible graphene oxide nanosheets
Graphene oxide is a promising material for molecular separation technologies. Here, the authors propose a realistic staggered stacking structure that plays a crucial role in H/D recognition in water adsorption, as well as high mobilities of water.
- Ryusuke Futamura
- , Taku Iiyama
- & Katsumi Kaneko

 Heat-activated growth of metastable and length-defined DNA fibers expands traditional polymer assembly
Heat-activated growth of metastable and length-defined DNA fibers expands traditional polymer assembly