Featured
-
-
Note
| Open Access Molecular dynamics simulation of complexation between plasmid DNA and cationic peptides
Molecular dynamics simulation of complexation between plasmid DNA and cationic peptides
Atomic molecular dynamics simulations of the complexation of plasmid DNA in the presence of two types of cationic peptides clear the mechanism of plasmid DNA condensation for gene delivery systems.
- Kousuke Tsuchiya
- , Joan Gimenez-Dejoz
- & Keiji Numata
-
Original Article |
 Adhesive-ligand-independent cell-shaping controlled by the lateral deformability of a condensed polymer matrix
Adhesive-ligand-independent cell-shaping controlled by the lateral deformability of a condensed polymer matrix
To clarify the role of lateral deformation of condensed polymer surface on cell adhesion, the responses of cell spreading were characterized at a cell culture temperature on the poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-grafted surfaces with different degree of graft-polymerization (DGP). A clear negative correlation between cell spreading and DGP of PNIPAAm was found regardless of the amount of fibronectin adsorbed on the substrates. The microscopic local strain of the condensed polymers by cellular traction forces was considered to modulate the density distribution of adsorbed adhesive ligands beneath the focal adhesions and the cell spreading.
- Sayaka Masaike
- , Saori Sasaki
- & Satoru Kidoaki
-
Original Article |
 Simulation study for the pulling translocation of a polymer globule
Simulation study for the pulling translocation of a polymer globule
Scaling relations of pulling translocation of a polymer globule through nanopores is studied by using the Langevin dynamics simulations. Under a constant pulling force, the scaling exponent is dependent on the intrapolymer interaction strength. Whereas under a constant pulling speed, it is independent of the intrapolymer interaction strength for sufficiently long polymer chains. The conformational changes of the polymer chain during the translocation and the entropic and enthalpic forces due to the straight conformation at the trans side play important roles on the pulling translocation of a polymer globule.
- Xian Chen
- , Jia Chen
- & Meng-Bo Luo
-
Focus Review |
 A new approach to explore the mechanoresponsiveness of microtubules and its application in studying dynamic soft interfaces
A new approach to explore the mechanoresponsiveness of microtubules and its application in studying dynamic soft interfaces
Recent studies on exploration of mechanical deformation of microtubules under tensile and compressive stress, using a newly developed methodology, have been reviewed. In the first part of this review article, development of the methodology and its utility in studying the mechanoresponsiveness of microtubules have been described. In the second part, applications of the recently developed methodology in studying dynamic soft interfaces have been elaborately discussed.
- Arif Md. Rashedul Kabir
- & Akira Kakugo
-
Review
| Open Access Stimuli-responsive hydrogels as a model of the dynamic cellular microenvironment
Stimuli-responsive hydrogels as a model of the dynamic cellular microenvironment
Stimulus-responsive hydrogels are highly attractive as the surrogate materials that can simulate dynamic mechanical microenvironments surrounding biological cells in vivo. This review tries to provide with comprehensive overviews on the previous achievements, present pitfalls and challenges, and future perspectives on the recent development on stimulus-responsive hydrogel materials for the dynamic control of cell behaviors.
- Motomu Tanaka
- , Masaki Nakahata
- & Stefan Kaufmann
-
Original Article |
 Comparison of microtubules stabilized with the anticancer drugs cevipabulin and paclitaxel
Comparison of microtubules stabilized with the anticancer drugs cevipabulin and paclitaxel
Stabilization of microtubules occurs by paclitaxel bound to the taxoid site and cevipabulin (and its derivative) bound to the taxoid site and/or vinca alkaloid domain of the β-tubulin in tubulin heterodimer.
- Syeda Rubaiya Nasrin
- , Tsukasa Ishihara
- & Akira Kakugo
-
Original Article |
 Effect of microtubule immobilization by glutaraldehyde on kinesin-driven cargo transport
Effect of microtubule immobilization by glutaraldehyde on kinesin-driven cargo transport
The graphical abstract shows that the kinesin-driven quantum dot transport along microtubule immobilized on a substrate using glutaraldehyde concentration ≤0.10% (v/v) remain unaltered, whereas, at higher glutaraldehyde concentration, >0.10% (v/v), the quantum dot transportation is slowed down.
- Syeda Rubaiya Nasrin
- , Arif Md. Rashedul Kabir
- & Akira Kakugo
-
Original Article |
 Viscoelasticity of poly(ethylene glycol) in aqueous solutions of potassium sulfate: a comparison of quartz crystal microbalance with conventional methods
Viscoelasticity of poly(ethylene glycol) in aqueous solutions of potassium sulfate: a comparison of quartz crystal microbalance with conventional methods
Viscoelasticity of PEG in aqueous solutions containing different concentrations of K2SO4 was studied by QCM-D, after coating a rigid supported lipid bilayer on the silicon oxide substrate. The obtained viscoelastic properties of PEG in K2SO4 solutions agree well with the Zimm model predictions for linear polymer chains. The gradual worsening of solvent quality by adding K2SO4 to aqueous PEG solutions is demonstrated by the obtained excluded volume exponents via QCM-D and the conventional intrinsic viscosity measurements.
- Xiaoxue Wu
- , Ziliang Zhao
- & Yonggang Liu
-
Focus Review |
 Study of active self-assembly using biomolecular motors
Study of active self-assembly using biomolecular motors
Recent advances in the study of active self-assembly utilizing biomolecular motors are reviewed. Various methodologies developed for demonstrating active self-assembly of biomolecular motors are discussed in detail with an emphasis on the morphological variations of the self-assembled structures.
- Arif Md. Rashedul Kabir
- & Akira Kakugo
-
Review |
 Water near bioinert self-assembled monolayers
Water near bioinert self-assembled monolayers
Recent works revealed that protein and cell resistance of bioinert self-assembled monolayers originates in the physical barrier of the interfacial water. We review the history of the previous works that attempted to clarify the underlying mechanism and discuss prospects to apply the findings to design new biomaterials.
- Ryongsok Chang
- , Syifa Asatyas
- & Tomohiro Hayashi
-
Focus Review |
 Advances in surface-coated single-walled carbon nanotubes as near-infrared photoluminescence emitters for single-particle tracking applications in biological environments
Advances in surface-coated single-walled carbon nanotubes as near-infrared photoluminescence emitters for single-particle tracking applications in biological environments
This review summarizes the recent advances in surface-coated single-walled carbon nanotubes as near-infrared nanometer-sized photoluminescent emitters for single-particle imaging and tracking applications in complex biological environments. It is focused on demonstrating surface coating identification, excitation strategies comparison, and long-term single-nanotube tracking inside the brain extracellular space in the live brain tissue.
- Zhenghong Gao
-
Original Article |
 SPR study for analysis of a water-soluble glycopolymer interface and molecular recognition properties
SPR study for analysis of a water-soluble glycopolymer interface and molecular recognition properties
A glycopolymer with different mannose incorporation ratios was synthesized via a reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer with acrylamide. The polymers were immobilized onto a gold substrate by the thiol terminate. The glycopolymer layer structures and the glycopolymer–protein interactions were analyzed using a surface plasmon resonance technique. The glycopolymers formed pancake-like structures under dry conditions and were swollen in water. The interaction between the glycopolymer and the protein was enhanced by the cluster effect of the mannose units.
- Yuhei Terada
- , Hirokazu Seto
- & Yoshiko Miura
-
Note |
 Anomaly in the coefficient of performance of the volume phase transition process of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gels induced by mechanical stress
Anomaly in the coefficient of performance of the volume phase transition process of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gels induced by mechanical stress
Model calculation results for the coefficient of performance c (solid) of a gel actuator driven by the shrinking transition and the increment of the transition temperature (ΔT/T0) (broken) of the gel plotted against applied force. The shape of these curves depends on the ratio α/β (see text), but the real gels seem to hold α/β >1. In this figure α=3 and β=2 are used for calculation. A reduced form is employed for these variables.
- Naoya Tochishita
- , Jun-ichi Horinaka
- & Toshikazu Takigawa
-
Original Article |
 The effects of seasonal changes on the molecular weight of Nephila clavata spider silk
The effects of seasonal changes on the molecular weight of Nephila clavata spider silk
The molecular weight of spider proteins contained in the major ampullate glands of spiders collected during different periods. The standard deviation is also indicated. A peak for molecular weight is observed in mid-autumn, which corresponds to the mating season.
- Shigeyoshi Osaki
- , Keizo Yamamoto
- & Hiromi Sakai
-
Original Article |
 Packing effects on polymerization of diacetylene lipids in liposomes and monolayers matrices
Packing effects on polymerization of diacetylene lipids in liposomes and monolayers matrices
Pore formation on the liposome resulted from the photo-cross-linking reaction between DC8,9PCs, which is a photo-polymerizable lipid, is only observed when the saturated lipids comprise of the hosting matrix. To understand the influence of the hosting matrix, the Langmuir monolayer is employed because the system is capable of precisely controlling the packing state and the compositions of the film. The kinetics of reaction is found to strongly depend on the packing state of the film, and the cross-distance between DC8,9PCs plays a key role for the polymerization reaction to proceed.
- Siyeon Baek
- , Minh Dinh Phan
- & Kwanwoo Shin
-
Original Article |
 Thermosensitive polymer-coated La0.73Sr0.27MnO3 nanoparticles: potential applications in cancer hyperthermia therapy and magnetically activated drug delivery systems
Thermosensitive polymer-coated La0.73Sr0.27MnO3 nanoparticles: potential applications in cancer hyperthermia therapy and magnetically activated drug delivery systems
poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylamide) copolymer-coated La0.73Sr0.27MnO3 nanoparticles were prepared through admicellar polymerization. The prepared nanoparticles with core-shell can be used as heat-generating agent in magnetic hyperthermia therapy.
- Meysam Soleymani
- , Mohammad Edrissi
- & Ali Mohammad Alizadeh
-
Original Article |
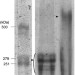 Molecular weight of Nephila clavata spider silk
Molecular weight of Nephila clavata spider silk
Band patterns for N. clavata spider silk protein and for three different markers in 3% SDS-PAGE. M: marker, A: spider silk solution under a reduced state, B: spider silk solution under an unreduced state. The reduction due to a reductant cleaves the disulfide bonds and decreases the molecular weight from ca. 600 to ca. 270 kDa. Spider silk protein with ca. 600 kDa is suggested to be crosslinked by disulfide bonding between the two proteins.
- Takashi Matsuhira
- & Shigeyoshi Osaki
-
Original Article |
 Change in local dynamics of bacteriorhodopsin with retinal isomerization under pressure as studied by fast magic angle spinning NMR
Change in local dynamics of bacteriorhodopsin with retinal isomerization under pressure as studied by fast magic angle spinning NMR
Bacteriorhodopsin (bR) has a retinal with all-trans and 13-cis, 15-syn configurations whose isomeric ratio is close to 1 in the dark and the population of 13-cis, 15-syn configuration can be increased under the pressurized condition. Increase of pressure by fast magic angle spinning (MAS) induced dynamics change at around Ala81 and Ala84 in bR together with retinal isomerization from all-trans to 13-cis configurations. We demonstrated that fast MAS NMR provides a pressure sauce for investigating the structure and dynamics change of biomacromolecules.
- Izuru Kawamura
- , Satoru Yamaguchi
- & Akira Naito
-
Original Article |
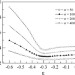 Conformational properties of a polymer tethered to an interacting flat surface
Conformational properties of a polymer tethered to an interacting flat surface
The mean square end-to-end distance 〈R2〉 is dependent on the polymer-surface interaction ɛ. It reaches minimum near critical adsorption point (CAP) ɛc≈−0.29. The result provides an alternate method to determine ɛc.
- Hong Li
- , Chang-Ji Qian
- & Meng-Bo Luo
-
Rapid Communication |
 Local conformation of serine residues in a silk model peptide, (Ala–Gly–Ser–Gly–Ala–Gly)5, studied with solid-state NMR:REDOR
Local conformation of serine residues in a silk model peptide, (Ala–Gly–Ser–Gly–Ala–Gly)5, studied with solid-state NMR:REDOR
- Yu Suzuki
- & Tetsuo Asakura

 Construction of functional microtubules and artificial motile systems based on peptide design
Construction of functional microtubules and artificial motile systems based on peptide design