Featured
-
-
Original Article
| Open Access Variable swelling behavior of and drug encapsulation in a maleimide-modified hyaluronic acid nanogel-based hydrogel
Variable swelling behavior of and drug encapsulation in a maleimide-modified hyaluronic acid nanogel-based hydrogel
Hydrogels have attracted considerable attention in the biomedical applications because of their high functionalities, biocompatibility and biodegradability. This study on the novel hyaluronic acid (HA) nanogel-based hydrogel comprising HA modified with cholesterol derivatives and maleimide crosslinking groups. Depending on the degree of cholesterol derivative substitution, the properties such as water uptake, gelation behavior and protein encapsulation was investigated. The results suggested that the hydrogels enhanced peptide and protein trapping abilities have potential as a new hyaluronan hydrogel for biomedical applications.
- Kohei Yabuuchi
- , Toru Katsumata
- & Akio Kishida
-
Focus Review |
 Design of supramolecular nanosheets for drug delivery applications
Design of supramolecular nanosheets for drug delivery applications
Two specific concepts have emerged in the field of materials science over the last several decades: nanosheets and supramolecular polymers. Based on this background, supramolecular nanosheets, in which these two concepts are integrated, have recently attracted particular attention. This review focuses on design of two supramolecular nanosheets. One is tubulin protein-based supramolecular nanosheet for applications to GTP-responsive drug delivery system. The other is phospholipid-based supramolecular nanosheets and their applications in blood-administrated drug delivery systems.
- Noriyuki Uchida
-
Focus Review
| Open Access A boronate gel-based synthetic platform for closed-loop insulin delivery systems
A boronate gel-based synthetic platform for closed-loop insulin delivery systems
Boronic acids (BA) are known for their ability to reversibly interact with the diol groups, a common motif of biomolecules including sugars, ribose, and catechols. One can tailor BAs to elicit a divergent profile of binding strength and specificity on the basis of stereochemistry and controlled electronic effects. This focus review provides an overview of a phenylboronic acid (PBA)-based, totally synthetic platform for insulin delivery applications developed in our group, with focuses on the development of new PBA derivatives, glucose-responsive gels, and the gel-combined medical devices.
- Akira Matsumoto
- & Siyuan Chen
-
Original Article |
 Fabrication and evaluation of durable, optically clear, and self-disinfecting films
Fabrication and evaluation of durable, optically clear, and self-disinfecting films
A transparent film with photoactive antiviral functions and minimal degradation over time was easily obtained by uniformly dispersing the phenoxy-substituted phthalocyanine zinc (PPcZn) in the cellulose acetate film. This film produced singlet oxygen (1O2) upon visible light irradiation, and the production capacity of 1O2 was maintained even when the film was exposed to indoor lighting for 6 months.
- Nobuyuki Harada
- , Kiyoshi Masuda
- & Hiroshi Uyama
-
Rapid Communication |
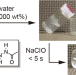 Superabsorbent polymer solubilized instantly by decrosslinking with sodium hypochlorite
Superabsorbent polymer solubilized instantly by decrosslinking with sodium hypochlorite
A novel superabsorbent polymer crosslinked with diacylhydrazine DC-SAP was prepared. A very-high water uptake (ca. 80,000%) was observed in DC-SAP at a crosslinking ratio of 1%. The swollen gel was instantly (<5 s) solubilized by treatment with a small amount of sodium hypochlorite solution. A commercially available bleacher could also be used for the solubilization of DC-SAP. Despite the high degradability of DC-SAP, it exhibited high chemical and thermal stability. The decomposition product is composed of pure poly(sodium acrylate), which is extremely safe substance.
- Kazuya Yanaze
- & Nobuhiro Kihara
-
Original Article |
 Direct observation of cyclic poly(N-substituted maleimide)s with broad size distributions synthesized by anionic polymerization using an N-heterocyclic carbene and successive ring closure without high dilutions
Direct observation of cyclic poly(N-substituted maleimide)s with broad size distributions synthesized by anionic polymerization using an N-heterocyclic carbene and successive ring closure without high dilutions
Direct Observation of Cyclic Poly(N-substituted maleimide)s with Broad Size Distributions Synthesized by Anionic Polymerization using an N-Heterocyclic Carbene and Successive Ring Closure Without High Dilutions.
- Yuki Muramatsu
- , Yosuke Oga
- & Masahiro Higuchi
-
Technical Review |
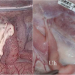 Development of a spray-type adhesion barrier
Development of a spray-type adhesion barrier
A novel spray-type dextrin hydrogel-based adhesion barrier is composed of N-hydroxysuccinimide-modified carboxymethyl dextrin that is biodegradable polymer material. The performance evaluation of a spray-type adhesion barrier in porcine laparoscopic model was showed significantly lowered adhesion rate than in the control group (p < 0.001), and no hydrogel residue was observed macroscopically at the spraying site 28 ± 1 days after surgery.
- Naotaka Chino
- , Hiroyuki Ishihara
- & Tetsuro Kawanishi
-
Original Article |
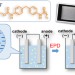 Synthesis of sulfone-containing non-ionic polyurethanes for electrophoretic deposition coating
Synthesis of sulfone-containing non-ionic polyurethanes for electrophoretic deposition coating
A new manipulation technique of polyurethane materials via electrophoretic deposition (EPD) is proposed. Polyurethanes with sulfonyl groups are synthesized for the EPD coatings on a stainless-steel electrode plate at the anode side selectively. The coating properties, including peeling resistance, scratch resistance, and transparency, are improved by optimizing soft segment fraction and also by reducing aromaticity of the polyurethanes.
- Akinori Ohno
- , Mikihiro Hayashi
- & Akinori Takasu
-
Focus Review |
 Highly sensitive and rapid biosensing on a three-dimensional polymer platform
Highly sensitive and rapid biosensing on a three-dimensional polymer platform
Highly sensitive and rapid biosensing on a three-dimensional polymer platform. Increasing sensitivity and decreasing assay time are two of the most crucial goals in the development of biosensing devices. We have developed three-dimensional (3D) nanospherical and microfiber structure for biosensing devices aimed at highly sensitive and rapid immunoassays. The system having polystyrene microfiber of 3D structure paired with vacuum pump pressurization to induce bulk flow enables an efficient and rapid immunoassay. Because it takes advantage of the increased amount of immobilized antibody on 3D structure and of the accelerated propagation of antigens by flowing through the microfiber.
- Madoka Takai
-
Original Article |
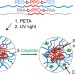 Cisplatin delivery vehicles based on stabilized polymeric aggregates comprising poly(acrylic acid) chains
Cisplatin delivery vehicles based on stabilized polymeric aggregates comprising poly(acrylic acid) chains
Complexation of cisplatin with stabilized ‘Pluronic’ aggregates, containig functional poly(acrylic acid) moieties was investigated as platform for drug delivery application. The advantageous characteristics of the system involve high drug payload, excellent stability upon storage and sustained drug release of the conjugated drug over 2 weeks.
- Ekaterina Stoyanova
- , Petar Petrov
- & Neli Koseva
-
Focus Review |
 Development of free-standing polymer nanosheets for advanced medical and health-care applications
Development of free-standing polymer nanosheets for advanced medical and health-care applications
This report reviews the seminal features and characteristics of free-standing polymeric ultrathin films (nanosheets), including fabrication methods, mechanical properties and biomedical and health-care applications (for example, wound dressings, tissue engineering materials and bioelectronic devices). ‘Nanosheet technology’ is a promising approach for the development of advanced medical applications and health-care practices in surgery and regenerative medicine, as well as for connecting the human body to electronic interfaces for future medical applications.
- Toshinori Fujie
-
Original Article |
 Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial properties of polyurethane material functionalized with quaternary ammonium salt
Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial properties of polyurethane material functionalized with quaternary ammonium salt
Block antibacterial polyurethane and terminated antibacterial polyurethane were prepared based on N-methyl-N-dodecyl-N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium bromide. Their antibacterial properties were determined using qualitative and quantitative tests, and the physical performances of the antibacterial polyurethane (APU) were also investigated. The results indicate that the APUs display marked mechanical properties, water absorption and improved antibacterial properties against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis, with the most potency against E. coli.
- Chun-Hua Wang
- , Gui-Ge Hou
- & Wen-Shuai Liu
-
Original Article |
 A novel substrate for testosterone: biodegradable and biocompatible oil gel
A novel substrate for testosterone: biodegradable and biocompatible oil gel
In this study, we prepared a novel oil gel composed of poly(L-lactide) and a poly(trimethylene carbonate) derivative. We investigated the release of testosterone, an inexpensive therapeutic drug for the segmental defect of bones, from the gel. Dimethyl sulfoxide and dimethyl carbonate, which are organic solvents with relatively low toxicities, were used as dispersion media. The oil gel in dimethyl sulfoxide released testosterone faster than that in dimethyl carbonate. In addition, the dimethyl carbonate oil gel was vacuum-dried to reduce the gel porosity and resulted in slow testosterone release.
- Kazuya Takemura
- , Hiroharu Ajiro
- & Mitsuru Akashi

 Micropatterned microplastic generation via degradation of polymeric films with micropatterned structures
Micropatterned microplastic generation via degradation of polymeric films with micropatterned structures