Featured
-
-
Original Article
| Open Access Variable swelling behavior of and drug encapsulation in a maleimide-modified hyaluronic acid nanogel-based hydrogel
Variable swelling behavior of and drug encapsulation in a maleimide-modified hyaluronic acid nanogel-based hydrogel
Hydrogels have attracted considerable attention in the biomedical applications because of their high functionalities, biocompatibility and biodegradability. This study on the novel hyaluronic acid (HA) nanogel-based hydrogel comprising HA modified with cholesterol derivatives and maleimide crosslinking groups. Depending on the degree of cholesterol derivative substitution, the properties such as water uptake, gelation behavior and protein encapsulation was investigated. The results suggested that the hydrogels enhanced peptide and protein trapping abilities have potential as a new hyaluronan hydrogel for biomedical applications.
- Kohei Yabuuchi
- , Toru Katsumata
- & Akio Kishida
-
Focus Review |
 Design of supramolecular nanosheets for drug delivery applications
Design of supramolecular nanosheets for drug delivery applications
Two specific concepts have emerged in the field of materials science over the last several decades: nanosheets and supramolecular polymers. Based on this background, supramolecular nanosheets, in which these two concepts are integrated, have recently attracted particular attention. This review focuses on design of two supramolecular nanosheets. One is tubulin protein-based supramolecular nanosheet for applications to GTP-responsive drug delivery system. The other is phospholipid-based supramolecular nanosheets and their applications in blood-administrated drug delivery systems.
- Noriyuki Uchida
-
Original Article |
 Synthesis of polycarbonates and polycarbonate/polyester copolymers through an ester-carbonate exchange reaction
Synthesis of polycarbonates and polycarbonate/polyester copolymers through an ester-carbonate exchange reaction
We describe the synthesis of polycarbonate (PC) by means of the polycondensation of diol formate and dialkyl carbonate through an ester-carbonate exchange reaction. Furthermore, the polycondensation of diol formate and diethyl carbonate in the presence of polyester (PEs) under reduced pressure affords a statistical copolymer of PC and PEs. The composition of PC and PEs in the copolymer can be arbitrarily altered by changing the feed ratio of the monomers to PEs.
- Takayoshi Katoh
- , Maai Saso
- & Tsutomu Yokozawa
-
Original Article
| Open Access Comparison of triblock copolymeric micelles based on α- and ε-poly(L-lysine): a Cornelian choice
Comparison of triblock copolymeric micelles based on α- and ε-poly(L-lysine): a Cornelian choice
Low-molecular-weight amphiphilic block copolymers with controlled architecture represent an interesting manner for safe delivery of siRNAs and hydrophobic anticancer drugs. The tailored synthesis, supramolecular assembly and morphology were investigated using triblock copolymers based on α- and ε-lysine oligomers.
- Franck Marquet
- , Viorica Patrulea
- & Gerrit Borchard
-
Focus Review |
 Construction of nanomaterials based on pH-responsive polymers for effective tumor delivery
Construction of nanomaterials based on pH-responsive polymers for effective tumor delivery
Acidic pH is identified for various types of tumors, whereby it can be employed for crafting tumor-targeted nanomaterials. Cationic net charge of the nanomaterials at tumorous pH achieves selective interaction with anionic tissue constituents at tumor sites, for the effective tumor accumulation. However, tumorous pH is ca. 6.5, whereas pH of normal tissues is 7.4, and therefore responsiveness to the small pH window is the key toward the success for tumor delivery. The present manuscript highlights the polymer designs that recognize tumorous pH to make tumor-targeted nanomaterials.
- Hiroyasu Takemoto
- & Nobuhiro Nishiyama
-
Original Article |
 Lysine-oligoether-modified electrospun poly(carbonate urethane) matrices for improving hemocompatibility response
Lysine-oligoether-modified electrospun poly(carbonate urethane) matrices for improving hemocompatibility response
In this work, we employed Carbothane® electrospun matrices (PCU) for lysine surface modification, using oligomers obtained from allyl glycidyl ether (AGE) reaction as spacers. The incorporation of AGE oligomers significantly reduced the nonspecific protein adsorption, while further modification with lysine led to a more pronounced decrease. The lysine-modified matrices presented increased plasminogen adsorption capacity and in vitro clot lysis ability, confirming the plasminogen adsorption selectivity and thus improving the hemocompatibility behavior of these matrices.
- Alfonso Pepe
- , Maria Gabriela Guevara
- & Pablo Christian Caracciolo
-
Focus Review
| Open Access A boronate gel-based synthetic platform for closed-loop insulin delivery systems
A boronate gel-based synthetic platform for closed-loop insulin delivery systems
Boronic acids (BA) are known for their ability to reversibly interact with the diol groups, a common motif of biomolecules including sugars, ribose, and catechols. One can tailor BAs to elicit a divergent profile of binding strength and specificity on the basis of stereochemistry and controlled electronic effects. This focus review provides an overview of a phenylboronic acid (PBA)-based, totally synthetic platform for insulin delivery applications developed in our group, with focuses on the development of new PBA derivatives, glucose-responsive gels, and the gel-combined medical devices.
- Akira Matsumoto
- & Siyuan Chen
-
Original Article |
 Fabrication and evaluation of durable, optically clear, and self-disinfecting films
Fabrication and evaluation of durable, optically clear, and self-disinfecting films
A transparent film with photoactive antiviral functions and minimal degradation over time was easily obtained by uniformly dispersing the phenoxy-substituted phthalocyanine zinc (PPcZn) in the cellulose acetate film. This film produced singlet oxygen (1O2) upon visible light irradiation, and the production capacity of 1O2 was maintained even when the film was exposed to indoor lighting for 6 months.
- Nobuyuki Harada
- , Kiyoshi Masuda
- & Hiroshi Uyama
-
Rapid Communication |
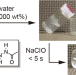 Superabsorbent polymer solubilized instantly by decrosslinking with sodium hypochlorite
Superabsorbent polymer solubilized instantly by decrosslinking with sodium hypochlorite
A novel superabsorbent polymer crosslinked with diacylhydrazine DC-SAP was prepared. A very-high water uptake (ca. 80,000%) was observed in DC-SAP at a crosslinking ratio of 1%. The swollen gel was instantly (<5 s) solubilized by treatment with a small amount of sodium hypochlorite solution. A commercially available bleacher could also be used for the solubilization of DC-SAP. Despite the high degradability of DC-SAP, it exhibited high chemical and thermal stability. The decomposition product is composed of pure poly(sodium acrylate), which is extremely safe substance.
- Kazuya Yanaze
- & Nobuhiro Kihara
-
Original Article |
 Direct observation of cyclic poly(N-substituted maleimide)s with broad size distributions synthesized by anionic polymerization using an N-heterocyclic carbene and successive ring closure without high dilutions
Direct observation of cyclic poly(N-substituted maleimide)s with broad size distributions synthesized by anionic polymerization using an N-heterocyclic carbene and successive ring closure without high dilutions
Direct Observation of Cyclic Poly(N-substituted maleimide)s with Broad Size Distributions Synthesized by Anionic Polymerization using an N-Heterocyclic Carbene and Successive Ring Closure Without High Dilutions.
- Yuki Muramatsu
- , Yosuke Oga
- & Masahiro Higuchi
-
Review |
 In vitro fabrication and application of engineered vascular hydrogels
In vitro fabrication and application of engineered vascular hydrogels
Hydrogels have been used in vascular engineering owing to their mechanical properties and tissue-like characteristics. Hydrogel-based blood vessels can be constructed from natural or synthetic materials alone, or require a combination of both. The manufacturing methods play an important role in constructing vascular engineering to induce the vascular endothelial cells function driven by shear stress and biomechanical force. The different components and methods of engineered vascular hydrogels described in this review would provide useful information for the desired applications of in vitro tissue models.
- Muhammad Asri Abdul Sisak
- , Fiona Louis
- & Michiya Matsusaki
-
Technical Review |
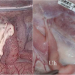 Development of a spray-type adhesion barrier
Development of a spray-type adhesion barrier
A novel spray-type dextrin hydrogel-based adhesion barrier is composed of N-hydroxysuccinimide-modified carboxymethyl dextrin that is biodegradable polymer material. The performance evaluation of a spray-type adhesion barrier in porcine laparoscopic model was showed significantly lowered adhesion rate than in the control group (p < 0.001), and no hydrogel residue was observed macroscopically at the spraying site 28 ± 1 days after surgery.
- Naotaka Chino
- , Hiroyuki Ishihara
- & Tetsuro Kawanishi
-
Note |
 Detection of influenza virus by agglutination using nanoparticles conjugated with a sialic acid-mimic peptide
Detection of influenza virus by agglutination using nanoparticles conjugated with a sialic acid-mimic peptide
This study examines the use of poly(glycidyl methacrylate) (PGMA)-coated polystyrene functionalized with peptides that mimic receptors found on red blood cells for detection of the influenza virus. Although the current method, the hemagglutination inhibition test, utilized by the World Health Organization, is simple, it has some limitations. We found that our peptide dimers attached to beads were efficiently agglutinated, leading us to detect the presence of the influenza virus antigens. We believe that our study makes a significant contribution to the fight against influenza because we provide an alternative method for the important task of influenza surveillance and diagnosis.
- Teruhiko Matsubara
- , Akane Kubo
- & Toshinori Sato
-
Original Article |
 Polymeric water-soluble activated esters: synthesis of polymer backbones with pendant N-hydoxysulfosuccinimide esters for post-polymerization modification in water
Polymeric water-soluble activated esters: synthesis of polymer backbones with pendant N-hydoxysulfosuccinimide esters for post-polymerization modification in water
Novel polymer backbones with pendant water-soluble activated esters were synthesized by a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization technique using an acrylamide derivative bearing an N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide (sulfoNHS) ester as a monomer substrate. To synthesize glycopolymers, the substitution reaction at the sulfoNHS esters on the polymer side chain with an amine-containing saccharide derivative was performed in water. The resulting glycopolymer exhibited a strong interaction with the corresponding lectin in aqueous solution, because the saccharide moieties are multivalent.
- Sotaro Tsuji
- , Yuji Aso
- & Tomonari Tanaka
-
Original Article |
 Synthesis of sulfone-containing non-ionic polyurethanes for electrophoretic deposition coating
Synthesis of sulfone-containing non-ionic polyurethanes for electrophoretic deposition coating
A new manipulation technique of polyurethane materials via electrophoretic deposition (EPD) is proposed. Polyurethanes with sulfonyl groups are synthesized for the EPD coatings on a stainless-steel electrode plate at the anode side selectively. The coating properties, including peeling resistance, scratch resistance, and transparency, are improved by optimizing soft segment fraction and also by reducing aromaticity of the polyurethanes.
- Akinori Ohno
- , Mikihiro Hayashi
- & Akinori Takasu
-
Review |
 Design and application of redox polymers for nanomedicine
Design and application of redox polymers for nanomedicine
Amphiphilic block polymers having nitroxide radicals (TEMPO) self-assemble in water to form nanoparticles. This is a new nanomedicine that avoids the adverse effects of conventional antioxidants, which destroy the intracellular redox environment, and makes it possible to treat various oxidative-stress-related diseases such as cerebral or cardiovascular ischemia-reperfusions, Alzheimer’s disease and cancer. In addition, we have designed a gelation function in these materials and developed them as a material for anti-tissue adhesion agents and periodontal diseases. Additionally, we succeeded in enhancing cultured cell functions using an antioxidant biointerface.
- Yukio Nagasaki
-
Focus Review |
 Highly sensitive and rapid biosensing on a three-dimensional polymer platform
Highly sensitive and rapid biosensing on a three-dimensional polymer platform
Highly sensitive and rapid biosensing on a three-dimensional polymer platform. Increasing sensitivity and decreasing assay time are two of the most crucial goals in the development of biosensing devices. We have developed three-dimensional (3D) nanospherical and microfiber structure for biosensing devices aimed at highly sensitive and rapid immunoassays. The system having polystyrene microfiber of 3D structure paired with vacuum pump pressurization to induce bulk flow enables an efficient and rapid immunoassay. Because it takes advantage of the increased amount of immobilized antibody on 3D structure and of the accelerated propagation of antigens by flowing through the microfiber.
- Madoka Takai
-
Original Article |
 Responsibility of lipid compositions for the amyloid ß assembly induced by ganglioside nanoclusters in mouse synaptosomal membranes
Responsibility of lipid compositions for the amyloid ß assembly induced by ganglioside nanoclusters in mouse synaptosomal membranes
Amyloid ß-protein (Aß) is converted to toxic forms through interactions with the ganglioside in neuronal membranes. The highly ganglioside-enriched microdomain (ganglioside cluster) in neuronal membranes plays a key role in Aß assembly. In the present study, lipid components of synaptosome extracted from mouse aged brain was determined by LC-MS spectroscopy. We demonstrated that ganglioside ratio (GM3 to GM1) and cholesterol content are an important factor for inducing Aß assembly. These results provides important insight into the mechanism of polypeptide assembly on the neuronal membrane in Alzheimer’s disease patients.
- Teruhiko Matsubara
- , Takahiro Kojima
- & Toshinori Sato
-
Original Article |
 Tissue-engineered scaffold based on carboxymethyl chitin or chitosan for corneal epithelial transplantation
Tissue-engineered scaffold based on carboxymethyl chitin or chitosan for corneal epithelial transplantation
6 groups of blend membranes based on carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCTS) or carboxymethyl chitin (CMCT) were prepared. CMCTS-Gel (1#) and CMCT-Gel (4#) blend membranes with high transmittance and surface properties were more suitable for cell growth. Although primary corneal epithelial cells (CECs) on the two blend membranes could keep marker proteins and prevent cell fibrosis, CECs on membrane 4# could maintain the original epithelial morphology and improve the K12 protein level seriously. The potential mechanism of anti-fibrosis effect was proved that both of the membranes could block phosphorylation levels of Smad2 and Smad3, and membrane 4# could also depress the total native Smad2 and Smad3 expressions.
- Tong Li
- , Ye Liang
- & Wenhua Xu
-
Original Article |
 Membranes based on carboxymethyl chitin as potential scaffolds for corneal endothelial transplantation
Membranes based on carboxymethyl chitin as potential scaffolds for corneal endothelial transplantation
The corneal endothelial scaffolds were prepared using carboxymethyl chitin (CMCT) or carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCTS) as the main ingredient. The transmittances of the membranes were examined at different wavelengths. The properties of both membranes, including cytotoxicity, histocompatibility, degradability and cytocompatibility, were determined by experiments on cultured cells or rats. By contrast, the CMCT membrane proved to be a more promising candidate for constructing CEC endothelial scaffold.
- Wenhua Xu
- , Zheying Wang
- & Chengyu Liu
-
Original Article |
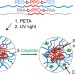 Cisplatin delivery vehicles based on stabilized polymeric aggregates comprising poly(acrylic acid) chains
Cisplatin delivery vehicles based on stabilized polymeric aggregates comprising poly(acrylic acid) chains
Complexation of cisplatin with stabilized ‘Pluronic’ aggregates, containig functional poly(acrylic acid) moieties was investigated as platform for drug delivery application. The advantageous characteristics of the system involve high drug payload, excellent stability upon storage and sustained drug release of the conjugated drug over 2 weeks.
- Ekaterina Stoyanova
- , Petar Petrov
- & Neli Koseva
-
Focus Review |
 Development of free-standing polymer nanosheets for advanced medical and health-care applications
Development of free-standing polymer nanosheets for advanced medical and health-care applications
This report reviews the seminal features and characteristics of free-standing polymeric ultrathin films (nanosheets), including fabrication methods, mechanical properties and biomedical and health-care applications (for example, wound dressings, tissue engineering materials and bioelectronic devices). ‘Nanosheet technology’ is a promising approach for the development of advanced medical applications and health-care practices in surgery and regenerative medicine, as well as for connecting the human body to electronic interfaces for future medical applications.
- Toshinori Fujie
-
Editorial |
Special Issue: Polymer surfaces, interfaces and thin films
- Keiji Tanaka
- , Takeshi Serizawa
- & Takashi Kato
-
Rapid Communication |
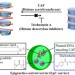 Design of epigenetics control carrier for simultaneous transfection of histone acetyltransferase with histone deacetylase inhibitor to continuous histone acetylation
Design of epigenetics control carrier for simultaneous transfection of histone acetyltransferase with histone deacetylase inhibitor to continuous histone acetylation
Epigenetics control carrier (EpC carrier) has been designed as a unique tool to control histone acetylation by simultaneous transfection of histone acetyltransferase gene and delivery of a histone deacetylase inhibitor.
- Yutaro Asaba
- , Shoichiro Asayama
- & Hiroyoshi Kawakami
-
Focus Review |
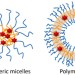 Polymeric nanocarriers incorporating near-infrared absorbing agents for potent photothermal therapy of cancer
Polymeric nanocarriers incorporating near-infrared absorbing agents for potent photothermal therapy of cancer
In this review, we highlight recent advances in polymeric hybrid nanocarriers for photothermal treatment of cancer. These polymeric hybrid nanocarriers can store and deliver NIR-absorbing agents to cancer cells and tumor sites, exhibiting significant cytotoxic effects upon treatment under external light irradiation. Possible challenges and future prospects in this field are also emphasized.
- Yuanyuan Zhang
- , Chung Yen Ang
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Original Article |
 Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial properties of polyurethane material functionalized with quaternary ammonium salt
Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial properties of polyurethane material functionalized with quaternary ammonium salt
Block antibacterial polyurethane and terminated antibacterial polyurethane were prepared based on N-methyl-N-dodecyl-N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium bromide. Their antibacterial properties were determined using qualitative and quantitative tests, and the physical performances of the antibacterial polyurethane (APU) were also investigated. The results indicate that the APUs display marked mechanical properties, water absorption and improved antibacterial properties against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis, with the most potency against E. coli.
- Chun-Hua Wang
- , Gui-Ge Hou
- & Wen-Shuai Liu
-
Original Article |
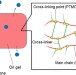 A novel substrate for testosterone: biodegradable and biocompatible oil gel
A novel substrate for testosterone: biodegradable and biocompatible oil gel
In this study, we prepared a novel oil gel composed of poly(L-lactide) and a poly(trimethylene carbonate) derivative. We investigated the release of testosterone, an inexpensive therapeutic drug for the segmental defect of bones, from the gel. Dimethyl sulfoxide and dimethyl carbonate, which are organic solvents with relatively low toxicities, were used as dispersion media. The oil gel in dimethyl sulfoxide released testosterone faster than that in dimethyl carbonate. In addition, the dimethyl carbonate oil gel was vacuum-dried to reduce the gel porosity and resulted in slow testosterone release.
- Kazuya Takemura
- , Hiroharu Ajiro
- & Mitsuru Akashi
-
Review |
 Characteristics of bacterial biofilm associated with implant material in clinical practice
Characteristics of bacterial biofilm associated with implant material in clinical practice
With the increase in the number of implant-dependent surgeries and biofilm-associated complications, there is a need to counteract and deal with this phenomenon. This has led to various approaches to elucidate the etiology and pathogenesis of the infection. This review critically evaluates the formation, characteristics, pathogenicity and the molecular genetics of both implant- and nonimplant-associated medical biofilm.
- Venkatesan Nandakumar
- , Samuel Chittaranjan
- & Mukesh Doble
-
Original Article |
 Self-assembled nanoparticles of PLGA-conjugated glucosamine as a sustained transdermal drug delivery vehicle
Self-assembled nanoparticles of PLGA-conjugated glucosamine as a sustained transdermal drug delivery vehicle
The present work deals with the chemical conjugation of biodegradable polymer, PLGA, with a natural anti-inflammatory drug, GlcN. PLGA–GlcN conjugate was self-assembled into NPs contained nanostructure with the aid of probe sonication. Self-assembled nanostructure is composed of hydrophobic PLGA at the surface and hydrophilic GlcN at inner core, which helps its enhanced transdermal permeation for GlcN delivery. Shortest lag time with high flux value obtained with transdermal permeation of nanostructures on human cadaver skin confirms its ability as efficient GlcN vehicle for treating inflammatory diseases.
- Mohana Marimuthu
- , Devasier Bennet
- & Sanghyo Kim

 Micropatterned microplastic generation via degradation of polymeric films with micropatterned structures
Micropatterned microplastic generation via degradation of polymeric films with micropatterned structures