Featured
-
-
Article |
 Stereoselective amino acid synthesis by photobiocatalytic oxidative coupling
Stereoselective amino acid synthesis by photobiocatalytic oxidative coupling
We report on the oxidative cross-coupling of organoboron reagents and amino acids via pyridoxal biocatalysis to produce non-canonical amino acids, uncovering stereoselective, intermolecular free-radical transformations.
- Tian-Ci Wang
- , Binh Khanh Mai
- & Yang Yang
-
News & Views |
 Trio of radicals choreographed for versatile chemical reaction
Trio of radicals choreographed for versatile chemical reaction
The idea that three different free radicals could be used together to carry out specific steps in a chemical reaction has long been implausible. A ‘radical sorting’ strategy now achieves this feat to make organic molecules.
- Kenneth F. Clark
- & John A. Murphy
-
Article |
 Copper-catalysed dehydrogenation or lactonization of C(sp3)–H bonds
Copper-catalysed dehydrogenation or lactonization of C(sp3)–H bonds
Use of N-methoxyamides as oxidants enables controllable, redox-neutral, green catalysis of bimodal dehydrogenation/lactonization reactions with methanol as the only by-product.
- Shupeng Zhou
- , Zi-Jun Zhang
- & Jin-Quan Yu
-
Research Briefing |
 ‘Bandit’ algorithms help chemists to discover generally applicable conditions for reactions
‘Bandit’ algorithms help chemists to discover generally applicable conditions for reactions
In organic chemistry, finding conditions that enable a broad range of compounds to undergo a particular type of reaction is highly desirable. However, conventional methods for doing so consume a lot of time and reagents. A machine-learning method has been developed that overcomes these problems.
-
Article |
 Couple-close construction of polycyclic rings from diradicals
Couple-close construction of polycyclic rings from diradicals
A couple-close approach used to build semisaturated ring systems from dual radical precursors allows sampling of regions of underexplored chemical space, leading to an annulation that can be used for late-stage functionalization of pharmaceutical scaffolds.
- Alice Long
- , Christian J. Oswood
- & David W. C. MacMillan
-
Article |
 Symmetry breaking and chiral amplification in prebiotic ligation reactions
Symmetry breaking and chiral amplification in prebiotic ligation reactions
A study of a new route to proteinogenic peptides reveals how heterochiral preference can lead to homochiral peptides in a prebiotic world.
- Min Deng
- , Jinhan Yu
- & Donna G. Blackmond
-
Article |
 Alkene dialkylation by triple radical sorting
Alkene dialkylation by triple radical sorting
We use bimolecular homolytic substitution catalysis to sort an electrophilic radical and a nucleophilic radical across an unactivated alkene, accelerating access to pharmaceutically relevant C(sp3)-rich molecules and defining a mechanistic approach for alkene dialkylation.
- Johnny Z. Wang
- , William L. Lyon
- & David W. C. MacMillan
-
Article
| Open Access Stereodivergent 1,3-difunctionalization of alkenes by charge relocation
Stereodivergent 1,3-difunctionalization of alkenes by charge relocation
We introduce a method for the direct 1,3-difunctionalization of alkenes, based on a concept termed ‘charge relocation’, which enables stereodivergent access to 1,3-difunctionalized products of either syn- or anti-configuration from unactivated alkenes.
- Bogdan R. Brutiu
- , Giulia Iannelli
- & Nuno Maulide
-
Where I Work |
 Giving thanks for a glovebox: helping to make medicines from natural substances
Giving thanks for a glovebox: helping to make medicines from natural substances
Richmond Sarpong wishes more people had access to the nitrogen-regulated device.
- James Mitchell Crow
-
Nature Careers Podcast |
 How ChatGPT and sounds from space brought a ‘luminous jelly’ to life
How ChatGPT and sounds from space brought a ‘luminous jelly’ to life
Engineer-turned-artist Diana Scarborough and inorganic chemist Anna Melekhova describe how their art–science collaboration gave voice and form to a new material.
- Julie Gould
-
Article |
 Carbon-to-nitrogen single-atom transmutation of azaarenes
Carbon-to-nitrogen single-atom transmutation of azaarenes
A new type of transformation converting a heteroaromatic carbon atom into a nitrogen atom, turning quinolines into quinazolines to enable manipulation of molecular properties, is reported.
- Jisoo Woo
- , Colin Stein
- & Mark D. Levin
-
News & Views |
 Atom-swap chemistry could aid drug discovery
Atom-swap chemistry could aid drug discovery
An unconventional route for modifying pharmaceutically relevant molecules swaps an atom of carbon for one of nitrogen. The resulting derivatives might open up avenues of research in medicinal-chemistry campaigns.
- Filippo Ficarra
- & Mattia Silvi
-
Article |
 Arenium-ion-catalysed halodealkylation of fully alkylated silanes
Arenium-ion-catalysed halodealkylation of fully alkylated silanes
A new method is described that uses arenium-ion-catalysed halodealkylation of silanes with four alkyl groups, typically considered synthetic dead ends, to convert Me4Si and related quaternary silanes into orthogonally substituted (functionalized) silanes.
- Tao He
- , Hendrik F. T. Klare
- & Martin Oestreich
-
Article |
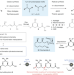 Complex molecule synthesis by electrocatalytic decarboxylative cross-coupling
Complex molecule synthesis by electrocatalytic decarboxylative cross-coupling
We report a radical-based Ni/Ag-electrocatalytic cross-coupling of substituted carboxylic acids, enabling an approach to accessing complex molecular architectures, which relies on a silver additive that forms an active Ag nanoparticle-coated electrode surface along with carefully chosen ligands.
- Benxiang Zhang
- , Jiayan He
- & Phil S. Baran
-
News & Views |
 An all-organic laser that is electrically driven
An all-organic laser that is electrically driven
An organic light-emitting diode has been integrated with an optically driven organic laser to produce laser light from electricity. The design bypasses many of the challenges posed by direct electrical input in such devices.
- Stéphane Kéna-Cohen
-
Research Briefing |
 The chemical synthesis and anti-cancer properties of portimines
The chemical synthesis and anti-cancer properties of portimines
The natural toxins portimine A and B have attracted interest for their unusual chemical architecture and potent anti-cancer activity. The first total synthesis of portimines enables the identification of portimine A’s molecular target and reveals that the toxin induces programmed cell death in human cancer cells.
-
Article |
 A crystalline doubly oxidized carbene
A crystalline doubly oxidized carbene
The synthesis and isolation of a crystalline dication derived from a bis(imino)carbene through a two-electron oxidation/oxide-ion abstraction strategy is reported that bypasses the carbene radical cation, maintaining significant electrophilicity with two accessible vacant orbitals.
- Ying Kai Loh
- , Mohand Melaimi
- & Guy Bertrand
-
Article |
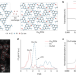 Geminal-atom catalysis for cross-coupling
Geminal-atom catalysis for cross-coupling
Heterogeneous geminal-atom catalysts, which pair single-atom sites in specific coordination and spatial proximity, offer a new avenue for the sustainable manufacture of fine chemicals.
- Xiao Hai
- , Yang Zheng
- & Jiong Lu
-
Article |
 Synthesis of portimines reveals the basis of their anti-cancer activity
Synthesis of portimines reveals the basis of their anti-cancer activity
A scalable total synthesis of portimines enables structural reassignment of portimine B and in-depth functional evaluation of portimine A, revealing that portimine A induces translation inhibition selectively in human cancer cells and is efficacious in vivo tumour-clearance models.
- Junchen Tang
- , Weichao Li
- & Phil S. Baran
-
Article
| Open Access A catalytically active oscillator made from small organic molecules
A catalytically active oscillator made from small organic molecules
We report a small-organic-molecule oscillator that catalyses an independent chemical reaction in situ without impairing its oscillating properties, allowing the construction of complex systems enhancing applications in automated synthesis and systems and polymerization chemistry.
- Matthijs ter Harmsel
- , Oliver R. Maguire
- & Syuzanna R. Harutyunyan
-
Article |
 Hydrogen-bond-acceptor ligands enable distal C(sp3)–H arylation of free alcohols
Hydrogen-bond-acceptor ligands enable distal C(sp3)–H arylation of free alcohols
Ligands enable alcohol-directed arylation of δ-C(sp3)–H bonds by stabilizing hydroxyl coordination to palladium through charge balance and hydrogen bonding.
- Daniel A. Strassfeld
- , Chia-Yu Chen
- & Jin-Quan Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Light-enabled deracemization of cyclopropanes by Al-salen photocatalysis
Light-enabled deracemization of cyclopropanes by Al-salen photocatalysis
Irradiation of chiral Al-salen complexes with violet light demonstrates efficient deracemization of cyclopropanes, enabling reactivity and enantioselectivity to be regulated simultaneously, negating the requirement for tailored catalyst–substrate recognition motifs.
- Carina Onneken
- , Tobias Morack
- & Ryan Gilmour
-
Article |
 Regioselective aliphatic C–H functionalization using frustrated radical pairs
Regioselective aliphatic C–H functionalization using frustrated radical pairs
Regioselective functionalization of aliphatic carbon–hydrogen bonds is achieved using frustrated radical pairs generated from disilazide donors and an N-oxoammonium acceptor.
- Zhipeng Lu
- , Minsoo Ju
- & Song Lin
-
Article |
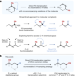 Functional-group translocation of cyano groups by reversible C–H sampling
Functional-group translocation of cyano groups by reversible C–H sampling
Using light-based, reversible C−H sampling catalysis, a cyano functional group can be swapped with a C−H bond in a molecule, providing access to valuable structures that are difficult to obtain by other methods.
- Ken Chen
- , Qingrui Zeng
- & Yan Xu
-
News & Views |
 Rarely used strained molecules step up for organic synthesis
Rarely used strained molecules step up for organic synthesis
Energy released from molecules under strain can promote difficult chemical reactions. A practical method has been developed that uses an overlooked, highly strained compound to rapidly construct complex organic products.
- Fahima I. M. Idiris
- & Christopher R. Jones
-
Research Briefing |
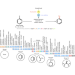 Nickel catalyses a host of chemical reactions in a general method
Nickel catalyses a host of chemical reactions in a general method
A minimal but general method has been developed for catalysing many different cross-coupling reactions — those in which two chemical fragments are joined. It requires only the two substrate substances, a nickel salt as a catalyst precursor, a catalyst for light-driven redox reactions and, in some cases, a nitrogen-containing base.
-
Article |
 Transannular C–H functionalization of cycloalkane carboxylic acids
Transannular C–H functionalization of cycloalkane carboxylic acids
Quinuclidine-pyridone and sulfonamide-pyridone ligands enable transannular γ-methylene C–H arylation of cycloalkane carboxylic acids with a range of ring sizes, bringing us closer to molecular editing of saturated carbocycles.
- Guowei Kang
- , Daniel A. Strassfeld
- & Jin-Quan Yu
-
Article |
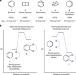 Strain-promoted reactions of 1,2,3-cyclohexatriene and its derivatives
Strain-promoted reactions of 1,2,3-cyclohexatriene and its derivatives
The strained C6H6 isomer 1,2,3-cyclohexatriene and its derivatives participate in a host of reaction modes which demonstrate their potential for selective chemical transformations and provide an unconventional entryway to complex scaffolds.
- Andrew V. Kelleghan
- , Ana S. Bulger
- & Neil K. Garg
-
Research Briefing |
 Enzyme-inspired catalyst helps to convert methane into methanol
Enzyme-inspired catalyst helps to convert methane into methanol
A catalyst with a hydrophobic cavity that contains an active iron centre has been developed to convert methane into methanol. It has a ‘catch-and-release’ mechanism whereby a hydrophobic methane molecule enters the cavity for oxidation and the resulting hydrophilic methanol molecule is released into the surrounding aqueous solution.
-
Article |
 General access to cubanes as benzene bioisosteres
General access to cubanes as benzene bioisosteres
The synthesis of 1,3- and 1,2-disubstituted cubanes is achieved using a cyclobutadiene precursor and a photolytic carboxylation reaction, respectively, and copper-catalysed amination, arylation, alkylation and trifluoromethylation reactions have been developed enabling the use of cubanes as bioisosteres of benzenes in drug design.
- Mario P. Wiesenfeldt
- , James A. Rossi-Ashton
- & David W. C. MacMillan
-
Article |
 Copper-catalysed enantioconvergent alkylation of oxygen nucleophiles
Copper-catalysed enantioconvergent alkylation of oxygen nucleophiles
The enantioconvergent alkylation of oxygen nucleophiles is achieved using α-haloamides and a readily available copper catalyst, and the reaction proceeds under mild conditions in the presence of a wide variety of functional groups.
- Caiyou Chen
- & Gregory C. Fu
-
Article |
 Enantioconvergent Cu-catalysed N-alkylation of aliphatic amines
Enantioconvergent Cu-catalysed N-alkylation of aliphatic amines
The chemoselective and enantioconvergent N-alkylation of aliphatic amines, including ammonia, is achieved using chiral tridentate anionic ligands and a copper catalyst; the method shows excellent enantioselectivity and functional-group tolerance.
- Ji-Jun Chen
- , Jia-Heng Fang
- & Xin-Yuan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Control of stereogenic oxygen in a helically chiral oxonium ion
Control of stereogenic oxygen in a helically chiral oxonium ion
The design, synthesis and characterization of a helically chiral triaryloxonium ion is reported, which is an example of a chiral non-racemic and configurationally stable molecule in which the oxygen atom is the sole stereogenic centre.
- Owen Smith
- , Mihai V. Popescu
- & Martin D. Smith
-
Article |
 Enantioselective transition-metal catalysis via an anion-binding approach
Enantioselective transition-metal catalysis via an anion-binding approach
Chiral hydrogen-bond donors bind anions of organometallic catalysts to achieve enantiocontrol and reaction-rate enhancement through ion pairing together with other non-covalent interactions.
- John M. Ovian
- , Petra Vojáčková
- & Eric N. Jacobsen
-
News |
 The surprising chemicals used to embalm Egyptian mummies
The surprising chemicals used to embalm Egyptian mummies
Resins used to prepare bodies for the afterlife are found in vessels in an ancient workshop.
- Ewen Callaway
-
News & Views |
 Machine learning classifies catalytic-reaction mechanisms
Machine learning classifies catalytic-reaction mechanisms
The study of how chemical reactions work is key to the design of new reactions, but relies on hard work and expert knowledge. A machine-learning tool has been developed that could change the way this challenge is approached.
- Danilo M. Lustosa
- & Anat Milo
-
Article |
 Organic reaction mechanism classification using machine learning
Organic reaction mechanism classification using machine learning
Mechanistic elucidation through currently available kinetic analysis is limited by mathematical approximations and human interpretation, here a deep neural network model has been trained to analyse ordinary kinetic data and automatically elucidate the corresponding mechanism class.
- Jordi Burés
- & Igor Larrosa
-
Article |
 Electrochemical reactor dictates site selectivity in N-heteroarene carboxylations
Electrochemical reactor dictates site selectivity in N-heteroarene carboxylations
An electrochemical strategy is described in which the direct carboxylation of pyridines and related N-heteroarenes with CO2 shows divergent site selectivity depending on the type of reactor used.
- Guo-Quan Sun
- , Peng Yu
- & Song Lin
-
Research Highlight |
 Tinkering with molecular ‘backbones’ holds promise for drug discovery
Tinkering with molecular ‘backbones’ holds promise for drug discovery
A method to edit the backbones of molecules allows chemists to modify ring-shaped chemical structures with greater ease.
-
Article |
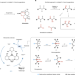 Electrophotocatalytic oxygenation of multiple adjacent C–H bonds
Electrophotocatalytic oxygenation of multiple adjacent C–H bonds
Installation of multiple C–O bonds by concurrent oxygenation of contiguous C–H bonds in a selective fashion is highly desirable, and this is achieved by repeated operation of a potent oxidative catalyst via electrophotocatalysis.
- Tao Shen
- , Yi-Lun Li
- & Tristan H. Lambert
-
Outlook |
 How to make plastic less of an environmental burden
How to make plastic less of an environmental burden
Plastic has long been an ecological problem. But emerging technologies and more awareness could make the ubiquitous material part of a circular economy.
- Sarah DeWeerdt
-
News & Views |
 A leap forward in the quest for general catalysts
A leap forward in the quest for general catalysts
Truly general chemical reactions work well regardless of the structural features and functional groups in the starting molecule. A new screening protocol speeds up the identification of such reactions in the field of asymmetric catalysis.
- Manuel J. Scharf
- & Benjamin List
-
News & Views |
 Machine assembly of carbohydrates with more than 1,000 sugar units
Machine assembly of carbohydrates with more than 1,000 sugar units
Efforts to probe the biological functions of carbohydrates have long been limited by the lack of such molecules with well-defined structures. An automated carbohydrate synthesizer has been developed that could remedy this.
- Hanchao Cheng
- & Peng George Wang
-
News & Views |
 A stable alternative to an explosive synthetic reaction
A stable alternative to an explosive synthetic reaction
The ozonolysis reaction is a classic of organic synthesis, but involves the formation of potentially explosive reaction intermediates. A modern, safer spin on this process makes use of previously overlooked chemistry.
- Vignesh Palani
- & Alison Wendlandt
-
Article |
 Synthesis of meta-substituted arene bioisosteres from [3.1.1]propellane
Synthesis of meta-substituted arene bioisosteres from [3.1.1]propellane
The potential power of the saturated carbocycle bicyclo[3.1.1]heptane as a beneficial motif for improving the pharmacokinetic and physicochemical properties of drug candidates is demonstrated.
- Nils Frank
- , Jeremy Nugent
- & Edward A. Anderson
-
Article |
 Screening for generality in asymmetric catalysis
Screening for generality in asymmetric catalysis
The analytical workflow outlined in this study allows multiple crude reaction mixtures to be analysed simultaneously, with substantial reductions in method development and analysis time, and maximizes the chances of finding catalytic systems with broad substrate scope.
- Corin C. Wagen
- , Spencer E. McMinn
- & Eric N. Jacobsen
-
Article |
 Photoexcited nitroarenes for the oxidative cleavage of alkenes
Photoexcited nitroarenes for the oxidative cleavage of alkenes
Oxidative cleavage of alkenes is achieved using nitroarenes and light irradiation as an alternative to using ozone to break the carbon–carbon bonds, avoiding the explosive intermediates formed with ozone.
- Alessandro Ruffoni
- , Charlotte Hampton
- & Daniele Leonori
-
Article |
 Molecular editing of aza-arene C–H bonds by distance, geometry and chirality
Molecular editing of aza-arene C–H bonds by distance, geometry and chirality
A unified catalytic remote-directing template strategy enabled precise differentiation of remote and adjacent C6–H and C7–H bonds, and similar C3–H and C7–H bonds of a pharmaceutically relevant bicyclic aza-arene scaffold.
- Zhoulong Fan
- , Xiangyang Chen
- & Jin-Quan Yu
-
Article |
 RETRACTED ARTICLE: Intrinsically unidirectional chemically fuelled rotary molecular motors
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Intrinsically unidirectional chemically fuelled rotary molecular motors
A homochiral rotary molecular motor shows autonomous unidirectional rotation around a single bond driven by a chemical fuel.
- Ke Mo
- , Yu Zhang
- & Depeng Zhao
