Original Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Original Article |
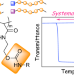 Facile synthesis of acrylamide derivative copolymers with side urethane groups for systematic variation of the thermoresponsive behavior
Facile synthesis of acrylamide derivative copolymers with side urethane groups for systematic variation of the thermoresponsive behavior
Simple control of the thermoresponsive properties of polymers in water over a broad range is achieved by using a designed urethane-containing acrylamide monomer in combination with a hydroxy-containing precursor monomer, which forms a statistical sequence due to its similar backbone. The copolymers exhibited a lower critical solution temperature-type responsive behavior in water, and the effects of structural factors such as composition, molecular weight, end groups and side-chain structure in urethane monomers were systematically evaluated.
- Shohei Ida
- , Ryu Hashiguchi
- & Shokyoku Kanaoka
-
Original Article
| Open Access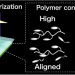 Effect of polymer concentration on molecular alignment behavior during scanning wave photopolymerization
Effect of polymer concentration on molecular alignment behavior during scanning wave photopolymerization
Schematic illustrations of the alignment behavior induced by SWaP. Photopolymerization was conducted with a scanned UV slit light. Uniaxial molecular alignment was induced when the polymer concentration in the exposure area was high, while it was random when the polymer concentration was low.
- Takuto Ishiyama
- , Yoshiaki Kobayashi
- & Atsushi Shishido
-
Original Article |
 Revisit of crystal orientation in a vulcanizate of natural rubber under planar elongation
Revisit of crystal orientation in a vulcanizate of natural rubber under planar elongation
Natural rubber exhibits the strain-induced crystallization (SIC). By using WAXD, the orientation of NR crystal formed by SIC under planar elongation was revisited. We found that the orientational state of the crystal lattice possesses a continuous margin of the orientation angle between 6.4 and 19.6° for the ac plane with respect to the surface of the specimen sheet in the real NR specimen. This orientational state could be accomplished as a result of balancing the preferential parallel orientation of (120) planes (the slip planes) and C = C planes with respect to the surface of the specimen sheet.
- Ruito Tanaka
- , Tomohiro Yasui
- & Shinichi Sakurai
-
Original Article
| Open Access A highly crystalline face-on π-conjugated polymer based on alkoxythiophene-flanked benzobisthiazole for organic photovoltaics
A highly crystalline face-on π-conjugated polymer based on alkoxythiophene-flanked benzobisthiazole for organic photovoltaics
We synthesized a new benzobisthiazole (BBTz) containing building unit in which two alkoxythiophenes were attached to the BBTz moiety so as to induce oxygen–sulfur noncovalent intramolecular interactions and thereby interlock the linkage. As a result, the π-conjugated polymer incorporating the new building unit, PDBTz2, had a more coplanar and rigid backbone than the alkyl counterpart, PDBTz1. Interestingly, the backbone orientation was completely altered from the edge-on orientation (PDBTz1) to the face-on orientation (PDBTz2), which is preferable for organic photovoltaics. Accordingly, PDBTz2 showed a much higher photovoltaic performance than PDBTz1.
- Shuhei Doi
- , Tsubasa Mikie
- & Itaru Osaka
-
Note |
 Surface zeta potential and protein adsorption on the coating surface of a heteroarm star polymer with a controlled hydrophilic/hydrophobic arm ratio
Surface zeta potential and protein adsorption on the coating surface of a heteroarm star polymer with a controlled hydrophilic/hydrophobic arm ratio
The surface properties of the star polymer coating were evaluated with their resistance to protein adsorption and surface zeta (ζ)-potential to clarify the mechanism for inhibition of cell adhesion. The surface of the star polymer coating with a high density of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) formed an electrically neutral diffuse brush structure in water and showed high resistance to protein adsorption. Considering the data obtained in the study, the surface ζ-potential and antibiofouling properties were correlated by controlling the molecular architecture of the coating material.
- Masayasu Totani
- , Hiroharu Ajiro
- & Tsuyoshi Ando
-
Focus Review
| Open Access Design of functional soft interfaces with precise control of the polymer architecture
Design of functional soft interfaces with precise control of the polymer architecture
Soft interfaces formed by polymer materials are important interfaces for biological systems (biointerfaces). Controlled radical polymerization (CRP) is highly suited for designing biointerfaces composed of polymer chains because it enables precise control of the polymer architecture at the nanoscale. This focus review describes the design of functional soft interfaces based on investigations of the structure-property relationships of CRPs. In particular, polymer brush surfaces showing autonomous property changes, comb-type copolymer-driven 2D/3D transformations of lipid bilayers, and molecular interactions in bactericidal cationic polymer brushes are depicted.
- Tsukuru Masuda
-
Note |
 Rapid and facile quantification of surface amino groups on chitin nanowhiskers and nanofibers via spectrophotometry
Rapid and facile quantification of surface amino groups on chitin nanowhiskers and nanofibers via spectrophotometry
Surface amino groups (SAGs) on nanochitin materials were quantified using three amino-labeling reagents and two cationic dyes. After binding to SAGs, the excess labeling reagents or generated molecules were assessed by spectrophotometry. The dyes were adsorbed onto SAGs, and the excess was similarly quantified. The obtained values were compared with the titration values. Although the values by labeling reagents were underestimated, some of the values were proportional to those by titration. Reliable results were attained using the two labeling reagents with conversion equations or using Acid Orange 7 adsorption.
- Jun Araki
- , Shiori Yoda
- & Riku Kudo
-
Note |
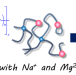 Effect of the Mg2+ ratio on the mechanical and self-healing properties of polyisoprene ionomers co-neutralized with Na+ and Mg2+
Effect of the Mg2+ ratio on the mechanical and self-healing properties of polyisoprene ionomers co-neutralized with Na+ and Mg2+
The morphology and physical properties of polyisoprene ionomers co-neutralized with Na+ and Mg2+ in different ratios have been studied. The mechanical and self-healing properties of the ionomer were reinforced and disturbed, respectively, at over 25 % of the Mg2+ ratio, where linkage via Mg2+ in the network is pervasive throughout the material.
- Rina Takahashi
- , Taro Udagawa
- & Yohei Miwa
-
Original Article |
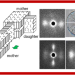 Three representative types of WAXD/SAXS patterns to establish the bimodal structure concept of stacked lamellae in isotactic polypropylene spherulites
Three representative types of WAXD/SAXS patterns to establish the bimodal structure concept of stacked lamellae in isotactic polypropylene spherulites
The in situ wide-angle (WAXD) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) measurements have been performed using a synchrotron microbeam technique for the melt-isothermally-growing iPP spherulites. The thus-collected data were found to be classified into three sets of totally different WAXD/SAXS patterns, from which the three different orientation modes of the stacked lamellae and related crystallographic axes were deduced. These structural information allowed us to discuss the growth mechanism of stacked lamellae in the iPP spherulites from the microscopic point of view.
- Kohji Tashiro
- , Hiroko Yamamoto
- & Yuichi Miyake
-
Original Article
| Open Access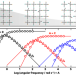 Predicting the effects of degradation on viscoelastic relaxation time using model transient networks
Predicting the effects of degradation on viscoelastic relaxation time using model transient networks
This study explores the effects of long-term degradation on the viscoelastic properties of viscoelastic liquids using tetra-armed polyethylene glycol (Tetra-PEG) slimes as model material. It aims to enhance control over the viscoelasticity of biomedical materials, like sodium hyaluronate, by introducing specific cleavage sites into the Tetra-PEG slimes to simulate degradation. The study reveals that despite degradation, the slimes maintain a single relaxation mode, offering a method to design viscoelastic liquids with predictable and controllable degradation for biomedical applications.
- Ryunosuke Kobayashi
- , Mitsuru Naito
- & Takuya Katashima
-
Note |
 Humidity responsiveness of a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel with a PEG/water mixed solvent
Humidity responsiveness of a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel with a PEG/water mixed solvent
We report the humidity-responsive volume changes of a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) gel and bending deformation of a PNIPAAm and poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide) (PDMAAm) complex gel.
- Ryotaro Makita
- , Aya M. Akimoto
- & Ryo Yoshida
-
Original Article |
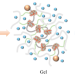 Optimal conditions for the use of polyrotaxane as a cross-linker in preparing elastomers with high toughnesses
Optimal conditions for the use of polyrotaxane as a cross-linker in preparing elastomers with high toughnesses
In this study, the effects of the polyrotaxane cross-linker concentration and solvent content on elastomer preparation were investigated to obtain elastomers with high toughnesses due to the properties of the polyrotaxane cross-linking agent. If elastomers were prepared in a state in which the slide-ring effect of the polyrotaxane was easily expressed by the concentration of the polyrotaxane cross-linker and the amount of solvent, the elastomers obtained elongated more and were tougher than elastomers made from conventional cross-linkers.
- Sizhe Liu
- , Tomoya Hayashi
- & Yukikazu Takeoka
-
Original Article |
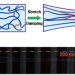 Ultrastretchable hydrogels with strong damping effects
Ultrastretchable hydrogels with strong damping effects
This study reports a method that significantly improved the stretchability and damping properties of hydrogels. The innovation is the replacement of traditional short-chain crosslinkers, such as N,N-methylenebis(acrylamide) (MBA), with long-chain crosslinkers. As a result, the molecular chains of the network could slide when stretched, which greatly increased the mechanical elongation and enabled damping by the hydrogel (up to 85%). The maximum elongation reached 21800%, with a toughness of 11.32 MJ m−3. This study provides a new approach for the development of highly stretchable and damping hydrogels.
- Ming Ge
- & Lidong Zhang
-
Original Article
| Open Access CO2 gas-triggered wettability control of silylation-modified CNC films by manipulating the surface structure and introducing tertiary amino groups
CO2 gas-triggered wettability control of silylation-modified CNC films by manipulating the surface structure and introducing tertiary amino groups
The modification of cellulose nanocrystal film using alkyl silane and silane containing tertiary amino groups was performed in a suspension state. Control of the surface structure and functionalization by silane compounds was conducted in the two-stage process. Wettability change property of the silylation-modified CNC triggered by CO2 was demonstrated.
- Hiroyuki Taniyama
- & Koji Takagi
-
Original Article
| Open Access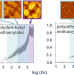 Melt adsorption of poly(tert-butyl methacrylate) and poly(ethyl methacrylate) on silica studied with chip nanocalorimetry
Melt adsorption of poly(tert-butyl methacrylate) and poly(ethyl methacrylate) on silica studied with chip nanocalorimetry
We examined the adsorption behavior of poly(tert-butyl methacrylate) (PtBMA) and poly(ethyl methacrylate) (PEMA), on a silica surface. Time-evolution of the degree of adsorption γ(t) was evaluated with chip nanocalorimetry. γ(t) revealed a two-step profile for both polymers. At the second stage of adsorption, the slope of γ(t) vs. log t increased as adsorption proceeded; this trend has not been reported for other polymers so far. In addition, atomic force microscopy images of the adsorbed layers revealed corresponding evolutions of the morphologies.
- Minato Ishihara
- , Tomoya Watanabe
- & Takashi Sasaki
-
Focus Review |
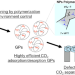 Hydrogel particles for CO2 capture
Hydrogel particles for CO2 capture
In this short review, we focus on the development of CO2 separation materials consisting of hydrogel particles. The review starts with development of stimuli responsive micro- and nano-gel particles that reversibly absorb CO2 isn response. The next chapter focuses on the development of temperature-responsive hydrogel films consisting of gel particles that reversibly absorb CO2 and the importance of optimizing the pKa values of the amines in the particles. In the end, assembly of defect-free nano-meter-thick CO2 separation membranes consisting of the amine containing hydrogel particles are introduced.
- Yu Hoshino
- & Shoma Aki
-
Note |
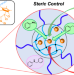 Selective N-alkylation catalyzed by polymer gels with crosslinked domains containing iridium complexes
Selective N-alkylation catalyzed by polymer gels with crosslinked domains containing iridium complexes
To develop a novel gel catalyst system for a selective reaction, we prepared a variety of gels with homogeneously dispersed crosslinked domain (CD) structures containing iridium complexes with various crosslinking densities. The designed CD gel catalyst catalyzed the N-alkylation of aniline with benzyl alcohol, and the steric effect of the CD structure allowed the selective formation of the secondary amine product by controlling the access of the substrate to the iridium complex.
- Shohichi Furukawa
- , Hiroki Takeshita
- & Shohei Ida
-
Original Article |
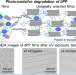 Photooxidative degradation and fragmentation behaviors of oriented isotactic polypropylene
Photooxidative degradation and fragmentation behaviors of oriented isotactic polypropylene
Photooxidation and fragmentation behaviors of itPP were studied. Photooxidation likely occurred in the amorphous regions of itPP due to the higher oxygen diffusion. Surface deterioration was observed on the UV-exposed itPP films. Pressed films exhibited much denser cracks compared to uniaxially oriented itPP films. Notably, cracks in the uniaxially oriented itPP films were formed along the direction of orientation and decreased with increasing draw ratio. The crystalline structure and oriented molecular chains notably inhibited the photooxidative degradation and fragmentation of the itPP films.
- Yingjun An
- , Tomoko Kajiwara
- & Atsushi Takahara
-
Original Article
| Open Access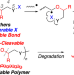 Synthesis of degradable polymers via 1,5-shift radical isomerization polymerization of vinyl ether derivatives with a cleavable bond
Synthesis of degradable polymers via 1,5-shift radical isomerization polymerization of vinyl ether derivatives with a cleavable bond
We developed a novel method for synthesizing degradable polymers based on 1,5-shift radical isomerization polymerizations of vinyl ethers with transferable atoms or groups and in-between acid-cleavable ether linkages in the side chains. In particular, vinyl ethers with side chains composed of thiocyano and p-methoxybenzyl ether groups underwent radical isomerization polymerizations via 1,5-shifts, in which a vinyl ether radical abstracted the cyano group intramolecularly to generate a thiyl radical and result in a polymer with a p-methoxybenzyl ether linkage in the main chain.
- Mineto Uchiyama
- , Masato Imai
- & Masami Kamigaito
-
Review
| Open Access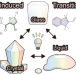 Recent progress in photoinduced transitions between the solid, glass, and liquid states based on molecular photoswitches
Recent progress in photoinduced transitions between the solid, glass, and liquid states based on molecular photoswitches
Photoinduced transitions between the solid, glass, and liquid states based on molecular photoswitches promise an enormous variety of applications, such as photoswitchable adhesives, which contribute to material recycling for a sustainable future in the era of composite materials. In this review, we highlight recent progress in the photoinduced transitions of small molecules and polymers and systematically discuss the molecular designs, mechanisms, applications, merits and demerits, and future challenges in each photoswitch and the whole field.
- Keiichi Imato
- , Naoki Kaneda
- & Yousuke Ooyama
-
Focus Review
| Open Access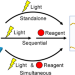 Recent progress in photoreactive crosslinkers in polymer network materials toward advanced photocontrollability
Recent progress in photoreactive crosslinkers in polymer network materials toward advanced photocontrollability
Photochemically adaptable polymer materials are widely used in the fields of medicine, electronics, and engineering due to their precise and remote processability. Diverse designs of light-responsive units have been developed to fabricate various photocontrollable materials with low-energy, rapid, and reversible photoreactivity. Recently, multiple stimuli-responsive materials have been demonstrated to further control their photoreactivity by combining light with another stimulus, leading to advanced photocontrollable capabilities. This Focus Review summarizes the recent progress in developing photochemically adaptable polymer network materials by designing photoresponsive units, focusing on the chemical structures of cleavable moieties.
- Hiroshi Masai
- , Tomoki Nakagawa
- & Jun Terao
-
Original Article |
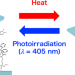 Reusable dismantlable adhesion interfaces induced by photodimerization and thermo/photocleavage reactions
Reusable dismantlable adhesion interfaces induced by photodimerization and thermo/photocleavage reactions
Overview of the reusable dismantlable adhesion interface system. Heating induces a cleavage reaction of the anthracene photodimer in the molecular layer at the adhesion interface, and the anthracene monomer remains on the substrate surface of the peeled specimen. Photoirradiation to the cleaved molecular layer induces the photodimerization of anthracenes, and the materials exhibit strong adhesion at the adhesion interface.
- Miho Aizawa
- , Haruhisa Akiyama
- & Atsushi Shishido
-
Review
| Open Access Leveraging mechanochemistry for sustainable polymer degradation
Leveraging mechanochemistry for sustainable polymer degradation
Mechanochemistry is a promising technology to tackle current and future polymer waste streams for a sustainable future. With this review, we take into account synthetic, computational, technical, and engineering perspectives to converge trituration and polymer mechanochemistry with a particular focus on the fate of commodity polymers and potential technologies to monitor mechanochemical reactions while they occur. We highlight the need for future transdisciplinary research to tackle the high-leverage parameters governing an eventually successful mechanochemical polymer degradation approach for a circular economy.
- Simay Aydonat
- , Adrian H. Hergesell
- & Robert Göstl
-
Original Article
| Open Access Hydrolyzable and biocompatible aliphatic polycarbonates with ether-functionalized side chains attached via amide linkers
Hydrolyzable and biocompatible aliphatic polycarbonates with ether-functionalized side chains attached via amide linkers
Aliphatic polycarbonates with ether side groups linked by amide bonds exhibit high hydrolyzability and antiplatelet properties due to enhanced hydration resulting from strong interactions with amide and ether side groups.
- Kazuki Fukushima
- , Shunta Hakozaki
- & Takashi Kato
-
Original Article
| Open Access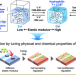 Design of dual stimuli-responsive gels with physical and chemical properties that vary in response to light and temperature and cell behavior on their surfaces
Design of dual stimuli-responsive gels with physical and chemical properties that vary in response to light and temperature and cell behavior on their surfaces
A buffer solution of dual stimuli-responsive polymer with photodimerizable groups and temperature-responsive moieties undergoes a phase transition from a sol state to a gel state by exposure to ultraviolet light. The resulting gels changed the physical (elastic modulus) and chemical (hydrophilicity) properties by varying UV exposure time and temperature, respectively. Cell adhesion, spreading, and proliferation were strongly influenced by the physical and chemical properties of the polymer gels, which were regulated by varying UV exposure time and temperature.
- Masaaki Okihara
- , Akana Matsuda
- & Takashi Miyata
-
Rapid Communication
| Open Access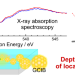 Depth analysis of local conformation in poly(methyl methacrylate) adsorbed onto SiOx studied by soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy combined with an Ar gas cluster ion beam
Depth analysis of local conformation in poly(methyl methacrylate) adsorbed onto SiOx studied by soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy combined with an Ar gas cluster ion beam
The aggregation states from the interface to the bulk of the adhesive/adherend is a key to unraveling adhesion at the molecular level. We applied X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) in combination with an Ar gas cluster ion beam (Ar GCIB) to poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) films adsorbed onto a SiOx/Si(111) surface. GCIB-XAS analysis revealed that the orientation of the C=O group in the side chain of PMMA differs between the region from the SiOx interface to a distance on the order of 1 nanometer and the bulk PMMA region.
- Hiroyuki Yamane
- , Masaki Oura
- & Takaki Hatsui
-
Review |
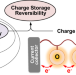 Reversible and high-density energy storage with polymers populated with bistable redox sites
Reversible and high-density energy storage with polymers populated with bistable redox sites
In this review, we show that reversibility of charge storage occurs in polymers with bistable redox-active groups populated in the repeat units of a nonconjugated backbone, especially when an electron self-exchange reaction spreads throughout the polymer. We will also show that extending the idea of electron exchange to electron/proton exchange leads to reversible hydrogen storage based on the bistability of hydrogenated and dehydrogenated states and the equilibrium for hydrogenation.
- Kenichi Oyaizu
-
Original Article |
 Enhancing the transparency and tensile properties of immiscible poly(methyl methacrylate)/ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer blends by lithium salt addition
Enhancing the transparency and tensile properties of immiscible poly(methyl methacrylate)/ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer blends by lithium salt addition
We added lithium (trifluoromethane sulfonyl) imide (LiTFSI) salt into an immiscible poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA)/ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer (EVOH) to improve the transparency and tensile properties. The addition of LiTFSI reduced the refractive index of EVOH, which matched the refractive index of PMMA, resulting in high transparency. In addition, LiTFSI interrupted the intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds between the OH groups in EVOH, resulting in decreased crystallinity. Consequently, the amorphous and flexible EVOH domains in the PMMA matrix changed the tensile properties from brittle to ductile by suppressing the stress concentration.
- Hana Watanabe
- , Mayu Horada
- & Shogo Nobukawa
-
Original Article |
 Phantom chain simulations for fracture of polymer networks created from star polymer mixtures of different functionalities
Phantom chain simulations for fracture of polymer networks created from star polymer mixtures of different functionalities
Although a fundamental problem, the effect of node functionality on network fracture has yet to be clarified. This study performed phantom chain simulations for networks made from star polymer mixtures with different functionalities. The results reveal that the fracture characteristics lie on the master curves if they are plotted as functions of the cycle rank of the network, irrespective of the mixing ratio and the conversion rate.
- Yuichi Masubuchi
-
Original Article |
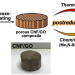 Electrical conductivities and mechanical properties of porous cellulose nanofiber/reduced graphene oxide composites prepared with postreduction processes
Electrical conductivities and mechanical properties of porous cellulose nanofiber/reduced graphene oxide composites prepared with postreduction processes
Electrically conductive porous materials consisting of cellulose nanofiber (CNF) and graphene were prepared with postreduction processes. Porous CNF/graphene oxide (GO) composites were used as precursors and the reduction of the GO under dry conditions was carried out. Both thermal and chemical reduction processes successfully proceeded to obtain the porous CNF/reduced GO (rGO) composites, in which the conductive path was effectively fabricated owing to the good dispersibility of GO sheets. As a result, the porous CNF/rGO exhibited high electrical conductivity of up to 1.39 × 10–3 S/m.
- Hiroshi Eguchi
- , Hiromichi Hayashi
- & Kenji Nagata
-
Original Article |
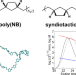 Conformations of hydrogenated ring-opened poly(norbornene)s in dilute solution
Conformations of hydrogenated ring-opened poly(norbornene)s in dilute solution
The characteristic ratios C∞ of syndiotactic, isotactic, and atactic hydrogenated ring-opened poly(norbornene)s, H-poly(NB)s, were determined in 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene at 140 °C with molecular dynamics simulations and size exclusion chromatography with a multiangle light-scattering online detector (SEC-MALS). The C∞ results were 11, 14 and 12 for syndiotactic, isotactic and atactic H-poly(NB), respectively, all of which were consistent with the rotational isomeric state model, and definitely larger than those for polyethylene and polypropylenes. The stiffness of the H-poly(NB) chains was induced by the cyclopentane ring in the chains.
- Yuki Nakama
- , Satoshi Natori
- & Takahiro Sato
-
Original Article
| Open Access Effect of thickness on the electrical properties of PEDOT:PSS/Tween 80 films
Effect of thickness on the electrical properties of PEDOT:PSS/Tween 80 films
This study explores enhanced electrical properties in conductive polymers, particularly PEDOT:PSS, by creating multilayered films. Initial findings show a sheet resistance of 1639 Ω□-1 for a single layer, but applying three additional layers reduces it to 29 Ω□-1, boosting conductivity from 2.6 to 18.3 Scm-1. Similar improvements are observed with formulations containing Tween 80. Analysis via X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy indicates increased crystalline order and a benzoid to quinoid shift. Surface profiling reveals growing roughness with additional PEDOT:PSS layers, partially mitigated by Tween 80.
- Joseph L. Carter
- , Catherine A. Kelly
- & Mike J. Jenkins
-
Original Article |
 Modified abaca fiber prepared by radiation-induced graft polymerization as a reinforcement for unsaturated polyester resin composites
Modified abaca fiber prepared by radiation-induced graft polymerization as a reinforcement for unsaturated polyester resin composites
The effect of radiation-induced graft polymerization (RIGP) on abaca fibers was evaluated for composite reinforcement. Using grafted fibers improved composite properties, especially when RIGP was carried out under reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) mechanism. Controlled chain growth of grafted polymer could be achieved by RAFT-RIGP and this led to the highest improvement in mechanical strength versus pristine fibers and those modified by conventional RIGP. These findings show the capability of RAFT-RIGP to optimize the effectiveness of natural fibers in the composite industry.
- Bin Jeremiah D. Barba
- , Noriaki Seko
- & David P. Penaloza Jr.
-
Original Article
| Open Access Enhanced adhesion of PEDOT:PSS to substrates using polydopamine as a primer
Enhanced adhesion of PEDOT:PSS to substrates using polydopamine as a primer
Poly(dopamine) (PDA) was investigated as a primer to enhance adhesion in flexible optoelectronic devices using the conducting polymer PEDOT:PSS. PDA improved wettability on polypropylene (PP) but reduced it on poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET). However, PDA enhanced the quality and adhesion of pristine PEDOT:PSS and PEDOT:PSS/Tween 80 films on glass, PP, and PET. Crucially, it did not negatively affect sheet resistance of PEDOT:PSS/Tween 80 films, establishing its suitability as a primer for flexible substrates. This research addresses a key challenge in utilizing PEDOT:PSS in flexible optoelectronics, enhancing its performance on various substrates.
- Joseph L. Carter
- , Catherine A. Kelly
- & Mike J. Jenkins
-
Focus Review
| Open Access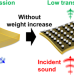 Acoustic metamaterials based on polymer sheets: from material design to applications as sound insulators and vibration dampers
Acoustic metamaterials based on polymer sheets: from material design to applications as sound insulators and vibration dampers
For uniform and flat materials, heavier plates show higher sound insulation performance because of the mass law. Acoustic metamaterials with periodic resonance structures have attracted attention as ultra-lightweight sound insulators that can break the mass law limit. Recently, practical acoustic metamaterial sheets that allow high-throughput fabrication and single-step implementation on target objects have been developed based on polymer materials. In this Focus Review, the polymer-based material design, the control of acoustic functions based on polymer properties, and applications as sound insulators and vibration dampers are described.
- Masanari Nakayama
-
Rapid Communication |
 Hydrolysis properties of polyglycolide fiber mats mixed with a hyperbranched polymer as a degradation promoter
Hydrolysis properties of polyglycolide fiber mats mixed with a hyperbranched polymer as a degradation promoter
The effects of the addition of a hyperbranched polymer (HBP) on the degradability characteristics of linear polyglycolide (PGA) fiber mats. It was revealed that HBP acted as a plasticizer, especially in underwater environments. The weight loss of the PGA fiber mats was accelerated with increasing HBP content. Considering that the structural changes in the PGA crystals depended on the feed amount of HBP, it was claimed that HBP promoted PGA degradation in both the amorphous and crystalline phases.
- Reiki Eto
- , Haruki Mokudai
- & Keiji Tanaka
-
Original Article |
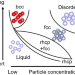 Unified explanation for self-assembly of polymer-brush-modified nanoparticles in ionic liquids
Unified explanation for self-assembly of polymer-brush-modified nanoparticles in ionic liquids
The higher-order structures of polymer-brush-modified nanoparticles (PSiPs) in ionic liquids were analyzed using ultrasmall-angle X-ray scattering. The self-assembly of the PSiPs was entropy-driven. The transition threshold concentration of the PSiPs was understood through the Kirkwood–Alder transition by considering the effective particle sizes. The random hexagonal close-packed structure in the concentrated-polymer-brush regime exhibited the characteristics of hard spheres, whereas face-centered cubic and body-centered cubic structures in the semidilute-polymer-brush regime reflected softening of the interparticle potential.
- Yohei Nakanishi
- , Ryohei Ishige
- & Yoshinobu Tsujii
-
Note |
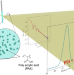 A surprisingly narrow particle size distribution for polyacrylic acid nanospheres produced by precipitation polymerization and revealed by small-angle X-ray scattering
A surprisingly narrow particle size distribution for polyacrylic acid nanospheres produced by precipitation polymerization and revealed by small-angle X-ray scattering
Narrow size distributions of spherical polyacrylic acid (PAA) particles are produced through precipitation polymerization without the need for stabilizers or emulsifiers. In this study, we employed small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) to investigate the polydispersity index (PDI) associated with the molecular weight distribution of the particles. By fitting the SAXS profiles, we were able to determine particle sizes, standard deviation, and the PDI with high precision. Our findings from SAXS confirmed that the PAA particles are monodisperse, both statistically and quantitatively, with a PDI of less than 1.05.
- Shin Takano
- , Ryohei Ono
- & Kazuo Sakurai
-
Original Article |
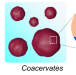 Microphase separation of double-hydrophilic poly(carboxybetaine acrylate)-poly(2-methoxyethyl acrylate) block copolymers in water
Microphase separation of double-hydrophilic poly(carboxybetaine acrylate)-poly(2-methoxyethyl acrylate) block copolymers in water
Double-hydrophilic block copolymers composed of a water-soluble poly(carboxybetaine acrylate) and a water-insoluble poly(2-methoxyethyl acrylate) (PCBA2n-b-PMEAm) produced particles in dilute aqueous solutions and microphase-separated structures in concentrated aqueous solutions. The microphase-separated structures were associated with the volume fraction and molecular weight-dependent water solubility of the PMEA chain. The morphology of the microphase-separated structure was independent of the polymer concentration, probably because the block copolymer aggregates were isolated as coacervates. The morphology was tolerant to NaCl concentration due to the nonelectrostatic aggregation of PMEA.
- Yuji Higaki
- , Honoka Toyama
- & Masaru Tanaka
-
Original Article |
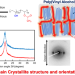 Selective acetylation of amorphous region of poly(vinyl alcohol) in supercritical carbon dioxide
Selective acetylation of amorphous region of poly(vinyl alcohol) in supercritical carbon dioxide
Postfunctionalization of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) was performed in supercritical carbon dioxide (sc-CO2) for the selective functionalization of the amorphous region. The crystalline region was retained in the amorphous-selective acetylated PVA. The oriented structure of crystallites of the drawn PVA was maintained even after acetylation in sc-CO2. Moisture adsorption behaviors affected the crystalline structure of PVA acetylated in sc-CO2. The PVA acetylated in sc-CO2 included a larger number of water molecules under humid conditions, but the increase in thickness after water adsorption was smaller than that of randomly acetylated PVA.
- Takuya Matsumoto
- , Miyabi Yorifuji
- & Takashi Nishino
-
Original Article |
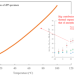 Thermal expansion of isotactic polypropylene Part I: temperature-dependent contributions of thermal expansions in its amorphous and crystalline phases
Thermal expansion of isotactic polypropylene Part I: temperature-dependent contributions of thermal expansions in its amorphous and crystalline phases
Using temperature variable SAXS and WAXS techniques, nature of thermal expansion behavior of injection molded iPP was investigated. The SAXS and WAXS provided the thermal expansion in amorphous phase and the one in crystal axes, respectively. The bulk thermal expansion was fully accounted for by the combination of them. It was found that the thermal expansion from the amorphous phase contributed significantly to the bulk thermal expansion.
- Michio Ono
-
Original Article |
 Characteristics of ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid treatment on iron(III)-induced modified catechol chitosan hydrogels under different pH conditions
Characteristics of ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid treatment on iron(III)-induced modified catechol chitosan hydrogels under different pH conditions
Iron-modified catechol hydrogel treatment with EDTA is investigated at three immersion pH levels – pH 3, 5, and 7. The introduction of EDTA facilitates the chelation of Fe3+ ions, resulting in a modified hydrogel with enhanced metal ion binding capacity. The functionalized catechol chitosan hydrogel after the treatment exhibits potential applications in biomedical and environmental fields. This research sheds light on the development of versatile hydrogel materials with tailored properties, showcasing the capabilities in diverse applications where metal ion interactions play a crucial role.
- Ngoc Quang Nguyen
- , Jungju Ryu
- & Daewon Sohn
-
Original Article |
 Tough citric acid-modified cellulose-containing polymer composites with three components consisting of movable cross-links and hydrogen bonds
Tough citric acid-modified cellulose-containing polymer composites with three components consisting of movable cross-links and hydrogen bonds
Polymer composites containing citric acid-modified cellulose (CAC) and hydrogen bonding moieties showed significant increases in mechanical toughness. In particular, an appropriate ratio of hydrogen bond donors and acceptors in the secondary linear polymer (poly(2-methoxyethyl acrylate)) maximized the toughness. The hydrogen bonds affected the phase. The maximum toughness was achieved for an amorphous structure without obvious phase separation.
- Junsu Park
- , Yuki Asaki
- & Yoshinori Takashima
-
Original Article |
 Thermal, mechanical, and morphological studies of a depolymerizable graft copolymer thermoplastic
Thermal, mechanical, and morphological studies of a depolymerizable graft copolymer thermoplastic
Polymers that can depolymerize into their constituent monomers are desirable sustainable materials, but demonstrations have focused on linear polymers. Here, a depolymerizable graft copolymer thermoplastic material is prepared by copolymerizing poly(L-lactide)-based and margaric acid-based trans-cyclobutane-fused trans-cyclooctene macromonomers. The two types of macromonomers are incorporated randomly. Proper thermal treatment is required to maximize, or even to observe, crystallinity in the microphase separated that persists over a range of temperature. The physical states of the soft and hard domains significantly impact the material’s tensile properties.
- Zeyu Wang
- , Mark D. Foster
- & Junpeng Wang
-
Original Article |
 Study on the elasticity of the crystalline lattice of α´-phase polyamide 6 and 11 under hydraulic pressures up to 100 MPa
Study on the elasticity of the crystalline lattice of α´-phase polyamide 6 and 11 under hydraulic pressures up to 100 MPa
Polyamide (PA) is a potential candidate for seals or barriers in systems used to supply high-pressure hydrogen gas to fuel cell vehicles. The elasticity of the crystalline lattice of PA6 and PA11 was investigated using a WAXD method and a high-pressure cell while applying hydraulic pressures up to 100 MPa. A linear decrease in the d-spacing for the (002) plane (PA6) and the (010) plane (PA11) followed by rapid recovery to the initial value after depressurization was observed as the pressure increased.
- Masahiro Kasai
- , Keiko Ohyama
- & Shin Nishimura
-
Original Article
| Open Access Evaluation of pigment distribution in contact lenses with iris patterns by multiprobe analysis methods
Evaluation of pigment distribution in contact lenses with iris patterns by multiprobe analysis methods
We propose a simple method to detect depth information of ink components and pigment distribution observed by transmission electron microscopy on commercially available cosmetic contact lenses using multiple probes such as STEM EDS, XPS, HAXPES, and XAFS. These provide important information on the safety of cosmetic contact lenses, which are medical devices.
- Eri Ito
- , Hiroshi Takase
- & Katsuhiro Yamamoto
-
Focus Review |
 Aggregation states, thermal molecular motion and carrier properties in functional polymer thin films
Aggregation states, thermal molecular motion and carrier properties in functional polymer thin films
Functional polymers such as semiconducting polymers and polyelectrolytes are essential materials for various polymer thin-film devices. Here we discuss the relationship among the aggregation states, the thermal molecular motion, the carrier properties of their thin films, and the interfacial effects.
- Daisuke Kawaguchi
-
Original Article |
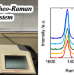 Flow-induced crystallization behavior of high-density polyethylene evaluated by Rheo-Raman spectroscopic system
Flow-induced crystallization behavior of high-density polyethylene evaluated by Rheo-Raman spectroscopic system
The flow-induced crystallization behavior of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) was investigated using Rheo-Raman spectroscopy. Although crystallization did not progress at 128 °C without shear flow, the formation of short and long consecutive trans chains was enhanced by applying shear flow, which resulted in an increased crystallization rate. In particular, by increasing the shear rate or shear-flow time, the fraction of long consecutive trans chains drastically increased prior to crystallization, and oriented crystals formed. These results indicated that the shear rate and applied work were the important parameters dominating the formation of oriented crystals.
- Takumitsu Kida
- , Khunanya Janchai
- & Masayuki Yamaguchi
-
Original Article |
 Effect of substituted positions of acetylene groups in benzene rings on the properties of poly(silane arylether arylacetylene)s
Effect of substituted positions of acetylene groups in benzene rings on the properties of poly(silane arylether arylacetylene)s
Poly(silane arylether arylacetylene) (PSEA) resins with acetylene groups at different substituted positions were synthesized and the effects of the substituted positions of acetylene groups on the properties of PSEA resins were investigated. The resins possess a wide processing window. The cured resins display high mechanical properties and thermal stability. mmm-PSEA-C possesses better mechanical properties than pmp-PSEA-C. The decomposition temperatures of pmp-PSEA-C and mmm-PSEA-C are over 530 °C.
- Jixian Li
- , Changjun Gong
- & Farong Huang

 Changes in crystal morphology induced by lanthanide doping into diacetylene lamellar crystals
Changes in crystal morphology induced by lanthanide doping into diacetylene lamellar crystals