Rapid Communication
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Original Article |
 Structure and mechanical properties of biobased polyamide 11 specimens subjected to different heat treatments
Structure and mechanical properties of biobased polyamide 11 specimens subjected to different heat treatments
The relationships between the macroscopic mechanical properties and lamellar structures of polyamide 11 obtained from different heat treatments were investigated. From the tensile tests, the maximum stress and strain at necking increase with the heat treatment temperature. WAXS measurements indicated that different crystalline phases formed depending on the heat treatment conditions. SAXS revealed that the lamellar thickness and long period increased with the heat treatment temperature. Based on these results, we elucidated that the macroscopic mechanical properties correlate with the lamellar thickness and long period.
- Toyoshi Yoshida
- , Mei Touji
- & Yoshihisa Kaneko
-
Review
| Open Access Recent advances in structurally elaborate triptycenes, triptycene-containing polymers and assemblies: structures, functions and applications
Recent advances in structurally elaborate triptycenes, triptycene-containing polymers and assemblies: structures, functions and applications
Triptycene-containing polymers featuring a rigid propeller-shaped structure have attracted attention for a wide range of potential applications including guest recognition, material transports, separations, catalysis, and organic electronics. Herein, with a thorough literature survey, we present the synthesis of the various types of triptycenes that provide components for functional polymers. We particularly focus on triptycene-containing polymers and two-dimensional assemblies based on the space-filling design that uses nested packing. Future perspectives on the functionalities brought about by the design of triptycene-containing polymers and molecular assemblies are also discussed.
- Fumitaka Ishiwari
- , Yoshiaki Shoji
- & Takanori Fukushima
-
Original Article |
 Exclusive formation of stereocomplex crystallites in PLLA/PDLA (50/50) blends by the addition of a plasticizer
Exclusive formation of stereocomplex crystallites in PLLA/PDLA (50/50) blends by the addition of a plasticizer
The effects of an organic monoglyceride (OMG) plasticizer on the crystallization of the PLLA/PDLA (50/50) blend were investigated by examining the isothermal crystallization of the blend with different contents of OMG (1–5 wt%) using POM, DSC, and time-resolved WAXD. It was found that the increase of the OMG content promoted the exclusive formation of stereocomplex crystallites and enhanced its crystallinity while suppressing the formation of homocrystals.
- Neimatallah Hosni Mohammed Mahmoud
- , Hideaki Takagi
- & Shinichi Sakurai
-
Original Article
| Open Access Ring-opening polymerization of six-membered cyclic hybrid dimers composed of an oxoester and thioester
Ring-opening polymerization of six-membered cyclic hybrid dimers composed of an oxoester and thioester
Three cyclic oxoester-thioester hybrid monomers were studied for anionic and cationic ring-opening polymerizations. Anionic polymerizations using thiol with 2,6-lutidine were successful for the chemoselective cleavage of the thioester with the thiol propagating end, exhibiting the living character to some extent. The polymerization in 2,6-lutidine without an initiator produced macrocyclic polymers. The cationic polymerizations occurred with the aid of CF3SO3H and benzyl alcohol but involved side reactions with low chemoselective ring cleavage. The thioester unit caused the polymers to exhibit a lower Tg with greater thermal and photo degradability.
- Mao Hirata
- , Tomoki Yoshimatsu
- & Masato Suzuki
-
Original Article
| Open Access Changes in crystal morphology induced by lanthanide doping into diacetylene lamellar crystals
Changes in crystal morphology induced by lanthanide doping into diacetylene lamellar crystals
Doping lanthanides into lamellar crystals of diacetylene derivatives with terminal carboxylic acids reorganized the lamellar structure and dramatically changed the crystal morphology. Detailed investigation of the crystal growth process revealed that the complexes of lanthanide and diacetylene derivatives, which are slightly formed in the solution phase during lanthanide doping, may act as a pseudonuclear agent and change the morphology of the lamellar crystals. Furthermore, the morphology changes of the lamellar crystal films significantly altered surface properties such as film appearance and water repellency.
- Michinari Kohri
- , Sojiro Isomura
- & Keiki Kishikawa
-
Original Article |
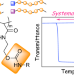 Facile synthesis of acrylamide derivative copolymers with side urethane groups for systematic variation of the thermoresponsive behavior
Facile synthesis of acrylamide derivative copolymers with side urethane groups for systematic variation of the thermoresponsive behavior
Simple control of the thermoresponsive properties of polymers in water over a broad range is achieved by using a designed urethane-containing acrylamide monomer in combination with a hydroxy-containing precursor monomer, which forms a statistical sequence due to its similar backbone. The copolymers exhibited a lower critical solution temperature-type responsive behavior in water, and the effects of structural factors such as composition, molecular weight, end groups and side-chain structure in urethane monomers were systematically evaluated.
- Shohei Ida
- , Ryu Hashiguchi
- & Shokyoku Kanaoka
-
Original Article
| Open Access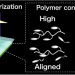 Effect of polymer concentration on molecular alignment behavior during scanning wave photopolymerization
Effect of polymer concentration on molecular alignment behavior during scanning wave photopolymerization
Schematic illustrations of the alignment behavior induced by SWaP. Photopolymerization was conducted with a scanned UV slit light. Uniaxial molecular alignment was induced when the polymer concentration in the exposure area was high, while it was random when the polymer concentration was low.
- Takuto Ishiyama
- , Yoshiaki Kobayashi
- & Atsushi Shishido
-
Original Article |
 Revisit of crystal orientation in a vulcanizate of natural rubber under planar elongation
Revisit of crystal orientation in a vulcanizate of natural rubber under planar elongation
Natural rubber exhibits the strain-induced crystallization (SIC). By using WAXD, the orientation of NR crystal formed by SIC under planar elongation was revisited. We found that the orientational state of the crystal lattice possesses a continuous margin of the orientation angle between 6.4 and 19.6° for the ac plane with respect to the surface of the specimen sheet in the real NR specimen. This orientational state could be accomplished as a result of balancing the preferential parallel orientation of (120) planes (the slip planes) and C = C planes with respect to the surface of the specimen sheet.
- Ruito Tanaka
- , Tomohiro Yasui
- & Shinichi Sakurai
-
Original Article
| Open Access A highly crystalline face-on π-conjugated polymer based on alkoxythiophene-flanked benzobisthiazole for organic photovoltaics
A highly crystalline face-on π-conjugated polymer based on alkoxythiophene-flanked benzobisthiazole for organic photovoltaics
We synthesized a new benzobisthiazole (BBTz) containing building unit in which two alkoxythiophenes were attached to the BBTz moiety so as to induce oxygen–sulfur noncovalent intramolecular interactions and thereby interlock the linkage. As a result, the π-conjugated polymer incorporating the new building unit, PDBTz2, had a more coplanar and rigid backbone than the alkyl counterpart, PDBTz1. Interestingly, the backbone orientation was completely altered from the edge-on orientation (PDBTz1) to the face-on orientation (PDBTz2), which is preferable for organic photovoltaics. Accordingly, PDBTz2 showed a much higher photovoltaic performance than PDBTz1.
- Shuhei Doi
- , Tsubasa Mikie
- & Itaru Osaka
-
Note |
 Surface zeta potential and protein adsorption on the coating surface of a heteroarm star polymer with a controlled hydrophilic/hydrophobic arm ratio
Surface zeta potential and protein adsorption on the coating surface of a heteroarm star polymer with a controlled hydrophilic/hydrophobic arm ratio
The surface properties of the star polymer coating were evaluated with their resistance to protein adsorption and surface zeta (ζ)-potential to clarify the mechanism for inhibition of cell adhesion. The surface of the star polymer coating with a high density of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) formed an electrically neutral diffuse brush structure in water and showed high resistance to protein adsorption. Considering the data obtained in the study, the surface ζ-potential and antibiofouling properties were correlated by controlling the molecular architecture of the coating material.
- Masayasu Totani
- , Hiroharu Ajiro
- & Tsuyoshi Ando
-
Original Article |
 Development of fluorescence sensors for quantifying anions based on polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane that contains flexible side chains with urea structures
Development of fluorescence sensors for quantifying anions based on polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane that contains flexible side chains with urea structures
Developing fluorescence anion sensors is important because anions play a significant role in various biological phenomena. Herein, we evaluated the anion binding properties of a polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) derivative with eight urea groups and a 3D structure. The results revealed that the POSS derivative with urea groups can bind to sulfate ions and exhibits a greater binding ability than that of the model compound because multiple urea groups exhibit cooperative effects. Through the introduction of naphthyl urea groups, the POSS derivative can be used as a fluorescence sensor for quantifying sulfate ions.
- Hayato Narikiyo
- , Masayuki Gon
- & Yoshiki Chujo
-
Focus Review
| Open Access Design of functional soft interfaces with precise control of the polymer architecture
Design of functional soft interfaces with precise control of the polymer architecture
Soft interfaces formed by polymer materials are important interfaces for biological systems (biointerfaces). Controlled radical polymerization (CRP) is highly suited for designing biointerfaces composed of polymer chains because it enables precise control of the polymer architecture at the nanoscale. This focus review describes the design of functional soft interfaces based on investigations of the structure-property relationships of CRPs. In particular, polymer brush surfaces showing autonomous property changes, comb-type copolymer-driven 2D/3D transformations of lipid bilayers, and molecular interactions in bactericidal cationic polymer brushes are depicted.
- Tsukuru Masuda
-
Note |
 Rapid and facile quantification of surface amino groups on chitin nanowhiskers and nanofibers via spectrophotometry
Rapid and facile quantification of surface amino groups on chitin nanowhiskers and nanofibers via spectrophotometry
Surface amino groups (SAGs) on nanochitin materials were quantified using three amino-labeling reagents and two cationic dyes. After binding to SAGs, the excess labeling reagents or generated molecules were assessed by spectrophotometry. The dyes were adsorbed onto SAGs, and the excess was similarly quantified. The obtained values were compared with the titration values. Although the values by labeling reagents were underestimated, some of the values were proportional to those by titration. Reliable results were attained using the two labeling reagents with conversion equations or using Acid Orange 7 adsorption.
- Jun Araki
- , Shiori Yoda
- & Riku Kudo
-
Note |
 Effect of the Mg2+ ratio on the mechanical and self-healing properties of polyisoprene ionomers co-neutralized with Na+ and Mg2+
Effect of the Mg2+ ratio on the mechanical and self-healing properties of polyisoprene ionomers co-neutralized with Na+ and Mg2+
The morphology and physical properties of polyisoprene ionomers co-neutralized with Na+ and Mg2+ in different ratios have been studied. The mechanical and self-healing properties of the ionomer were reinforced and disturbed, respectively, at over 25 % of the Mg2+ ratio, where linkage via Mg2+ in the network is pervasive throughout the material.
- Rina Takahashi
- , Taro Udagawa
- & Yohei Miwa
-
Original Article |
 Conjugation in polysiloxane copolymers via unexpected Si-O-Si dπ-pπ overlap, a second mechanism?
Conjugation in polysiloxane copolymers via unexpected Si-O-Si dπ-pπ overlap, a second mechanism?
a Column separation under black light illumination. b Calculated overlap of dπ-pπ orbitals demonstrating conjugation
- Jose Jonathan Rubio Arias
- , Zijing Zhang
- & Richard M. Laine
-
Original Article |
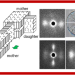 Three representative types of WAXD/SAXS patterns to establish the bimodal structure concept of stacked lamellae in isotactic polypropylene spherulites
Three representative types of WAXD/SAXS patterns to establish the bimodal structure concept of stacked lamellae in isotactic polypropylene spherulites
The in situ wide-angle (WAXD) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) measurements have been performed using a synchrotron microbeam technique for the melt-isothermally-growing iPP spherulites. The thus-collected data were found to be classified into three sets of totally different WAXD/SAXS patterns, from which the three different orientation modes of the stacked lamellae and related crystallographic axes were deduced. These structural information allowed us to discuss the growth mechanism of stacked lamellae in the iPP spherulites from the microscopic point of view.
- Kohji Tashiro
- , Hiroko Yamamoto
- & Yuichi Miyake
-
Original Article |
 Cage octasilsesquioxane-pendant polynorbornenes connected with short spacers exhibiting optical transparency
Cage octasilsesquioxane-pendant polynorbornenes connected with short spacers exhibiting optical transparency
Side-chain typed POSS-based polynorbornenes connecting with a short spacer exhibiting optical transparency owing to prevention of POSS crystallization to provide amorphous character. In addition, the resulting amorphous polymers exhibited excellent thermal stability.
- Yu Tomioka
- , Ryota Tanaka
- & Kensuke Naka
-
Rapid Communication |
 Click synthesis of an adhesive block copolymer with poly(3-hexylthiophene) and poly(vinyl catechol) segments
Click synthesis of an adhesive block copolymer with poly(3-hexylthiophene) and poly(vinyl catechol) segments
A novel block copolymer, poly(3-hexylthiophene)-b-poly(vinyl catechol) (P3HT-b-PVC) was successfully synthesized via a Click reaction between chain-endfunctionalized P3HT with an alkyne group (P3HT-Alkyne) and chain-end-functionalized poly(3,4-di-tert-butyldimethylsilyloxystyrene) with an azide group (PSVC-Azide), followed by deprotection of tert-butyldimethylsilyloxy groups from the PSVC-Azide segment. Tape test results showed that the adhesion property of the P3HT-b-PVC film was considerably better than that of the corresponding P3HT film. Furthermore, despite the presence of an insulating PVC block in P3HT-b-PVC, the P3HT-b-PVC thin film exhibited a hole mobility comparable to that of the corresponding P3HT thin film.
- Shin Inagaki
- , Kazuhiro Nakabayashi
- & Tomoya Higashihara
-
Original Article
| Open Access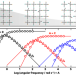 Predicting the effects of degradation on viscoelastic relaxation time using model transient networks
Predicting the effects of degradation on viscoelastic relaxation time using model transient networks
This study explores the effects of long-term degradation on the viscoelastic properties of viscoelastic liquids using tetra-armed polyethylene glycol (Tetra-PEG) slimes as model material. It aims to enhance control over the viscoelasticity of biomedical materials, like sodium hyaluronate, by introducing specific cleavage sites into the Tetra-PEG slimes to simulate degradation. The study reveals that despite degradation, the slimes maintain a single relaxation mode, offering a method to design viscoelastic liquids with predictable and controllable degradation for biomedical applications.
- Ryunosuke Kobayashi
- , Mitsuru Naito
- & Takuya Katashima
-
Original Article
| Open Access Construction of peptide/plasmid DNA complexes for plant gene transfection via the basic leucine zipper domain
Construction of peptide/plasmid DNA complexes for plant gene transfection via the basic leucine zipper domain
A new peptide carrier that mimics the basic leucine zipper domain (bZIP) of DNA-binding proteins was designed, in which (LU)4 is the leucine zipper motif and (KUA)3 is the basic DNA-binding motif (U = α-aminoisobutyric acid). When mixed with pDNA, (KUA)3-(LU)4 peptide condensed DNA molecules to form nanoparticles. Furthermore, when complexes of the (KUA)3-(LU)4 peptide and pDNA were introduced into the leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana (A. thaliana), the reporter protein was expressed in plant cells. Thus, (KUA)3-(LU)4 is an efficient carrier of pDNA with high dissociation efficiency.
- Kota Nomura
- , Seiya Fujita
- & Keiji Numata
-
Note |
 Humidity responsiveness of a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel with a PEG/water mixed solvent
Humidity responsiveness of a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel with a PEG/water mixed solvent
We report the humidity-responsive volume changes of a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) gel and bending deformation of a PNIPAAm and poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide) (PDMAAm) complex gel.
- Ryotaro Makita
- , Aya M. Akimoto
- & Ryo Yoshida
-
Original Article |
 Optimal conditions for the use of polyrotaxane as a cross-linker in preparing elastomers with high toughnesses
Optimal conditions for the use of polyrotaxane as a cross-linker in preparing elastomers with high toughnesses
In this study, the effects of the polyrotaxane cross-linker concentration and solvent content on elastomer preparation were investigated to obtain elastomers with high toughnesses due to the properties of the polyrotaxane cross-linking agent. If elastomers were prepared in a state in which the slide-ring effect of the polyrotaxane was easily expressed by the concentration of the polyrotaxane cross-linker and the amount of solvent, the elastomers obtained elongated more and were tougher than elastomers made from conventional cross-linkers.
- Sizhe Liu
- , Tomoya Hayashi
- & Yukikazu Takeoka
-
Original Article |
 Postpolymerization modification of poly(2-alkoxyethoxycarbonylmethylene)s: Efficient formation and reactivity of the ketene silyl acetal repeating units in the polymer main chain
Postpolymerization modification of poly(2-alkoxyethoxycarbonylmethylene)s: Efficient formation and reactivity of the ketene silyl acetal repeating units in the polymer main chain
Postpolymerization modifications of poly(2-methoxyethoxycarbonylmethylene) and poly(2-phenoxyethoxycarbonylmethylene) with mixtures of Me3SiCl and LDA efficiently transformed the alkoxycarbonylmethylene repeating units to ketene silyl acetals to yield a product with up to 93 mol% composition of the latter unit. TBAF-mediated benzylation of the highly silylated polymer with benzyl bromide yielded a polymer containing side chain O (major)- and main chain C (minor)-benzylated units along with the unreacted ketene silyl acetal unit.
- Hiroaki Shimomoto
- , Shota Inouchi
- & Eiji Ihara
-
Original Article |
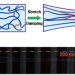 Ultrastretchable hydrogels with strong damping effects
Ultrastretchable hydrogels with strong damping effects
This study reports a method that significantly improved the stretchability and damping properties of hydrogels. The innovation is the replacement of traditional short-chain crosslinkers, such as N,N-methylenebis(acrylamide) (MBA), with long-chain crosslinkers. As a result, the molecular chains of the network could slide when stretched, which greatly increased the mechanical elongation and enabled damping by the hydrogel (up to 85%). The maximum elongation reached 21800%, with a toughness of 11.32 MJ m−3. This study provides a new approach for the development of highly stretchable and damping hydrogels.
- Ming Ge
- & Lidong Zhang
-
Original Article |
 Thermal denaturation and renaturation of a double-helical polysaccharide xanthan in acidic and basic solutions
Thermal denaturation and renaturation of a double-helical polysaccharide xanthan in acidic and basic solutions
Structural changes induced by thermal denaturation and renaturation of a double-helical polysaccharide xanthan in acidic and basic solutions were investigated mainly by light scattering measurements and circular dichroism spectroscopy. In acidic solution, the renatured components were almost the same as those in native components, while small amounts of aggregates and a hairpin structure were produced via denaturation and renaturation processes. In basic solution, the double helices were dissociated upon heating into the single coils, and high molar mass sample produced a hairpin structure after subsequent renaturation.
- Yasuhiro Matsuda
- , Ryoga Saiki
- & Kazuto Yoshiba
-
Original Article
| Open Access CO2 gas-triggered wettability control of silylation-modified CNC films by manipulating the surface structure and introducing tertiary amino groups
CO2 gas-triggered wettability control of silylation-modified CNC films by manipulating the surface structure and introducing tertiary amino groups
The modification of cellulose nanocrystal film using alkyl silane and silane containing tertiary amino groups was performed in a suspension state. Control of the surface structure and functionalization by silane compounds was conducted in the two-stage process. Wettability change property of the silylation-modified CNC triggered by CO2 was demonstrated.
- Hiroyuki Taniyama
- & Koji Takagi
-
Original Article
| Open Access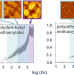 Melt adsorption of poly(tert-butyl methacrylate) and poly(ethyl methacrylate) on silica studied with chip nanocalorimetry
Melt adsorption of poly(tert-butyl methacrylate) and poly(ethyl methacrylate) on silica studied with chip nanocalorimetry
We examined the adsorption behavior of poly(tert-butyl methacrylate) (PtBMA) and poly(ethyl methacrylate) (PEMA), on a silica surface. Time-evolution of the degree of adsorption γ(t) was evaluated with chip nanocalorimetry. γ(t) revealed a two-step profile for both polymers. At the second stage of adsorption, the slope of γ(t) vs. log t increased as adsorption proceeded; this trend has not been reported for other polymers so far. In addition, atomic force microscopy images of the adsorbed layers revealed corresponding evolutions of the morphologies.
- Minato Ishihara
- , Tomoya Watanabe
- & Takashi Sasaki
-
Original Article |
 Crystallinity improvements in cellulose II after multiple posttreatment cycles with a dilute NaOH solution
Crystallinity improvements in cellulose II after multiple posttreatment cycles with a dilute NaOH solution
The study on the improvement of the crystallinity of cellulose II by post-treatment with dilute NaOH solution showed that the crystallinity was significantly improved by post-treatment with multiple cycles. The NaOH in an aqueous NaOH solution penetrated only inaccessible surface regions, and cellulose rearrangement occurred only in these regions during post-treatment, improving crystal size. In the second and subsequent posttreatment cycles, cellulose rearrangement occurred only at the inaccessible surfaces expanded during the previous post-treatment cycle, crystallization progressed toward amorphous regions away from the initial crystalline regions.
- Yuki Kugo
- , Satoshi Nomura
- & Kenji Tajima
-
Original Article |
 Fluorophore-glucan conjugate for oligosaccharide sensing in aqueous media
Fluorophore-glucan conjugate for oligosaccharide sensing in aqueous media
The fluorophore-modified glucan, TPE-6BG3 adopts an extended, random-coiled form in DMSO, which does not fluoresce. The morphology of the TPE-6BG3 chemosensor changes drastically to a dynamic globule in aqueous media. The dynamic, “induced-fit” globule selectively and sensitively recognizes the medicinally-useful tetrasaccharide, acarbose via glucan-saccharide coaggregation.
- Hiroki Kurohara
- , Yumiko Hori
- & Gaku Fukuhara
-
Original Article |
 Preparation of molecularly well-defined silicone resins based on trifluoropropyl-substituted trisilanol and their thermal, mechanical, and UV-resistance properties
Preparation of molecularly well-defined silicone resins based on trifluoropropyl-substituted trisilanol and their thermal, mechanical, and UV-resistance properties
Free-standing films of trifluoropropyl-substituted open-cage silsesquioxane-pendant polysiloxane by optimizing sol-gel reaction condition of tris(dimethoxysilyl-ethyl-dimethylsiloxy)-heptatrifluoropropyl-substituted open-cage silsesquioxane. Elastic modulus and the decomposition temperature for 5% weight loss under N2 of the product by polycondensation at 180 °C were significantly higher than that by polycondensation at 50 °C. Significant changes in the UV-vis spectra of the resulting transparent films were hardly observed even after 13 days of UV irradiation.
- Miku Kosaka
- , Taishi Nakano
- & Kensuke Naka
-
Focus Review |
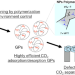 Hydrogel particles for CO2 capture
Hydrogel particles for CO2 capture
In this short review, we focus on the development of CO2 separation materials consisting of hydrogel particles. The review starts with development of stimuli responsive micro- and nano-gel particles that reversibly absorb CO2 isn response. The next chapter focuses on the development of temperature-responsive hydrogel films consisting of gel particles that reversibly absorb CO2 and the importance of optimizing the pKa values of the amines in the particles. In the end, assembly of defect-free nano-meter-thick CO2 separation membranes consisting of the amine containing hydrogel particles are introduced.
- Yu Hoshino
- & Shoma Aki
-
Note |
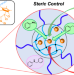 Selective N-alkylation catalyzed by polymer gels with crosslinked domains containing iridium complexes
Selective N-alkylation catalyzed by polymer gels with crosslinked domains containing iridium complexes
To develop a novel gel catalyst system for a selective reaction, we prepared a variety of gels with homogeneously dispersed crosslinked domain (CD) structures containing iridium complexes with various crosslinking densities. The designed CD gel catalyst catalyzed the N-alkylation of aniline with benzyl alcohol, and the steric effect of the CD structure allowed the selective formation of the secondary amine product by controlling the access of the substrate to the iridium complex.
- Shohichi Furukawa
- , Hiroki Takeshita
- & Shohei Ida
-
Original Article |
 Photooxidative degradation and fragmentation behaviors of oriented isotactic polypropylene
Photooxidative degradation and fragmentation behaviors of oriented isotactic polypropylene
Photooxidation and fragmentation behaviors of itPP were studied. Photooxidation likely occurred in the amorphous regions of itPP due to the higher oxygen diffusion. Surface deterioration was observed on the UV-exposed itPP films. Pressed films exhibited much denser cracks compared to uniaxially oriented itPP films. Notably, cracks in the uniaxially oriented itPP films were formed along the direction of orientation and decreased with increasing draw ratio. The crystalline structure and oriented molecular chains notably inhibited the photooxidative degradation and fragmentation of the itPP films.
- Yingjun An
- , Tomoko Kajiwara
- & Atsushi Takahara
-
Rapid Communication |
 Synthesis and urea adsorption capacity of a strong, acidic hollow nanoparticle
Synthesis and urea adsorption capacity of a strong, acidic hollow nanoparticle
Achieving a wearable artificial kidney hinges on overcoming the critical challenge of developing efficient urea adsorption materials for dialysate regeneration. An acidic hollow polystyrene nanoparticle was synthesized by modified emulsion polymerization, DMF etching and sulfuric acid treatment sequentially. The nanoparticles had a urea absorption capacity of up to 1 mmol/g after two hours of adsorption in a 30 mM urea aqueous solution at 37 °C. Additionally, the adsorption capacity dramatically increased with increasing urea concentration, while sharply decreased with increasing ionic strength.
- Yiheng Huang
- , Yifan Jiang
- & Yong Guo
-
Original Article
| Open Access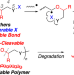 Synthesis of degradable polymers via 1,5-shift radical isomerization polymerization of vinyl ether derivatives with a cleavable bond
Synthesis of degradable polymers via 1,5-shift radical isomerization polymerization of vinyl ether derivatives with a cleavable bond
We developed a novel method for synthesizing degradable polymers based on 1,5-shift radical isomerization polymerizations of vinyl ethers with transferable atoms or groups and in-between acid-cleavable ether linkages in the side chains. In particular, vinyl ethers with side chains composed of thiocyano and p-methoxybenzyl ether groups underwent radical isomerization polymerizations via 1,5-shifts, in which a vinyl ether radical abstracted the cyano group intramolecularly to generate a thiyl radical and result in a polymer with a p-methoxybenzyl ether linkage in the main chain.
- Mineto Uchiyama
- , Masato Imai
- & Masami Kamigaito
-
Original Article
| Open Access Improving the marine biodegradability of poly(alkylene succinate)-based copolymers
Improving the marine biodegradability of poly(alkylene succinate)-based copolymers
We report the syntheses of novel marine biodegradable poly(ethylene succinate) (PES)- and poly(butylene succinate) (PBS)-based copolymers containing different dicarboxylic acid (DCA) units with various carbon numbers and different feed ratios. Specifically, the copolymers with longer-chain DCA units, even at low contents, exhibited marine biodegradability. The thermomechanical properties also varied with the DCA contents. These results indicated that the thermomechanical properties and the marine biodegradability of the PES- and PBS-based copolymers were regulated by controlling their structures and DCA contents.
- Sumito Kumagai
- , Senri Hayashi
- & Yasumasa Takenaka
-
Review
| Open Access Recent progress in photoinduced transitions between the solid, glass, and liquid states based on molecular photoswitches
Recent progress in photoinduced transitions between the solid, glass, and liquid states based on molecular photoswitches
Photoinduced transitions between the solid, glass, and liquid states based on molecular photoswitches promise an enormous variety of applications, such as photoswitchable adhesives, which contribute to material recycling for a sustainable future in the era of composite materials. In this review, we highlight recent progress in the photoinduced transitions of small molecules and polymers and systematically discuss the molecular designs, mechanisms, applications, merits and demerits, and future challenges in each photoswitch and the whole field.
- Keiichi Imato
- , Naoki Kaneda
- & Yousuke Ooyama
-
Focus Review
| Open Access Recent progress in photoreactive crosslinkers in polymer network materials toward advanced photocontrollability
Recent progress in photoreactive crosslinkers in polymer network materials toward advanced photocontrollability
Photochemically adaptable polymer materials are widely used in the fields of medicine, electronics, and engineering due to their precise and remote processability. Diverse designs of light-responsive units have been developed to fabricate various photocontrollable materials with low-energy, rapid, and reversible photoreactivity. Recently, multiple stimuli-responsive materials have been demonstrated to further control their photoreactivity by combining light with another stimulus, leading to advanced photocontrollable capabilities. This Focus Review summarizes the recent progress in developing photochemically adaptable polymer network materials by designing photoresponsive units, focusing on the chemical structures of cleavable moieties.
- Hiroshi Masai
- , Tomoki Nakagawa
- & Jun Terao
-
Review
| Open Access Leveraging mechanochemistry for sustainable polymer degradation
Leveraging mechanochemistry for sustainable polymer degradation
Mechanochemistry is a promising technology to tackle current and future polymer waste streams for a sustainable future. With this review, we take into account synthetic, computational, technical, and engineering perspectives to converge trituration and polymer mechanochemistry with a particular focus on the fate of commodity polymers and potential technologies to monitor mechanochemical reactions while they occur. We highlight the need for future transdisciplinary research to tackle the high-leverage parameters governing an eventually successful mechanochemical polymer degradation approach for a circular economy.
- Simay Aydonat
- , Adrian H. Hergesell
- & Robert Göstl
-
Original Article |
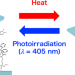 Reusable dismantlable adhesion interfaces induced by photodimerization and thermo/photocleavage reactions
Reusable dismantlable adhesion interfaces induced by photodimerization and thermo/photocleavage reactions
Overview of the reusable dismantlable adhesion interface system. Heating induces a cleavage reaction of the anthracene photodimer in the molecular layer at the adhesion interface, and the anthracene monomer remains on the substrate surface of the peeled specimen. Photoirradiation to the cleaved molecular layer induces the photodimerization of anthracenes, and the materials exhibit strong adhesion at the adhesion interface.
- Miho Aizawa
- , Haruhisa Akiyama
- & Atsushi Shishido
-
Original Article |
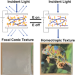 Improving the electro-optical properties of cholesteric liquid crystal devices via cellulose nanoparticle dopants
Improving the electro-optical properties of cholesteric liquid crystal devices via cellulose nanoparticle dopants
Fabrication of LCD cell without alignment layer on substrates was achieved via simply adding the chiral polymer nanoparticles into CLC mixtures. The fabricated chiral nanoparticle (CNP) doped CLC cell shows a high contrast 97.4% and a fast response time 7.6 ms.
- Chung-Yu Kuo
- , A. V. Emelyanenko
- & Chun-Yen Liu
-
Original Article
| Open Access Hydrolyzable and biocompatible aliphatic polycarbonates with ether-functionalized side chains attached via amide linkers
Hydrolyzable and biocompatible aliphatic polycarbonates with ether-functionalized side chains attached via amide linkers
Aliphatic polycarbonates with ether side groups linked by amide bonds exhibit high hydrolyzability and antiplatelet properties due to enhanced hydration resulting from strong interactions with amide and ether side groups.
- Kazuki Fukushima
- , Shunta Hakozaki
- & Takashi Kato
-
Original Article |
 Characterization and ammonolysis behavior of poly(isosorbide carbonate)-based copolymers
Characterization and ammonolysis behavior of poly(isosorbide carbonate)-based copolymers
To functionalize a poly(isosorbide carbonate) (PIC)-based polymer and evaluate its recyclability, several types of diol comonomers were copolymerized with isosorbide. The thermal and mechanical properties and decomposition behavior of the PIC copolymers were investigated. The thermal stability of PIC was retained, and its glass transition temperature was systematically controlled by copolymerization. The decomposition of the PIC copolymers upon treatment with aqueous ammonia yielded monomers and urea, and the decomposition rate was governed by the structure of the comonomer.
- Kazuaki Rikiyama
- , Akari Matsunami
- & Daisuke Aoki
-
Original Article
| Open Access Selective synthesis of α-vinyl-ω-vinylidene-oligoisoprene as a macromonomer via ethenolysis of polyisoprene
Selective synthesis of α-vinyl-ω-vinylidene-oligoisoprene as a macromonomer via ethenolysis of polyisoprene
Oligoisoprene macromonomer, which bears a terminal vinyl group and cis-1,4 regularity, was prepared by the metathesis degradation of high-molecular-weight polyisoprene with ethylene in a high selectivity and yield. The ethenolysis is also applicable for the degradation of natural rubber-derived polyisoprene, although the catalytic activity decreased. The prepared oligoisoprene macromonomer was successfully copolymerized with ethylene similarly with 1-hexadecene using a phenoxyimine-ligated titanium catalyst. The oligoisoprene-grafted polyethylene showed a typical stress‒strain curve, of which the tensile modulus and yielding stress are comparable to those of linear low-density polyethylene.
- Ryo Tanaka
- , Akane Shimmei
- & Takeshi Shiono
-
Original Article |
 Study on the deformation and fracture of epoxy monoliths through mechanical tensile and compressive tests and X-ray CT imaging
Study on the deformation and fracture of epoxy monoliths through mechanical tensile and compressive tests and X-ray CT imaging
As porous polymer materials with continuous epoxy skeletons and pores, epoxy monoliths exhibit unique mechanical properties and fracture behavior different from the bulk thermoset of epoxy resins. In this article, we describe the thermal properties, pore structures, and mechanical properties of epoxy resins with tensile and compressive deformation of the monoliths. In addition, a change in the inner porous structure after large deformation was nondestructively observed by X-ray CT imaging.
- Kazuma Aragishi
- , Yoshihiro Takeda
- & Akikazu Matsumoto
-
Original Article |
 Hydrolytic degradation and biomineralization of amine-cured epoxy resin based on glycidate
Hydrolytic degradation and biomineralization of amine-cured epoxy resin based on glycidate
Amine-cured epoxy resins bearing ester moieties were synthesized, and their properties, hydrolytic degradation behavior, and biomineralization were investigated. Neopentyl glycol diglycidate (NPG) was used as the epoxide and was cured with diethylenetriamine and isophoronediamine at different ratios. The Tgs and degradability were controlled using the composition of amines. To demonstrate their potential application as degradable materials for bone and dental repair, composites containing hydroxyapatite were prepared by curing NPG and the amines in the presence of HA. Bone-like apatite was grown on a composite by immersion in synthetic biofluid.
- Bungo Ochiai
- , Yutaka Nakazawa
- & Takahiro Kawai
-
Focus Review |
 Synthesis, characterization, degradation and applications of vinyl polyperoxides
Synthesis, characterization, degradation and applications of vinyl polyperoxides
Our recent studies on the synthesis, characterization, degradation and applications of vinyl polyperoxides are reviewed. Primarily, the recent achievements in the design, biocompatibility, thermal and enzymatic degradation of water-soluble vinyl polyperoxides and copolyperoxides are described. Finally, future development possibilities and challenges of vinyl polyperoxides for various potential applications are summarised.
- Pousali Samanta
- , Sourav Mete
- & Priyadarsi De
-
Original Article |
 B(C6F5)3-based Lewis pair-catalyzed acrylate polymerization: Lewis base effects on pairing interactions
B(C6F5)3-based Lewis pair-catalyzed acrylate polymerization: Lewis base effects on pairing interactions
Acrylate polymerizations catalyzed by Lewis pairs (LP) composed of B(C6F5)3 and various Lewis bases were investigated using two procedures based on different monomer/catalyst addition sequences. When Lewis bases were added to B(C6F5)3-activated n-butyl acrylate (nBA) (procedure 1), the polymerization proceeded quantitatively using all Lewis bases. In contrast, the type of Lewis base significantly affected the polymerization results when nBA was added to interacting LPs (procedure 2). 19F nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of the LPs indicated that weakly interacting LPs efficiently initiated the polymerizations in procedure 2.
- Yuka Naganawa
- , Kazumasa Mori
- & Masato Suzuki
-
Original Article |
 Alcoholysis of oxyphenylene-based super engineering plastics mediated by readily available bases
Alcoholysis of oxyphenylene-based super engineering plastics mediated by readily available bases
The depolymerization of super engineering plastics such as polysulfone (PSU) smoothly proceeded in the presence of methanol mediated by sodium hydroxide in 1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone (DMI) at 80 °C to form bis(4-methoxyphenyl)sulfone and 4,4’-(propane-2,2-diyl)diphenol (bisphenol A) in high yields. These products were readily isolated by simple filtration. The DMI solvent effectively promoted depolymerization and allowed insoluble resins such as polyetheretherketone (PEEK) to undergo the reaction. This method was applicable to other alcohols, such as ethanol and isopropyl alcohol.
- Yasunori Minami
- , Rena Honobe
- & Masaru Yoshida

 Supracolloidal step-growth polymerization of isotropic silica nanoparticles: a time-resolved small-angle X-ray scattering study
Supracolloidal step-growth polymerization of isotropic silica nanoparticles: a time-resolved small-angle X-ray scattering study