Original Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Note |
 Humidity responsiveness of a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel with a PEG/water mixed solvent
Humidity responsiveness of a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel with a PEG/water mixed solvent
We report the humidity-responsive volume changes of a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) gel and bending deformation of a PNIPAAm and poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide) (PDMAAm) complex gel.
- Ryotaro Makita
- , Aya M. Akimoto
- & Ryo Yoshida
-
Focus Review
| Open Access Recent progress in photoreactive crosslinkers in polymer network materials toward advanced photocontrollability
Recent progress in photoreactive crosslinkers in polymer network materials toward advanced photocontrollability
Photochemically adaptable polymer materials are widely used in the fields of medicine, electronics, and engineering due to their precise and remote processability. Diverse designs of light-responsive units have been developed to fabricate various photocontrollable materials with low-energy, rapid, and reversible photoreactivity. Recently, multiple stimuli-responsive materials have been demonstrated to further control their photoreactivity by combining light with another stimulus, leading to advanced photocontrollable capabilities. This Focus Review summarizes the recent progress in developing photochemically adaptable polymer network materials by designing photoresponsive units, focusing on the chemical structures of cleavable moieties.
- Hiroshi Masai
- , Tomoki Nakagawa
- & Jun Terao
-
Original Article |
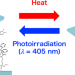 Reusable dismantlable adhesion interfaces induced by photodimerization and thermo/photocleavage reactions
Reusable dismantlable adhesion interfaces induced by photodimerization and thermo/photocleavage reactions
Overview of the reusable dismantlable adhesion interface system. Heating induces a cleavage reaction of the anthracene photodimer in the molecular layer at the adhesion interface, and the anthracene monomer remains on the substrate surface of the peeled specimen. Photoirradiation to the cleaved molecular layer induces the photodimerization of anthracenes, and the materials exhibit strong adhesion at the adhesion interface.
- Miho Aizawa
- , Haruhisa Akiyama
- & Atsushi Shishido
-
Original Article |
 Improving the electro-optical properties of cholesteric liquid crystal devices via cellulose nanoparticle dopants
Improving the electro-optical properties of cholesteric liquid crystal devices via cellulose nanoparticle dopants
Fabrication of LCD cell without alignment layer on substrates was achieved via simply adding the chiral polymer nanoparticles into CLC mixtures. The fabricated chiral nanoparticle (CNP) doped CLC cell shows a high contrast 97.4% and a fast response time 7.6 ms.
- Chung-Yu Kuo
- , A. V. Emelyanenko
- & Chun-Yen Liu
-
Review
| Open Access Leveraging mechanochemistry for sustainable polymer degradation
Leveraging mechanochemistry for sustainable polymer degradation
Mechanochemistry is a promising technology to tackle current and future polymer waste streams for a sustainable future. With this review, we take into account synthetic, computational, technical, and engineering perspectives to converge trituration and polymer mechanochemistry with a particular focus on the fate of commodity polymers and potential technologies to monitor mechanochemical reactions while they occur. We highlight the need for future transdisciplinary research to tackle the high-leverage parameters governing an eventually successful mechanochemical polymer degradation approach for a circular economy.
- Simay Aydonat
- , Adrian H. Hergesell
- & Robert Göstl
-
Original Article |
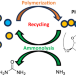 Characterization and ammonolysis behavior of poly(isosorbide carbonate)-based copolymers
Characterization and ammonolysis behavior of poly(isosorbide carbonate)-based copolymers
To functionalize a poly(isosorbide carbonate) (PIC)-based polymer and evaluate its recyclability, several types of diol comonomers were copolymerized with isosorbide. The thermal and mechanical properties and decomposition behavior of the PIC copolymers were investigated. The thermal stability of PIC was retained, and its glass transition temperature was systematically controlled by copolymerization. The decomposition of the PIC copolymers upon treatment with aqueous ammonia yielded monomers and urea, and the decomposition rate was governed by the structure of the comonomer.
- Kazuaki Rikiyama
- , Akari Matsunami
- & Daisuke Aoki
-
Original Article |
 Influence of thermal treatment on the elastic modulus of a nano-dispersed elastomer domain in an injection-molded isotactic polypropylene/thermoplastic elastomer binary blend
Influence of thermal treatment on the elastic modulus of a nano-dispersed elastomer domain in an injection-molded isotactic polypropylene/thermoplastic elastomer binary blend
Elastic moduli of nano-dispersed elastomer domains in injection molded isotactic polypropylene (iPP)/ethylene-co-octene elastomer (EO) binary blends were investigated by an atomic force microscopy. The EO domains were highly elongated to the flow direction. The elastic modulus distribution of the EO domains was quite different depending on the annealing conditions.
- Michio Ono
- & Ken Nakajima
-
Original Article |
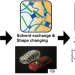 Shape reprogramming of 3D printed ionogels by solvent exchange with deep eutectic solvents
Shape reprogramming of 3D printed ionogels by solvent exchange with deep eutectic solvents
This work presents a simple strategy to prepare 3D printable and tough ionogels that can adjust to arbitrary topography. Inks for direct ink writing were prepared by dispersing cellulose nanocrystals in an aqueous solution of polyvinyl alcohol. After printing, the ink underwent a freeze-thaw process to form soft and stretchable hydrogels. Further reshaping and solvent exchange with deep eutectic solvents led to geometrically complex and tough ionogels for wearable sensors.
- Hung-Yue Tsai
- , Hao-Jing Hsu
- & Sheng-Sheng Yu
-
Original Article |
 Tailoring the mechanical properties of binary polypropylene blends with polymorphic and oriented hierarchical structures
Tailoring the mechanical properties of binary polypropylene blends with polymorphic and oriented hierarchical structures
In our study, a continuous change of tensile strength (26.9–49.5 MPa) and impact strength (4.7–23.2 KJ/m2) of iPP samples is successfully accomplished without the specific catalysts. The high content of γ-crystal with thin lamellar thickness related to the ductility property is also experimentally confirmed. A morphology of the diagram is proposed based on the composition and molded technology.
- Yan Wang
- , Yisu Wang
- & Jia-Zhuang Xu
-
Original Article |
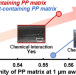 Effects of different types of maleic anhydride-modified polypropylene on the interfacial shear strengths of carbon fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites
Effects of different types of maleic anhydride-modified polypropylene on the interfacial shear strengths of carbon fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites
The effect of different types of maleic anhydride-modified polypropylene on interfacial shear strength for carbon fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites: The effect of three types of maleic anhydride-modified polypropylenes (MAPP) on the interfacial shear strength (IFSS) of PP and carbon fiber (CF) were investigated. The localization of MAPP at the interface enabled sufficient chemical interaction regardless of MA content of MAPP, and the differences of MA content had little IFSS dependences. When the chemical interaction is sufficient at the interface, the IFSS values were attributed to the crystallinity at the interphase, which depends on the natures such as crystallinity of MAPP added.
- Ayaka Yamaguchi
- , Michio Urushisaki
- & Tamotsu Hashimoto
-
Original Article |
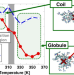 Molecular dynamics simulations of the folding structure of a thermoresponsive 2-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate oligomer in the globule state
Molecular dynamics simulations of the folding structure of a thermoresponsive 2-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate oligomer in the globule state
The folding behavior of a 2-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate oligomer with alternately protonated side chains surrounded by water molecules was evaluated using molecular dynamics simulations in the temperature range of 280–360 K. Radial distribution functions (RDFs) around the geometric center of the oligomer were evaluated; they indicated that protonated amine groups surrounded the aggregating deprotonated amine groups in the globule state. The calculation of RDFs around the geometric center is a highly reliable strategy to evaluate the folding behavior of stimuli-responsive polymer gels during the coil-to-globule transition.
- Ryo Nagumo
- , Kazuma Nishikawa
- & Shuichi Iwata
-
Original Article |
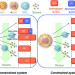 Comparative study on the effects of incorporating poly(d,l-lactide) and solvent on stereocomplex crystallization and homocrystallization in unconstrained and constrained poly(l-lactide)/poly(d-lactide) systems
Comparative study on the effects of incorporating poly(d,l-lactide) and solvent on stereocomplex crystallization and homocrystallization in unconstrained and constrained poly(l-lactide)/poly(d-lactide) systems
The effects of incorporating poly(d,l-lactide) (PDLLA) and solvent on the stereocomplex (SC) crystallization and homocrystallization of poly(l-lactide) (PLLA) and poly(d-lactide) (PDLA) chains were explored using linear one-armed PLLA (1-L)/PDLA (1-D) and linear one-armed PDLLA (1-DL) as an unconstrained system and using four-armed PLLA-b-PDLA (4-L-D) and linear one-armed 1-DL as a constrained system. The dilution effects of PDLLA and solvent enhanced SC crystallization and suppressed homocrystallization, with the exception of the constrained 4-L-D/1-DL blends in the presence of both PDLLA and solvent.
- Hideto Tsuji
- , Sena Nogata
- & Yuki Arakawa
-
Rapid Communication |
 Kinesin motors driven microtubule swarming triggered by UV light
Kinesin motors driven microtubule swarming triggered by UV light
We demonstrated biomolecular motors driven swarming of microtubules and their dissociation under UV and visible light irradiation, respectively. A photoresponsive molecule, para tert-butyl-substituted azobenzene was incorporated to the backbone of single strand DNA, which functions as a photoswitch to control the swarming of microtubules in a reversible manner. This work is expected to expand the potential applications of biomolecular motors in developing photoregulated molecular machines.
- Satsuki Ishii
- , Mousumi Akter
- & Akira Kakugo
-
Original Article |
 Isolation of hetero-telechelic polyethylene glycol with groups of different reactivity at the chain ends
Isolation of hetero-telechelic polyethylene glycol with groups of different reactivity at the chain ends
Hetero-telechelic poly(ethylene glycol)s that contain a hydroxy group and a maleimide-furan adduct their α and ω ends, respectively, were isolated as a novel type of hetero-telechelic polymers (HTPs) via the post-modification of commercially available hydroxy-terminated PEGs with furan-protected p-maleimidophenyl isocyanate and subsequent purification with reversed-phase column chromatography at critical conditions.
- Tatsuki Sato
- , Rikito Takashima
- & Hideyuki Otsuka
-
Rapid Communication |
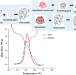 Role of the nucleating agent masterbatch carrier resin in the nonisothermal crystallization kinetics of polypropylene
Role of the nucleating agent masterbatch carrier resin in the nonisothermal crystallization kinetics of polypropylene
The effect of the nucleating agent masterbatch carrier resin on the nonisothermal crystallization of a pipe-grade polypropylene block copolymer was investigated at three different cooling rates using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Crystallization kinetic parameters obtained from DSC cooling curves showed that incorporation of a nucleating agent by means of a masterbatch increased the crystallization rate by approximately two times compared to that of the sample with the same concentration of nucleating agent without the use of a masterbatch.
- Maryam Shokrollahi
- , Bahereh T. Marouf
- & Reza Bagheri
-
Focus Review |
 Polymer/nanocarbon nanocomposites with enhanced properties
Polymer/nanocarbon nanocomposites with enhanced properties
Dispersibility and interfacial interactions are the important factors to exploit the high potential of nanocarbons for polymer/nanocarbon nanocomposites. However, carbon backbone with low reactivity has often cause agglomerations and defects from the interfaces. The use of surfactants and the surface modifications of nanocarbons have widely been conducted to improve these issues. This paper reviews recent advances in the design of polymer/nanocarbon nanocomposites, focusing on our research on the reinforcement effect of nanodiamond on polymer nanocomposites.
- Seira Morimune-Moriya
-
Original Article |
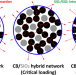 Carbon black/silica hybrid filler networking and its synergistic effects on the performance of styrene-butadiene rubber composites
Carbon black/silica hybrid filler networking and its synergistic effects on the performance of styrene-butadiene rubber composites
Synergistic effects of adding silica, as a secondary filler, to styrene-butadiene rubber composites highly filled with carbon black was investigated. It was shown that there is a critical concentration of silica at which improvements in the Payne effect, mechanical properties, abrasion resistance, and heat build-up were at extrema. This behavior was attributed to the filler networking in the hybrid filler systems, at which work of adhesion in a three-component system was considered as the driving force for flocculation of the primary filler and final morphology of fillers in hybrid composites.
- Arshia Amrollahi
- , Mehdi Razzaghi-Kashani
- & Neda Habibi
-
Original Article |
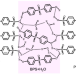 Effect of bisphenols on the electrical conductivity and structure of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): poly(styrene sulfonate)
Effect of bisphenols on the electrical conductivity and structure of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): poly(styrene sulfonate)
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) doped with poly(4-styrene sulfonate) (PEDOT: PSS) films have strong potential for application in flexible transparent conductive electrodes. In this study, the electrical conductivity of PEDOT: PSS is shown to be enhanced by a bisphenol additive, bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) sulfone (BPS). The effects of BPS on the chemical structure of PEDOT: PSS were investigated using X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The PEDOT: PSS conformation is found to undergo a transformation into a highly conductive structure following the addition of BPS.
- Seira Morimune-Moriya
- , Hiroaki Tanahashi
- & Shigeji Konagaya
-
Original Article |
 Thermoresponsive PEDOT:PSS/PNIPAM conductive hydrogels as wearable resistive sensors for breathing pattern detection
Thermoresponsive PEDOT:PSS/PNIPAM conductive hydrogels as wearable resistive sensors for breathing pattern detection
The PEDOT: PSS/PNIPAM hydrogel was simply prepared by ultrasound-enhanced free radical polymerization in an ice bath, in open air rather than spending hours under an N2 purged environment. The resulting conductive hydrogel had a uniform texture and good flexibility for rapid resistance responses and color changes when it was exposed to temperature stimulations. The dual actions of hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic aggregation weaken the Coulomb interaction between PEDOT+ and PSS− for better conductivity that is suitable for breathing monitoring and other wearable sensing applications.
- Mengwei Jia
- & Jie Zhang
-
Note |
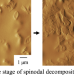 AFM observation of crystalline morphologies developed by cooperative progress with spinodal decomposition in dissimilar polycarbonate blends
AFM observation of crystalline morphologies developed by cooperative progress with spinodal decomposition in dissimilar polycarbonate blends
Crystalline embryos initiated at early stage of the spinodal decomposition (SD) grew to anisotropically shaped crystallites and then the neighboring crystallites were collided by interpenetration of the lamellae within the continuous bisphenol-A polycarbonate (BPA-PC) rich phase at late stage of the SD. Such characteristic crystallization behavior is attributed to the constraint crystallization growth within the continuous BPA-PC rich region due to interconnected phase structure obtained by the liquid–liquid phase separation via SD.
- Koudai Takamatsu
- & Hiromu Saito
-
Original Article |
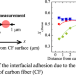 Growth of polypropylene crystals in the vicinity of carbon fibers and improvement of their interfacial shear strength
Growth of polypropylene crystals in the vicinity of carbon fibers and improvement of their interfacial shear strength
In the polypropylene (PP)/carbon fiber (CF) composite, it has been well known that maleic acid modified PP (MAPP) improves the interfacial adhesion with CF. However, the effect of maleic acid modification on the PP crystals around CF, and that of the PP crystals on the interfacial adhesion have not been clarified well. In this study, the local crystal structure of PP near CF was investigated using micro-Raman spectroscopy, and it was demonstrated that the crystal growth of PP near CF contributes significantly to the interfacial adhesion.
- Hideyuki Uematsu
- , Shunya Nishimura
- & Shuichi Tanoue
-
Original Article |
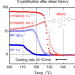 Crystallization behavior of isotactic polypropylene containing a fibrous nucleating agent in a flow field
Crystallization behavior of isotactic polypropylene containing a fibrous nucleating agent in a flow field
The addition of a fibrous nucleating agent (MDBS) significantly enhanced the crystallization temperature of PP with the accelerated crystallization rate, which was barely affected by the applied shear flow. In the case of pure PP, rapid crystallization was detected only after the history at a high shear rate. Furthermore, the shear history enhanced the chain orientation of PP greatly especially for the sample with MDBS, which resulted in a good transparency.
- Khunanya Janchai
- , Takumitsu Kida
- & Masayuki Yamaguchi
-
Focus Review |
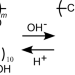 Development and application of pH-responsive polymers
Development and application of pH-responsive polymers
Random pH-responsive copolymers, P(A/AaU) have been prepared from a pH-responsive pendant fatty acid-containing monomer (AaU) and a pendant sulfonate-containing monomer (AMPS). In water, P(A/AaU) formed unimer micelles under acidic conditions. Under basic conditions, the P(A/AaU) polymer chains expand due to the electrostatic repulsions. Although pH-responsive sunscreen shows waterproof properties under neutral conditions, it disperses under weakly basic conditions such as soap water. pH-responsive diblock copolymers with a pendant fatty acid-containing block were prepared. This review also discusses pH-responsive gelling agents based on ABA triblock copolymers.
- Shin-ichi Yusa
-
Original Article |
 Novel degradable acetal-linkage-containing epoxy resins with high thermal stability: synthesis and application in carbon fiber-reinforced plastics
Novel degradable acetal-linkage-containing epoxy resins with high thermal stability: synthesis and application in carbon fiber-reinforced plastics
Novel alcohol-derived degradable acetal-linkage-containing epoxy resins HBA–CHDMVG and HOBA–CHDMVG were synthesized. The thermal decomposition temperature of HOBA–CHDMVG was higher than 300 °C; moreover, HOBA–CHDMVG exhibited excellent Charpy impact strength. The cured HOBA–CHDMVG was completely decomposed during the hydrolysis reaction under acidic conditions, and the reaction products were soluble in a tetrahydrofuran/H2O mixed solvent. Furthermore, the carbon fibers in the carbon-fiber-reinforced plastic with a HOBA–CHDMVG matrix were recovered via the complete decomposition of HOBA–CHDMVG.
- Mayo Kuroyanagi
- , Ayaka Yamaguchi
- & Kazumasa Kawabe
-
Original Article |
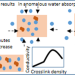 Effect of crosslink-induced heterogeneities on the transport and deformation behavior of hydrophilic ionic polymer membranes
Effect of crosslink-induced heterogeneities on the transport and deformation behavior of hydrophilic ionic polymer membranes
Hydration and crosslinking in hydrophilic ionic polymers give rise to microstructural features which affect diffusion of water and proton conductivity in them. Crosslinking in these systems gives rise to the presence of crosslink heterogeneities resulting in more-crosslinked domains and less-crosslinked regions. Because of the difference in elasticity between the two regions the polymer matrix swells differentially resulting in anomalous water sorption kinetics. The diffused water is distributed among hydroxyl and sulfonic groups and the crosslinking alters this distribution resulting in an increase in conductivity.
- C. Ajith
- , Abhijit P. Deshpande
- & Susy Varughese
-
Rapid Communication |
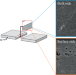 Cross-sectional observation of a weak boundary layer in polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) using scanning electron microscope
Cross-sectional observation of a weak boundary layer in polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) using scanning electron microscope
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has a weak boundary layer (WBL) on the surface. A cross-section of PTFE was observed using a scanning electron microscope for investigating the difference in morphology between WBL and bulk layer. Large voids of 0.5–2.0 µm in diameter were observed on the surface side of PTFE but not on the bulk side. These voids existed up to approximately 5 µm from the outermost surface of the PTFE. This result indicated that the thickness of WBL of PTFE was in the order of single µm.
- Yosuke Seto
- , Misa Nishino
- & Yuji Ohkubo
-
Original Article |
 Boosting sericin extraction through alternative silk sources
Boosting sericin extraction through alternative silk sources
Three different silk sources were explore for sericin (SS) extraction and film formation. Features of each raw material, especially the degree of processing, have remarkable effects on the primary structure and the presence of nonprotein compounds in the sericin extract. As a result, sericin films exhibited distinctive properties that seemed to be correlated with the amount of natural impurities and the molecular properties of the SS extract obtained from each raw material.
- Natalia Jaramillo-Quiceno
- , Emanuela Callone
- & Antonella Motta
-
Original Article |
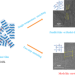 Enhanced in-plane thermal conductivity of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene films via a new design of a two-step biaxial stretching mode
Enhanced in-plane thermal conductivity of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene films via a new design of a two-step biaxial stretching mode
A mesh-like crystal structure of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) films is achieved through a two-step biaxial stretching mode to construct a planar-oriented crystal network. This mesh-like crystal network structure was investigated through scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and 1-dimensional wide-angle X-ray diffraction (1D-WXRD). The corresponding in-plane thermal conductivity increases to 7.3 W.m/K at a total draw ratio of 25, much higher than samples with single temperature biaxial stretching modes.
- Qi Zhang
- , Tianci Zhang
- & Shaoyun Guo
-
Focus Review |
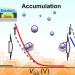 Chemical sensing based on water-gated polythiophene thin-film transistors
Chemical sensing based on water-gated polythiophene thin-film transistors
Water-gated polymer thin-film transistors (WG-PTFTs) fabricated by a simple procedure can be operated at an ultralow voltage, whereby the WG-PTFTs with molecular recognition units allow chemical sensing. Upon the addition of analytes, the electric double layer capacitance of the WG-PTFTs can be changed by accumulation and desorption of charged species at the interface of the semiconductor and electrolytes. For example, the WG-PTFTs have successfully detected biogenic amines and a herbicide glyphosate. In short, our proposed WG-PTFTs are among the most promising platforms for sensing applications based on π-conjugated polymer materials.
- Tsuyoshi Minami
- , Wei Tang
- & Koichiro Asano
-
Original Article |
 Confined crystallization and chain conformational change in electrospun poly(ethylene oxide) nanofibers
Confined crystallization and chain conformational change in electrospun poly(ethylene oxide) nanofibers
The confinement effect on the chain conformation and crystallization behavior of poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) in electrospun nanofibers was investigated. The PEO chains in electrospun nanofibers were tightly packed and exhibited a zigzag conformation. Increasing the fiber diameter reduced the packing of polymer chains, resulting in increases in the melting temperature and crystallite size. Thermal treatment relaxed the stretched chains, which induced a change from the metastable zigzag conformation to a stable helical conformation. Additionally, the melting temperature, degree of crystallinity, and crystallite size increased with increasing annealing temperature.
- Nhu Quynh Nguyen
- , Ting-Fang Chen
- & Chieh-Tsung Lo
-
Original Article
| Open Access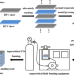 Preparation and properties of silicone rubber materials with foam/solid alternating multilayered structures
Preparation and properties of silicone rubber materials with foam/solid alternating multilayered structures
The silicone rubber materials with foam/solid alternating multilayered structure have been constructed by combining two methods of the multilayered hot-pressing and supercritical carbon dioxide (SCCO2) foaming. The growth of the cell is restrained by the solid layer, resulting in a decrease of the cell size. In addition, the introduction of the solid layer can effectively improve the mechanical properties of the microcellular silicone rubber foam. The experimental results are analyzed by finite element analysis (FEA).
- Wenhuan Zhang
- , Zhaoping Deng
- & Tao Liu
-
Original Article |
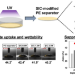 Fabrication of single-ion conducting polymer-coated separators and their application in nonaqueous Li-O2 batteries
Fabrication of single-ion conducting polymer-coated separators and their application in nonaqueous Li-O2 batteries
A facile modification method for a commercial polyethylene membrane separator using a cross-linked single-ion conducting polymer network with a highly delocalized anionic group was developed. A cross-linker, poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate, and a delocalized anionic monomer, lithium (4-styrenesulfonyl)(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide, were used to modify the surface of the polyethylene separator via UV-initiated polymerization. The resulting polymer coating improves the electrolyte wettability and suppresses the diffusion of anionic species across the separator. The effect of the polymer modification of the separator on the electrochemical properties of nonaqueous Li-O2 cells was investigated.
- Peeranuch Poungsripong
- , Ryota Tamate
- & Makoto Ue
-
Original Article |
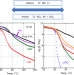 Application of the Hofmeister series to the structure and properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) films containing metal salts
Application of the Hofmeister series to the structure and properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) films containing metal salts
The salt addition affects the structure and properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) films as it reduces the hydrogen bonding in PVA chains and decreases the crystallinity. Consequently, the Tg shifts to low temperatures, and the modulus beyond Tg decreases markedly. This study confirmed that the impact of bromine salts on the structure and properties followed the order of Hofmeister series, i.e., Li+ > Na+ > K+. Although cations play an important role, the data obtained also demonstrated that the strong ion–dipole interactions between anions and PVA chains have a significant impact on the crystallinity and Tg.
- Riza Asmaa Saari
- , Muhammad Shahrulnizam Nasri
- & Masayuki Yamaguchi
-
Original Article |
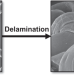 Nanoribbons fabricated by melt electrospinning
Nanoribbons fabricated by melt electrospinning
This study focuses on employing multilayer melt electrospinning of polymers coupled with a delamination step to obtain nonwoven webs of ribbon-shaped fibers. A coextrusion technique with layer multipliers was used to melt electrospin cylindrical microfibers that have up to 257 alternating layers within each fiber prior to delamination. The bicomponent layered cylindrical microfibers are delaminated using sonication or solvent rinsing to obtain flat nanoribbon fibers, that are 150 nanometers to 200 nanometers thick.
- Eugene G. Joseph
- , Naresh Budhavaram
- & Arit Das
-
Original Article |
 Autopolymerization of 2-bromo-3-methoxythiophene, analysis of reaction products and estimation of polymer structure
Autopolymerization of 2-bromo-3-methoxythiophene, analysis of reaction products and estimation of polymer structure
The mechanism of intense autopolymerization reaction of 2-bromo-3-methoxythiophenes spewing brownish gas was clarified from UV-Vis, ESR, GC/MS, elemental analysis, NMR, and FT-IR spectroscopy. The reaction contained the formation of the hydrogen bromide gas during the autopolymerization. The gas induced the cleavage of the methoxy group on the thiophene ring to form the methyl bromide gas as the side reaction. This work provides an important guide for the application of the autopolymerization of thiophene derivatives to design new polymer materials.
- Ryo Nishimura
- , Yohei Hattori
- & Kingo Uchida
-
Focus Review
| Open Access A new strategy for membrane-based direct air capture
A new strategy for membrane-based direct air capture
Direct CO2 capture from the air (DAC), is inevitable to reduce the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere. Recent reports of ultrahigh CO2 permeances in gas separation membranes indicate a potential of new technology for DAC (m-DAC). In this paper, we use chemical process simulation to discuss the potential of m-DAC considering the state-of-the-art performance of organic polymer membranes. Based on the analysis, we propose the target properties for separation membranes required for m-DAC with competitive energy expenses as well as the direction of future membrane development for DAC.
- Shigenori Fujikawa
- , Roman Selyanchyn
- & Toyoki Kunitake
-
Original Article |
 Structural evolution of β-iPP with different supermolecular structures during the simultaneous biaxial stretching process
Structural evolution of β-iPP with different supermolecular structures during the simultaneous biaxial stretching process
The structural evolution of β-iPP with two different supermolecular structures during the simultaneous biaxial stretching process was studied. The two samples showed different structural evolution modes. β-hedrites exhibited violent cavitation behavior during the initial stage of deformation, but in the late stages of stretching β-hedrites formed numerous dense regions, which hindered microvoid formation and led to a poor pore size distribution. Conversely, β-spherulite generated abundant microfibrillar structures, and abundant microvoids were formed, forming a membrane with a superior pore size distribution.
- Daoxin Zhang
- , Lei Ding
- & Ming Xiang
-
Original Article |
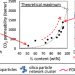 Inorganic/organic double-network ion gel membrane with a high ionic liquid content for CO2 separation
Inorganic/organic double-network ion gel membrane with a high ionic liquid content for CO2 separation
The effect of the ionic liquid content in tough inorganic/organic double-network (DN) ion gel membrane on the CO2 permeability was investigated. By optimizing the composition of the inorganic and organic networks, the mechanical strength of the DN ion gel was significantly increased, and the DN ion gel membrane with more than 95 wt% of an ionic liquid was successfully prepared. With the increase in the ionic liquid content, the CO2 permeability of the DN ion gel membrane exponentially increased up to ~67% of the theoretical maximum CO2 permeability.
- Eiji Kamio
- , Masayuki Minakata
- & Hideto Matsuyama
-
Original Article |
 Effect of the silica-rubber interface on the mechanical, viscoelastic, and tribological behaviors of filled styrene-butadiene rubber vulcanizates
Effect of the silica-rubber interface on the mechanical, viscoelastic, and tribological behaviors of filled styrene-butadiene rubber vulcanizates
Molecular structure of silica surface modifiers greatly controls the performance of silica-filled styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) through interfacial characteristics of the composites. Soft nature of low molecular-weight hydroxyl terminated polybutadiene (HTPB) and small number of its covalent bounds to the rubber matrix was compared with large number of rigid covalent bounds made between bis(3-triethoxysilylpropyl)tetrasulfide (TESPT) and rubber. Despite the better dispersion of silica modified with the former, the latter ensures higher transfer of stress to particles at large strains, inducing improved strength and abrasion resistance to composites.
- Nafise Torbati-Fard
- , Seyed Mostaffa Hosseini
- & Mehdi Razzaghi-Kashani
-
Original Article |
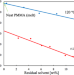 Effect of tetrahydrofuran on poly(methyl methacrylate) and silica in the interfacial regions of polymer nanocomposites
Effect of tetrahydrofuran on poly(methyl methacrylate) and silica in the interfacial regions of polymer nanocomposites
When the neat PMMA samples were dried at room temperature, the glass transition temperature (Tg) increases linearly with the decrease in the amount of residual solvent. However, even if the residual solvent is extrapolated to 0 wt%, the Tg is significantly lower than the bulk Tg despite no residual solvent. The Tg of heat-dried samples heat treated at 120 °C also increases linearly with decreasing residual solvent content. However, Tg was significantly different depending on the drying temperature even with the same residual solvent amount. These results indicated that the PMMA samples dried at room temperature have a distinctly different molecular mobility from the heated sample.
- Kazuki Matsuura
- , Keiichi Kuboyama
- & Toshiaki Ougizawa
-
Original Article |
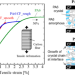 Mechanical behavior of unidirectional carbon fiber-reinforced polyamide 6 composites under transverse tension and the structure of polyamide 6 among carbon fibers
Mechanical behavior of unidirectional carbon fiber-reinforced polyamide 6 composites under transverse tension and the structure of polyamide 6 among carbon fibers
The mechanical properties of a unidirectional carbon fiber (CF)-reinforced polyamide 6 (PA6) composite subjected to a tension perpendicular to the CFs was studied by using two types of CFs with different surface profile. The difference of local crystalline structure of PA6 among CFs can be affected to the mechanical behavior of unidirectional PA6/CF composite under transverse tension.
- Hideyuki Uematsu
- , Daisuke Kurita
- & Shuichi Tanoue
-
Original Article |
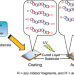 Effect of UV-curing conditions on the polymer structures: a comparison between coating and adhesive
Effect of UV-curing conditions on the polymer structures: a comparison between coating and adhesive
We examined the differences between the resulting polymer structures in the cases of a coating and an adhesive employing the same formulation. The UV-curable coating yielded polymers terminated by either a hydroxyl group or a terminal carbonyl group as the main products, suggesting that bimolecular termination was strongly inhibited by oxygen. On the other hand, the UV-curable adhesive yielded a multitude of disproportionation products, whereas some polymers underwent hydrogen abstraction from the polymer backbone, resulting in β-scission of the midchain radical to generate polymers with an α-substituted acryloyl group.
- Yasuyuki Sanai
- & Kouzou Kubota
-
Original Article |
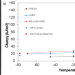 Polypropylene after thirty years of storage: mechanical proof of heterogeneous aging
Polypropylene after thirty years of storage: mechanical proof of heterogeneous aging
Long-term storage of isotactic polypropylene caused a dramatic loss of ductility, as manifested by the mechanical tensile and impact behavior. The embrittlement was accompanied by an increase in the crystallinity. A comparison of static and dynamic mechanical data suggests the development of structural heterogeneities upon aging that serve as fracture loci under mechanical stress. Subsequent annealing of the aged samples reversed the loss of ductility. This indicates healing of the hypothetical irregularities by the thermal treatment.
- Marta Sližová
- , Martin Stašek
- & Miroslav Raab
-
Original Article |
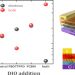 Solution-processable ambipolar organic field-effect transistors with bilayer transport channels
Solution-processable ambipolar organic field-effect transistors with bilayer transport channels
An efficient ambipolar organic transistor (A-OFET) based on the bilayer architecture of p-type poly(benzodithiophene(2-thienyl)-pyrrolopyrrole-dione) (PBDTTPPD) and n-type [6,6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PCBM) was demonstrated. The A-OFET exhibits clear bipolar transport and operates as an n-type and a p-type transistor in a single device.
- Dal Yong Lee
- , Vellaiappillai Tamilavan
- & Sung Heum Park
-
Original Article |
 Fine-tuning of the surface porosity of micropatterned polyethersulfone membranes prepared by phase separation micromolding
Fine-tuning of the surface porosity of micropatterned polyethersulfone membranes prepared by phase separation micromolding
This work presents a method on tailoring open pores on the patterned surface of polyethersulfone membrane prepared by the phase separation micromolding. By modifying both the thermodynamics of the casting solution and the dynamics of solvent/nonsolvent demixing, micropatterned membrane with average surface open pores in the diameter of 1095 nm and porosity as high as 31.4% was achieved. The size and number of pores were different depending on their locations on the patterned surface, which was caused by different solvent/nonsolvent demixing dynamics resulting from the physical discontinuity of micro-patterned membranes.
- Yida Liu
- , Takashi Kodama
- & Yu Hoshino
-
Original Article |
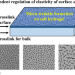 Precise design of microwrinkles through the independent regulation of elasticity on the surface and in the bulk of soft hydrogels
Precise design of microwrinkles through the independent regulation of elasticity on the surface and in the bulk of soft hydrogels
To precisely design microwrinkles on a biomimetic hydrogel, a two-step photocrosslinking process with VIS and UV irradiation was developed. Photocurable gelatin was first crosslinked with VIS light in the presence of the water-soluble radical generator to form thick bulk gels. Next, the top surface of the gels was irradiated with UV light in the presence of surface-coated water-insoluble radical generator. This two-step photocrosslinking process enabled to independently control the elastic moduli of the surface and the bulk lower than 100 kPa and to generate several-micron-scale wrinkles on the soft hydrogels.
- Saori Sasaki
- & Satoru Kidoaki
-
Original Article |
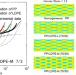 Experimental and numerical study on transient elongational viscosity for PP/LDPE blends
Experimental and numerical study on transient elongational viscosity for PP/LDPE blends
Transient elongational viscosity for polypropylene (PP)/low-density polyethylene (LDPE) blends was evaluated. Because deformed LDPE droplets act as rigid fibers due to its strain hardening, the blends show a strain hardening behavior. The growth curves are, however, affected by their viscosity ratio. These behaviors are calculated by the Phan–Thien Tanner model by assuming a symmetric geometry with a periodic structure. Based on the simulation, we propose an appropriate LDPE to modify the processability, at which the strain hardening in the elongational viscosity is required.
- Yasuhiko Otsuki
- , Yoko Fujii
- & Masayuki Yamaguchi
-
Original Article |
 Cluster growth from a dilute system in a percolation process
Cluster growth from a dilute system in a percolation process
The osmotic pressure during the gelation process below the overlapping concentration of prepolymers was investigated using a series of model polymer gels, namely, tetra-polyethylene glycol gels. The osmotic pressure decreased during the gelation reaction and was constant after the sol–gel transition, suggesting that the clusters grow and fill the system, at the sol–gel transition point. This representation of the sol–gel transition at the overlapping condition of the critical clusters corresponds well to the aggregation process prediction.
- Ikuo Fujinaga
- , Takashi Yasuda
- & Takamasa Sakai
-
Original Article |
 X-ray scattering study on the changes in the morphology of low-modulus polypropylene under cyclic uniaxial elongation
X-ray scattering study on the changes in the morphology of low-modulus polypropylene under cyclic uniaxial elongation
Low-modulus polypropylene (LMPP) with controlled stereoregularity showed elastic recovery. To understand the underlying mechanism, changes in the morphology of LMPP under cyclic uniaxial elongation were investigated using in situ SAXS and WAXD. During the first cycle, the undulating structure of the crystal lamellae is large, and fragmentation of the lamellae occurs. On the other hand, during the second cycle, the little fragmentation of the lamellae occurs and that only the lamellae were rotating under elongation. Based on these results, lamella fragmentation has a significant effect on the elastic-recovery rate.
- Shotaro Nishitsuji
- , Yuki Watanabe
- & Mikihito Takenaka

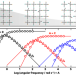 Predicting the effects of degradation on viscoelastic relaxation time using model transient networks
Predicting the effects of degradation on viscoelastic relaxation time using model transient networks